![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the energy of the photon whose momentum is equal to that of a 5 MeV electron? |
5.487 MeV |
|
|
Calculate the ratio v/c and m/m0 |
Electron: v/c = .979 m/m0 = 4.91
Proton v/c = 0.462 m/m0 = 1.001 |
|
|
Two electrons are initially at rest, separated by 0.1 nm. After the electrons are released, they repel each other. What is the kinetic energy of each electron when they are 1 nm apart? |
6.48 eV |
|
|
(a) What is the kinetic energy of an electron whose velocity is 90% of the speed of light? (b) How much additional energy is required (c) What is the mass of the electron in (b)? |
(a) 0.661 MeV (b) 2.450 MeV (c) 3.622 MeV/c^2 |
|
|
Assume an uncertainty in the momentum of an electron is equal to one-half of its momentum. Calculate the uncertainty in position |
1.40 * 10^-13 m |
|
|
What is the wavelength of |
(a) 2.02 * 10^-14 m (b) 3.88 * 10^-11 m (c) 6.626 * 10^-24 m |
|
|
What is the closest distance that a 4.0 MeV alpha particle can make a gold nucleus? |
5.69 * 10^-14 m |
|
|
Calculate the uncertainty in position of an electron that was accelerated across a potential difference 10^5 ± 100 V . |
5.41 * 10^-10 m |
|
|
A pi+ meson at rest decays into a μ+ meson and a neutrino in 2.5 × 10^−8 s. Assuming that the pi+ meson has kinetic energy equal to its rest energy. What distance would the meson travel before decaying as seen by an observer at rest? |
12.98 m |
|
|
Consider a symmetric elastic collision between a particle of mass m and kinetic energy T and a particle of the same mass at rest. Relativistically, show that the cosine of the angle between the two particles after the collision is T/(T+4mc^2) |
Conservation of energy, conservation of momentum |
|
|
A rod having a slope m relative to the x−axis of S, moves in the x direction at speed u. What is the rod’s slope in the usual second frame S'? |
m' = m = m/(sqrt(1-(v/c)^2)) |
|
|
Find < x > and < x^2 > for the first excited state ( n = 2) in an infinite square-well potential. |
< x > = L/2 < x^2> = (1/3 - 1/(8*pi))L^2
|
|
|
A particle of rest mass 1 MeV/c2 and kinetic energy 4 MeV collides with a stationary particle of rest mass 3 MeV/c2. After the collision, the two particle stick together. Find (a) the initial momentum of the system (b) the final velocity of the two-particle system, and (c) the rest mass of the two-particle system. |
(a) 4.889 MeV/c (b) 0.612 c [v/c = pc/E] (c) 6.36 MeV/c^2
|
|
|
Two particles with the same mass m are emitted in the same direction, with momenta 10mc and 20mc respectively. As seen from the slower one what is the velocity of the faster particle, and vice |
0.599 c and -0.599 c |
|
|
A particle is in the ground state of an infinite square well potential. Find the probability of finding the particle (a) in the range 0 < x < L/4 (b) in Δx = 0.02L at x = L/2 |
(a) 0.09808 (b) 0.0400 |
|
|
How much energy is required to accelerate an electron from rest to a speed of 0.9c? |
0.66 MeV |
|
|
How fast must a particle move before its kinetic energy equals its rest energy? |
0.866c |
|
|
What is the factor of a proton accelerated to an energy of 20 TeV ? |
21,316 |
|
|
A particle has a velocity u_x' = dx'/dt in S' frame which is moving at v along x' direction relative to S frame. The velocity of the particle measured in S frame is u_x. show that, |
Lorentz Transformations |
|
|
Two particles are aimed directly at each other. The first particle is moving at a speed of 0.8c to the right and the second particle is moving to the left at a speed of 0.7c. Assume both speeds are measured relative to the laboratory frame. |
(a) -0.962 (b) 0.962 |
|
|
Two particles with rest masses m1 and m2 move collinearly in some inertial frame, with uniform velocities u1 and u2, respectively. They collide and form a single particle with rest mass m moving at velocity u. Prove that m^2 = m1^2 + m2^2 + 2*m1m2(u1)(u2)(1-u1u2/c^2) |
Conservation of energy Conservation of momentum |
|
|
A meter stick is observed to be only 0.9 m long to an inertial observer. At what speed, relative to the observer, must the meter (c) 0.95 × 108 m/s (d) 1.31 × 108 m/s (e) 2.70 × 108 m/s |
D |
|
|
The temperature of a 5.00 kg lead brick is increased by 225 C0. If the specific heat capacity of lead is 128 J.kg−1C0−1 , what is the (c) 1.60 × 10−12 kg (d) 9.66 × 10−11 kg (e) 4.33 × 10−11 kg |
C |
|
|
The average power output of a nuclear power plant is 5.00 × 102 MW. In one minute, what is the change in the mass of the nuclear fuel due to the energy being taken from the reactor? (Assume 100% efficiency) (c) 3.3 × 10−13 kg (d) 9.3 × 10−11 kg (e) 9.3 × 10−17 kg |
B |
|
|
The rest energies of three subatomic particles are: |
D |
|
|
The starship Enterprise approaches the planet Risa at a speed of 0.8c relative to the planet. On the way, it overtakes the intergalactic freighter Astra. The relative speed of the two ships as measured by the navigator on the Enterprise is 0.5c. At what speed is Astra approaching the planet? |
C |
|
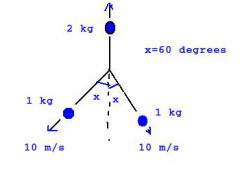
A stationary 4 kg shell explodes in three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third fragment moves upward as |
v = 5 m/s v_cm = 0 m/s |
|
|
A 0.015 kg marble moving to the right at 0.40 m/s has a head-on elastic collision with a 0.045 kg marble sitting at rest on a smooth, level surface. Which of the following are the correct magnitudes and directions of the velocities of the two marbles after the collision? |
v1 = -0.2 v2 = 0.045 |
|
|
A 35 kg girl is standing near and to the left of a 43 kg boy on the frictionless surface of a frozen pond. The boy tosses a 0.75 kg ice ball to the girl with a horizontal speed of 6.2 m/s. What are the velocities of the boy and the girl immediately after the girl catches the ice ball? |
v_boy = 0.11 m/s v_girl = -0.13 m/s |
|
|
The position of a hydrogen atom ( m = 1.7 × 10^−27 kg) is known to within 2.0 × 10−6 m. What is the minimum uncertainty in the atom’s velocity? (c) 0.015 ms−1 (d) 0.031 ms−1 |
C |
|
|
The position of a 0.001 kg object moving in the x direction at 1 cm/s is known to within ±10 nm. In which range is the fractional uncertainty in the x component of its momentum? (c) 10^−16 to 10^−18 (d) 10^−20 to 10^−22 (e) 10^−25 to 10^−30 |
D |
|
|
A photon has a collision with a stationary electron ( h/mc = 2.43 × 10^−12m) and loses 5.0% its energy. The photon scattering angle is 180. What is the wavelength of the incident photon in this scattering process? (c) 9.2 × 10−11 m (d) 1.9 × 10−10 m (e) 3.1 × 10−12 m |
C |
|
|
Photon of what minimum frequency are required to remove electrons from gold? The work function for gold is 4.8 eV . (a) 7.3 × 10^14 Hz (b) 1.2 × 10^15 Hz (c) 3.8 × 10^17 Hz (d) 6.5 × 10^15 Hz (e) 4.6 × 10^14 Hz |
B
|
|
|
The de Broglie wavelength of the matter wave associated with an electron accelerated by a voltage of 50 V is about, |
C |
|
|
Ba137 emits a gamma-ray photon of 0.66 MeV during an isomeric transition. Estimate the recoil kinetic energy of the atom in eV . (c) 17.0 eV (d) 170.0 eV (e) 1.7 eV |
E |
|
|
How many degrees of freedom does a rigid body have? |
6 |
|
|
The following set of counts readings was made in a gradient-free ray field, using a suitable detector for repetitive time periods of one minute: 18500; 18410; 18250; 18760; 18600; 18220; 18540; 18270; 18670; 18540. |
(a) 18476 (b) 58.29 (c) 42.98 (d) 184.34 (c) 153.93 |
|
|
A point source emits beta particles at a rate of 107 s^−1. What is the fluence density at a distance of 30 cm from the source? |
884.2 cm^-2 s^-1 |
|
|
An ion exchange column contains radioactive materials that emits 5.5 × 10^5 cm^−1 of length. This column rests horizontally on the floor of a plant. Column is 9 m long and has a diameter of 5 cm. What is the unshielded fluence at a point 12 m away and 1 m above the floor? |
2.60*10^5 m^-2 |
|
|
A solution of I (131) containing an activity of 107 |
7947.82 m^-2 s^-1 |
|
|
A point source of Co (60) gamma rays emits equal numbers of photons of 1.17 and 1.33MeV , giving a flux density of 3.7×10^9 photons cm^−2 sec^−1 at a specified location. What is the energy flux density there, expressed in erg.cm^−2.s^−1 and in J.m^−2.min^−1? |
7411 erg cm^-2 s^-1 444.7 J m^-2 min^-1 |
|
|
A 6 cm diameter pipe containing Co (60) with a lineal emission rate of 10^6 photons cm^−1s^−1 curves half-way around the ceiling of a circular |
4.31 * 10^6 m^-2 s^-1 |
|
|
( Problem #08 on page 18 of Attix ) |
(a) 6.75*10^10 m^-2 s^-1 (b) 2.43 * 10^14 m^-2 (c) 2.14 J m^-2 and 2.14 * 10^3 erg cm^-2 |
|
|
Find |
(a) -∝^2*m_e*c/(4*n^2) (b) 2*a_0 (c)E_H/2 |
|
|
A hydrogen-like ion has the wavelength difference between the first lines of the Balmer and Lyman series equal to 16.58 nm. What |
Li 2+ |
|
|
Use the uncertainty principle to estimate ground state energy of a two-electron atom of nuclear charge Ze. |
E = -(z-1/4)^2*27.2 eV |
|
|
Electrons have been removed from a beryllium atom (Z = 4) until only one remains. Determine the energy of the photon that can be emitted, if the remaining electron is in the n = 2 level. (c) 122.0 eV (d) 164.0 eV (e) 218.0 eV |
D |
|
|
Which one of the following will result in an electron transition from the n = 4 level to n = 7 level in a hydrogen atom? (b) emission of a 0.57 eV photon (d) absorption of a 0.28 eV photon (e) absorption of a 0.57 eV photon |
E |
|
|
A bullet of mass 40 gm travels at 1000 ms−1. What wavelength can we associate with it? (c) 1.7 × 10−35 m (d) 1.7 × 10−40 m (e) 1.7 × 10−45 m |
C |
|
|
The wavelength of the first line of the Lyman series of a ten time ionized Na atom ( Z = 11) is about ( the first line of the Lyman series of hydrogen is 1216 Å ) |
B |
|
|
The total number of electron states with n = 2, l = 1 for Hydrogen atom is |
C |
|
|
An electron in an atom has the following set of quantum numbers n = 3, l = 2,m_l = +1,m_s = +1/2 |
C |
|
|
Of the following, the particle which most easily penetrates the nucleus of an atom is the, (c) deuteron (d) electron (e) neutron |
E |
|
|
Which one of the followings would constitute an inertial reference frame? |
C |
|
|
Which one of the following statements is a consequence of special relativity? |
B |
|
|
Two helium-filled balloons are released simultaneously at points A and B on the x-axis in an earth-based reference frame. Which one |
E |
|
|
The proper time between two events is measured by clocks at rest in a reference frame in which the two events: |
A |
|
|
A meter stick moves at 0.95c in the direction of its length through a laboratory. According to measurements taken in the laboratory, its length is |
C |
|
|
Observer A measures the relativistic velocity of a rocket as v and a comet as u. Here u and v are parallel and in the direction of observer’s positive x-axis. The speed of the comet as measured by an observer on the rocket is? |
(u-v)/(1-uv/c^2) |
|
|
An object A moving away from us at a speed of 0.8c. A second |
C
|
|
|
A meson when at rest decays 2 μs after it is created. If moving in laboratory 0.99c, its lifetime according to laboratory clock would |
C |
|
|
A mass of a particle is m. In order for its total energy to be twice its rest energy, its momentum must be? |
sqrt(3)*mc |
|
|
The units of h are those of: (a) power (b) energy |
D |
|
|
The frequency of light beam A is twice that of light beam B. The ratio EA/EB of photon energies is: |
B |
|
|
In Compton scattering the frequency of the emitted light is independent of : |
E |
|
|
In Compton scattering from stationary electrons the largest change in wavelength that can occur is? |
4.85*10^-12 m |
|
|
Of the following, Compton scattering from electrons is most easily observed for: |
A |
|
|
Which type of wave motion does not involve photon? |
A |
|
|
The work function for a particular metal is 4.0 eV . Which one of the following best describes the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation needed to eject electrons from the metal? |
A |
|
|
Frame S’ moves in the x-direction at 0.6c with respect to frame S. A particle moves in the x direction at 0.4c as measured by an observer in S’. The speed of the particle as measured by an observer in S is? |
25c/31 |
|
|
Which one of following is a consequence of the postulate of the special theory of relativity? |
D |
|
|
A particle of rest mass m moves with a speed 0.6c. Its kinetic energy is: |
B |
|
|
Which one of the following statements concerning the proper time interval between two events is true? |
D |
|
|
How much energy will be released if 1.0 g of material were completely converted into energy? |
9*10^13 J |
|
|
A laser emits pulse of light with energy 5 × 103 J Determine the number of photons in the pulse if the wavelength of the light is 480 nm |
1.2*10^22 |
|
|
What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron ( m = 9.11 × 10^−31 kg ) in a 5.0 × 10^3 V x-ray tube? |
0.017 nm |
|
|
A 2 MeV photon is scattered by a Compton interaction. What is the maximum energy transferred to the recoiled electron? |
? |
|
|
What is the angular momentum of the electron in the n = 5 state of the Hydrogen? |
5.27*10^-34 J*s |
|
|
Calculate the ionization potential of Li 2+ |
122.4 |
|
|
Calculate the radius of the n = 2 electron orbit in the Bohr hydrogen atom. |
5.29*10^-11 m (n^2/Z) |
|
|
Calculate the orbital radius for the n = 2 state of Li2+. |
5.29*10^-11 m (2^2/3) |
|
|
What are the energies of the photons with the two longest wavelengths in the Paschen series? |
1.51 m |
|
|
How many energy levels of the He+ ion lie below −1 eV ? |
7 |
|
|
Calculate the current of the electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom. |
1.05*10^-3 A |
|
|
Calculate the reduced mass of the He+ system. |
9.108*10^-31 kg |
|
|
What is the reduced mass of a system of two particles of equal mass, such as an electron and positron, orbiting about their center of mass? |
? |
|
|
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of a 245 keV electron. |
2.23*10^-12 m |
|
|
How much energy is required to remove an electron from the n = 5 state of He+? |
?
|
|
|
What is the momentum of a photon of lowest energy in the Balmer series of hydrogen? |
? |
|
|
How many electrons per second strike the target in an X-ray tube operating at current of 50 mA. (b) if the potential difference between the anode and cathode is 100 kV , how much power is expended? |
?
|
|
|
The configuration of boron is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^1. |
? |
|
|
What is incorrect in the electron configuration 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^8 3d^10? |
? |
|
|
How much force acts on the electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom? |
? |
|
|
The length of an uniform radioactive rod is L. Derive an expression for the fluence at a point P. The shortest distance to from the middle of the rod to P is x and assume the rate of emission of |
s_l/(4*pi*x)*2*tan^-1(L/(2x)) |
|
|
The diagram shows a circular radioactive disc source with emission rate SA s^−1 and radius R. Derive an expression for the fluence |
S_A/(4*pi*R)*ln(1+R^2/x^2) |
|
|
A point source emits beta particles at a rate of 10^7 s^−1. What is the fluence density at a distance of 30 cm from the source? |
?
|
|
|
Calculate the (a) fluence rate (b) energy fluence density from a 10^11 sec^−1, 137 Cs (0.662 MeV ) point source at a distance of 1.25 m. |
? |
|
|
Which one of the following will result in an electron transition from the n = 4 level to n = 7 level in a hydrogen atom? |
? |
|
|
A bullet of mass 40 gm travels at 1000 ms−1. What wavelength can we associate with it? (c) 1.7 × 10−35 m (d) 1.7 × 10−40 m (e) 1.7 × 10−45 m |
?
|
|
|
The classical electron radius is of the order of (c) 10^−15 cm (d) 10^−10 cm (e) 10^−13 cm |
E |
|
|
Electrons have been removed from a beryllium atom (Z = 4) until only one remains. Determine the energy of the photon that can be emitted if the remaining electron is in the n = 2 level. |
? |
|
|
Determine the wavelength of incident EM radiation required to cause an electron transition from n = 6 to n = 8 level in a hydrogen atom. |
? |
|
|
Which one of the following will result in an electron transition from the n = 4 level to n = 7 level in the hydrogen atom? |
? |
|
|
The kinetic energy of the ground state electron in hydrogen is 13.6 eV . What is its potential energy? |
C |
|
|
An electron is in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. A photon is absorbed by the atom and the electron is excited to the n=2 level. What is the energy in eV of the photon? |
10.2 eV |
|
|
The electron in a hydrogen atom is in the n=3 state. What is(are) the possible value(s) for an emitted photon? |
A |
|
|
Determine the maximum wavelength of incident radiation that can be used to remove the remaining electron from a singly ionized |
A |
|
|
An x-ray beam produced at 200 kVp has a Half Value Layer of 1.5 mm Cu. (a) What are the coefficient of linear and mass attenuation coefficients? |
0.46 mm^-1 0.52 cm^2/g |
|
|
A narrow beam containing 2000 monoenergetic photons is reduced to 1000 photons by a slab of copper 1 cm thick. (a) What is the total linear attenuation coefficient of the copper slab for these photons? (b) What are the mass, atomic and electronic attenuation coefficients of the copper slab? ( copper density = 8.9 gmcm−3). (c) To the 1 cm copper slab, 2 cm of copper are added. How many photons remain in the beam emerging from the slab? |
(a) 0.693 cm^-1 (b) 0.0779 cm^2 g^-1, 8.23*10^-24 cm^2 atom^-1, 2.84*10^-25 cm^2 electrons^-1 (c) 250 |
|
|
The photon flux density is 10^9 photons m^−2 sec^−1 for a beam of rays. One fourth of the photons have an energy of 500 keV and three fourth of the photons have an energy of 1.25 MeV . What is the energy flux density of the beam? |
1.06*10^9 MeV s^-1 |
|
|
A sphere and a cylinder start from rest at the same position and roll down the same incline. |
E |
|
|
As white light enters a lens it undergoes a change in |
D |
|
|
The Pauli exclusion principle states that |
E |
|
|
The moon revolves about the earth making a complete revolution in 27.3 days. Assume that the orbit is circular and has a radius of 385 × 10^6 meters. The magnitude of the acceleration of the moon toward the earth is about |
C |
|
|
A sub-atomic particle traveling at a constant speed of 6 × 10^6 m/s enters a region of an electric field where it is decelerated at the rate of 1.2 × 10^14 m/s^2. The linear distance the particle travels before coming to rest is, |
? |
|
|
Electrons have been removed from a Beryllium atom (Z = 4) until only one remains. Determine the energy of the photon that can be emitted if the remaining electron is in the n = 2 level. (d) 164.0 eV (e) 218.0 eV |
D |
|
|
If the absolute value of the wave function of a proton is twice as large at location A than at location B, how many times is it more likely to find the proton in location A than in B? |
A |
|
|
Why was it necessary for Bohr to require that electrons remain in stationary orbits? |
E |
|
|
The total number of electron states with n = 2, l = 1 for hydrogen atom is |
C |
|
|
At what speed is a particle traveling, if its kinetic energy is three times its rest energy? (d) 0.968c (e) 0.989c |
D |
|
|
What are the possible values of n and m if (a) l = 3 and (b) l = 0? |
(a) n = 4,5,6,... m = -3,-2,...2,3 (b) n = 1,2,3,... m = 0 |
|
|
The wavelength of the K_a line in iron (Z = 26) is known to be 193 pm. Then what would be the wavelength of the K_a line for copper (Z = 29)? |
153.8 pm |
|
|
rocket moving at 0.500c relative to some inertial observer fires a missile at a speed of 0.300c (as measured by the rocket pilot) in the direction of the rocket velocity. What can you say about the missile’s velocity relative to the inertial observer? |
C |
|
|
Which particle has the greatest speed? |
A |
|
|
A proton and an electron have the same kinetic energy and are moving at speeds much less than the speed of light. The ratio of De Broglie wave length of the electron to that of proton is? |
sqrt(m_e/m_p) |
|
|
The ground state electronic configuration of a neon atom is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. How many of these electrons have magnetic quantum number m_l = 0? |
C |
|
|
A beam of 4.5 MeV neutrons is directed at a 0.030 kg tissue sample. Each second, 1.5 × 10^6 neutrons strike the sample. If the RBE of these neutrons is 7.0, what biological equivalent dose is received by the sample in 65 seconds? |
?
|
|
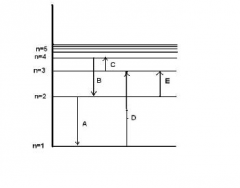
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and labeled by letters. Determine the wavelength of the radiation involved in transition B. |
? |
|
|
A photon in light beam A has twice the energy of a photon in light beam B. The ratio P_A/P_B (a) 1/2 (b) 1/4 (c) 1 (d) 2 (e) 4 |
?
|
|
|
The absorption coefficient of aluminum is 0.73 cm^−1 for X rays of wavelength 0.20 A and the density of aluminum is 2.1 g.cm^−3. The mass absorption coefficient is: (c) 1.5 cm^2.g (d) 0.15 cm^2.g (e) 0.73 cm^2.g |
? |
|
|
Find the orbital radius and energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom characterized by the principal quantum number n = 3. (c) 0.476 nm,−1.51 eV (d) 0.476 nm,−13.6 eV (e) 0.0529 nm,−13.6 eV |
? |
|
|
If the uncertainty in the position of a moving particle increases, |
?
|
|
|
Which color of photons will have the least momentum? |
? |
|
|
What is the minimum potential difference that must be applied to an X ray tube to knock a K shell electron completely out of an atom in a copper (Z = 29) target? (c) 1.07 × 10^4 V (d) 1.30 × 10^4 V |
? |
|
|
In the Compton effect, a photon of wavelength and frequency f hits an electron that is initially at rest. Which one of the following occurs as a result of the collision? |
? |
|
|
Which one of the following electronic configuration corresponds to an atomic (c)1s^1 2s^2 3p^1 (d)1s^2 2s^2 2p^1 (e)1s^1 2s^2 2p^1 |
D |
|
|
Calculate the K X ray wavelength for a gold atom (Z = 79). (c) 2.00 × 10^−11 m (d) 3.60 × 10^−11 m (e) 2.47 × 10^−13 m |
?
|
|
|
A photon source emits photons of 1.50 MeV giving a flux density of 2.3 × 10^8 photons.cm−2.sec−1 at a specified location. What is the energy flux density at this location? (a) 5.53×10^−5 J.cm^−2.s^−1 (b) 5.53×10^−11 J.cm^−2.s^−1 (c) 3.45×10^8 J.cm^−2.s^−1 (d) 5.53 × 10^8 J.cm^−2.s^−1 (e) none of the above |
? |
|
The total energy E of a free moving particle of mass m with speed v is given
|
? |
|
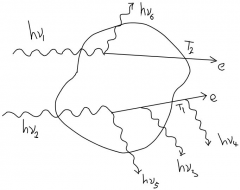
What are the values of (Rin)_u, (Rout)nonr_u , (R)r_u, (Rout)_c, (Rout)_u, sum(Q )for the given volume? |
(Rin)_u = hv_1+hv_2 (Rout)nonr_u = hv_5+hv_6 (R)r_u = hv_3+hv_4 (Rout)_c = T_1+T_2 sum(Q ) = 0 |
|
|
A fluence, differential in energy has the form |
(a) N*[1/Emin-1/Emax] (b) N/E (c) N*ln(Emax/Emin) |
|
|
The flux density of 5 MeV gamma rays is 3.0 × 10^6 cm^−2s^−1 at a point in Pb. What are the the kerma and collision kerma after one hour? |
? |
|
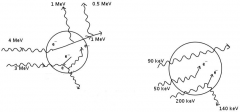
Calculate the Kerma, collision Kerma, and absorbed dose in spherical volume of |

|
|
|
At a depth of 47 cm in a medium the absorbed dose is found to be 3.95 Gy, while that resulting only from primary radiation is 3.40 Gy. At the front surface of the medium, the dose from primary radiation is 10.0 Gy. Calculate the followings: ( Assume CPE and plane, monoenergetic primaries.) |
? |
|
|
Consider a beam of 3 MeV rays perpendicularly incident on an Fe foil that is very thin in comparison with the range of the secondary electrons. |
? |
|
|
In the electronic configuration 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 the number of electrons having l = 1 is? |
6 |
|
|
The electron in a hydrogen atom is in a state with l= 5. The minimum angle between L and the z-axis is? |
24.1 |
|
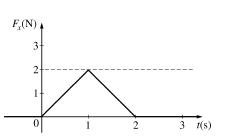
The figure above shows a plot of the time- dependent force F_x(t) acting on a particle in motion along the x-axis. What is the total impulse delivered to the particle? |
2 kg m/s |
|
|
The momentum of an electron is 1.60 times larger than the value computed non-relativistically. What is the speed of the electron? |
2.34E+08 m/s |
|
|
In the hydrogen spectrum, the ratio of the wavelengths for Lyman- radiation (n = 2 to n = 1) to Balmer- radiation (n = 3 to n = 2) is? |
5/27 |
|
|
An astronomer on earth observes two galaxies moving away from each other along a line that passes through the earth. The astronomer finds that each is moving with a speed of 2.1E+8 m/s relative to the earth. At what speed are the galaxies moving apart relative to each other? |
2.8E+8 m/s |
|
|
n the production of X rays, the term (a) The cut-off wavelength, , of the X-ray tube (b) The discrete X-ray lines absorbed when an (c) The smooth, continuous X-ray spectra (d) The smooth, continuous X-ray spectra (e) The discrete X-ray lines emitted when an |
D |
|
|
Figure shows a 2.50 MeV photon that undergoes a Compton interaction at point A in the volume V.The kinetic energy of the Compton electron is 1.10 MeV . At point B, electron ejects a bremsstrahlung photon with energy 0.60 MeV. It spends the rest of the energy along the track BC and stops at C. |
1.4 MeV, 0.6 MeV, and 2.0 MeV |
|
|
A 10 MeV gamma ray enters a volume V and undergoes pair production, thereby disappearing and giving rise to an electron and positron of equal energies. The electron spends half of its kinetic energy in collision interactions before escaping from V. The positron spends half of its kinetic energy in collisions in V before annihilated in flight. The resulting photons escape from V. What are the energies of particles escaped from V? (Assume two equal photons and an electron) |
1.633 MeV photon, 1.633 MeV photon and 2.245 MeV electron |
|
|
Calculate the probability that a 2 MeV photon in a narrow collimated beam will be removed from the beam by Lead of 1.0 cm thick. ( linear attenuation coefficient for lead : µPb = 0.516 cm^-1 ) |
0.403 |

