![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is ionizing radiation?
|
Particles (or photons) with sufficient enegry to remove electrons (or ionize) molecules with which they interact.
|
|
|
Natural sources of ionizing radiation?
|
Radon
Cosmic radiation |
|
|
Man-made sources of ionizing radiation?
|
Diagnostic x-rays
Nuclear medicine Consumer products |
|
|
Occupational radiation sources
|
Density gauges
Point level gauges Examining materials for cracks X-rays, medical, welding Laboratory analysis - XRF Nuclear medicine Nuclear energy |
|
|
Types of ionizing radiation
|
Alpha
Beta Gamma Other: neutrons, protons, neutral mesons, etc |
|
|
Alpha particles are the same as the nuclei of?
Examples? Size / mass? How far do they travel and what can stop it ? Internal or external hazard? QF = ? |

Alpha particles are the same as the nuclei of helium atoms
Po-210, Am-241, Cm-244 Largest radiation particle. Travel and inch or less, stopped by sheet of paper or outer layers of skin. Significant internal hazard. QF = 20 |
|
|
Beta
___-speed electrons. Released during what process? QF = ? |
Beta
High-speed electrons. Released in decay process of neutrons transforming into proton. QF = 1 |
|
|
Beta
Energy level of β radiation ranges from ? High or low energy β can penetrate deeper into material? Sr-90 can penetrate up to ___ into the body? |
Energy level of β radiation ranges from a few eV to 2.24 MeV.
Higher energy β can penetrate deeper into material. Sr-90 can penetrate up to 1.1 cm into the body. |
|
|
Gamma
How do gamma rays travel in space? Energy levels range from? QF = ? |
Gamma rays will continue through any medium until they have a chance encounter with an atom.
Energy levels vary from a few eV to billion eVs. QF= ? |
|
|
Radiation is a product of what?
Activity =? 1 Becquerel = ? 1 Curie = ? |
Radiation is a product of spontaneous atomic decay (transformation of an atom into a different element).
Activity is the number of decays/time. 1 Becquerel = 1 disintegration/sec 1 Curie = 3.7*10^10 disintegration/sec |
|
|
Radiation Activity
How does activity behave over time? |
Activity changes over time.
Activity decays exponentially. |
|
|
What is absorbed dose?
|
Absorbed dose is the energy imparted to matter by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material
|
|
|
Rad = ?
|
Rad = a unit of absorbed dose (0.01 J/kg)
|
|
|
Dose Equivalent
|
Numerically equivalent to absorbed dose in rads multiple by a quality factor (QF) to indicate biological effectiveness.
|
|
|
REM = ?
|
Rem = unit of dose equivalent
Rem = QF * Rad |
|
|
100 Rem causes ?
|
100 Rem causes radiation sickness and increases cancer risk by 1-5%
|
|
|
500 Rem causes?
|
500 Rem causes death in 50% of exposed persons.
|
|
|
Dose Rate = ?
U.S. radiation workers are allowed whole body dose rate of ? ICRP recommends? |
Dose Rate = Dose equivalent per unit time (mrem/hr, mrh).
U.S. radiation workers are allowed whole body dose rate of 5 rem/yr. ICRP recommends 2 rem/year (averaged over 5 years) |
|
|
Which form of ionizing radiation produces the greatest amount of damage in the body?
A. Alpha B. Beta C. Gamma D. Laser |
Alpha.
Alpha radiation has a quality factor (Q) rating of 20. Beta and gamma radiation have Q factors of 1. This means that alpha particles in the body produces 20 times the damage caused by beta particles or gamma photons. |
|
|
Ionization versus Excitation.
___ transfers enough engery to an orbital electron to displace it futher away from the nucleus? |
Excitation
|
|
|
Ionization versus Excitation.
The electron is removed, results in an ion pair (the newly freed electron and the (-)and the rest of the atome (+) |
Ionization
|
|
|
What are two types of electromagnetic radiation?
|
Gamma (γ) - orginates from the atomic nucleus.
X-rays: orginals in the orbital elecron cloud. Has identical properties as γ radiation and interacs identicallly in matter. X-rays typically have less energy (500eV to 500KeV). |
|
|
Gamma (γ)
Charge =? penetrating capability? energy? |
Gamma (γ)
Charge = 0 Highly penetrating to tissue energey up to 10MeV. |
|
|
Alpha (α)
Composed of? Range in air? What is needed to stop α particles? External hazard? Internal hazard? |
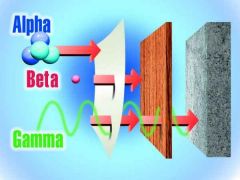
Alpha (α) is composed of Helium nuclei (2 neutrons and 2 protons).
Range in air = ~2cm, because its a highly charged particle. A sheet of paper will stop α. Not external hazard and will not penetrate skin. Serious internal hazard as it creates many ions as it travel though matter (ie radon in the lungs) |
|
|
Beta (β)
Where does it come from? |
β are high speed electrons ejected from the nucleus of an atome caused by neturon to proton conversion.
|
|
|
How far do β particles travel?
|
β particles can travel longer distance because they have smaller charge and less mass.
|
|
|
How far can β particles penetrate into the skin?
|
few millimeters
|
|
|
What is Bremsstrahlung radiation?
|
"Braking Radiation"
The EM interaction btw the nucleus and the electron causes the e- to violently accelerate, resulting in a sharp deflection of the e- orignal course. X-ray is release, |
|
|
what is a sufficient sheild for alpha particles?
|
paper
|
|
|
what is a potential problem to for beta sheilding?
what are preferred sheilds? |
Bremsstahling effect (creates x-rays). Use a material with an atomic number of 13 or less.
Pastics and glass are preferred sheilds for beta radiation. |
|
|
what is a recommended material to sheid x-ray and gamma?
|
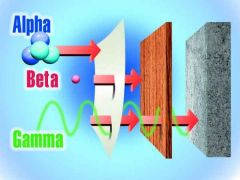
lead or concrete
|
|
|
Geiger-mueller tube measures?
tyipcally used for? |

Geiger mueller tube measures beta and gamma radiation (except low energy beta).
Used for radiation surveys |
|
|
Describe how Scintillation dector works?
|
Sample is placed in vial with scintillation liquid. Radiation causes small light flashes in liquid. Flashes are counted with photomultipler tube.
|
|
|
What are film badges?
|
A dosimeter used for monitoring cumulative exposure to ionizing radiation. The badge consists of two parts: photographic film, and a holder. The film is removed and developed to measure exposure.
|
|
|
What is the QF for gamma, x-ray, beta ?
|
QF = 1
|
|
|
What is the QF for alpha ?
|
QF =20
|
|
|
What is absorbed dose ?
|
Absorbed dose is a physical quantity and is defined as the energy absorbed per unit mass of the object irradiated.
Rad: unit of absorbed dose (0.01 j/kg) |
|
|
Dose equivalent
|
Numberically equivalent to absorbed dose in Rads multiplied by a quality factor (QF) to indicate biological effectiveness.
Rem: QF * rad |
|
|
U.S. radiation workers are allowed whole body dose rate of?
|
5rem/yr.
ICRP recommends 2rem/yr (averaged over 5yrs) |
|
|
Alpha decay.
What happens to atomic number and atomic mass ? |
Atom emits alpha particle.
Atomic number : reduced by 4. Atomic mass: reduced by 2. |
|
|
Beta decay
Atomic number ? Atomic mass ? |
Atom emits a beta electron. Atomic number increases by 1. No change in atomic mass.
|
|
|
2 types of lasers
|
Continous Wave (CW)
Pulsed |
|
|
Continous Wave Laser
|
light is emitted continuously
t > 0.25 seconds |
|
|
Pulsed Laser
|
light is emitted in pulses
t,0.25 seconds |
|
|
Laser safety quantities:
Irradiance (dose rate) |
Irradiance (dose rate):
E = P / area E= 4P/π(diameter)2 E= irradiance P= power (W) A= area (cm2) |
|
|
Laser safety quantities:
Radiant Exposure (dose) |
Radiant Exposure (dose):
Energy/area (J/cm2); generally used for puled lasers |
|
|
joules = ?
|
watts × seconds
|
|
|
Describe divergence (milliradians) and the emergent beam diameter (mm)
|
see picture
|
|
|
What are the target organs of the laser?
|
eye and skin
|
|
|
Describe the laser health effects of the eyes and skin
|
Eyes are most vunerable
-thermal damage -photreceptors Skin -thermal -photochemical |
|
|
UV < 220 nm creates?
|
O3
|
|
|
Cornea hazard range
|
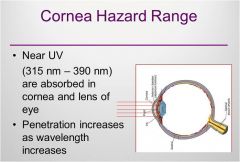
|
|
|
Retinal hazard range
|
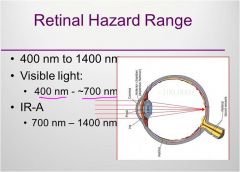
|
|
|
Eye surfaces
|
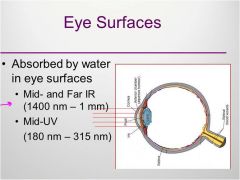
|
|
|
Laser exposure limits.
TLV changes based on ? Pulsed lasers have a TLV in? CW lasers have a TLV in? |
the wavelength of the laser.
Pulsed lasers have a TLV in radiant exposure (J/cm2) CW lasers have TLV in irradiance (W/cm2). |
|
|
What is the frequency of RF?
|
30 kHz - 300 MHz
|
|
|
What is the frequency of Microwaves?
|
300 MHz - 300 GHz
|
|
|
Health effects of RF and microwaves?
|
Electrical currents induced in the body
Heating of tissue- major concern Other reports: nervous system, reporductive effects, cataracts, cancer |
|
|
Wavelength = ?
|

|
|
|
Exposure limits
SAR: Specific Absorption Rate (watts/kg) |
TLV: SAR<0.4 W/kg
|
|
|
Exposure limits
Human body absorption rate varies with ? |
frequency
|
|
|
UV health hazards for the Skin?
|
Skin hazards
Erythema (skin burns) (250nm-300nm) Photosensitization (UV-A) Skin Cancer (UV-B) |
|
|
UV health hazards for the eye?
|
Photokeratoconjunctivits (damage to corneal epithelial cells; UV-C most effective)
Cataracts (opacification of oculat lens: UV-B) Retinal lesion (photochemical damage to retina; UV-A) |
|
|
UV-A wavelegth?
|
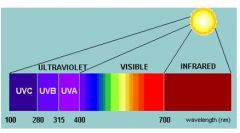
315nm - 400nm
|
|
|
UV-A exposure to the eyes should not exceed?
|
A radiant exposure of 1.0J/cm2 for periods lasting less than 1000 seconds
An irradiance of 1.0mW/cm2 for periods lasting 1000 seconds or more. |
|
|
1 cm = _ mm?
|
10mm
|
|
|
1 meter = _ cm?
|
100cm
|
|
|
what are the wavelenths of UV-B (mid UV) ?
|
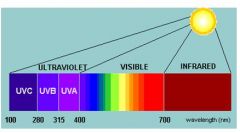
280 - 320nm
|
|
|
what are the wavelenths of UV-C (far UV) ?
|
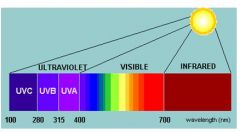
< 280nm
|
|
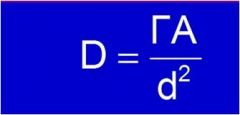
What units is D?
|
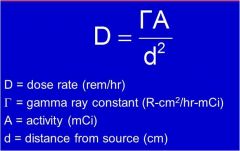
D = dose rate (rem/hr)
|
|
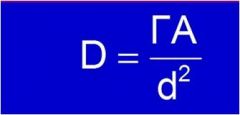
What unit is A?
|
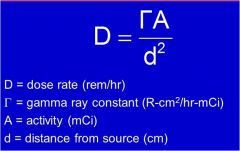
A = activity (mCi)
|
|
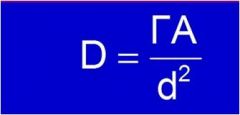
What unit is d^2?
|
D = distance from source (cm)
|

