![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
134 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the threshold refresh rate that reduces the amount of flickering in the fluoro TV monitor?
|
1/30 sec
|
|
|
What piece of x-ray equipment contains a photocathode, input, and output phosphors?
|
image intensifer (II)
|
|
|
What is vignetting?
|
falling off of sharpness toward the edges of an II image
|
|
|
What piece of equipment functions to stop the exposure once the film is correctly exposed?
|
phototimer (AEC)
|
|
|
Mandatory types of radiographic equipment.
|
collimation, light, mirror in collimator, protective curtain, bucky slot cover
|
|
|
Accessory types of radiographic equipment.
|
positioning sponges, compression bands, sandbags
|
|
|
List 5 advantages of 105 mm strip spot filming over cassette spot filming.
|
1. less patient dose
2. lower film contrast (more gray tones) 3. practical storage 4. decreased fluoro tube heat load 5. shortened exam times |
|
|
zinc cadmium sulfide; converts electors to bright image (light photons); 1 in diameter; smaller than input; 5th or last section of II tube
|
output phosphor
|
|
|
metal rings inside the II tube; lenses have a positive charge to attract the negative electrons from photocathode; increasing voltages on each lens from cathode to anode; controls path of electron flow to output phosphor; 3rd section of II tube
|
electrostatic lens
|
|
|
cesium iodide; converts x-rays to light; 9 in diameter; larger than output; 1st layer of II tube; exiting x-rays from patient hit the input
*more x-rays exiting patient= more light photons emitted in II (this is a direct proportion!) |
input phosphor
|
|
|
draws electrons from photocathode; uses 25 kV to attract electrons; image crosses over here; 4th section of II tube
|
accelerating anode
|
|
|
holds all parts of II tube; vacuumed state so electrons will not collide with anything else (gas particles)
|
vacuum glass envelope
|
|
|
converts light to electrons (photoemission); serves as the II's cathode; 2nd layer of II tube
|
photocathode
|
|
|
Brightness gain of an image intensifier is a result of what two things?
|
MG x FG
|
|
|
An x-ray unit's shortest possible exposure time is known as what?
|
minimum response time
|
|
|
What radiographic modality uses cinefluorography the most?
|
cardiac catheterization
|
|
|
List three things that can vary the brightness level of a fluoroscopic image.
|
1. mA (specifically the fluoro mA)
2. kV 3. patient thickness |
|
|
What is the advantage of using a large format spot film (105 mm) over a smaller format (70 mm)?
|
improved image quality
|
|
|
What is the most common diameter of the image intensifier's input phosphor?
|
9"
|
|
|
What is the formula for "minification gain"?
|

|
|
|
How much kVp does the accelerating anode need to function?
|
25 kV (25,000 volts)
|
|
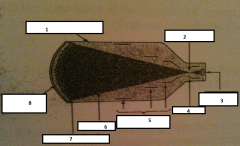
1
|
glass envelope
|
|
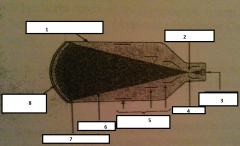
2
|
focal point
|
|
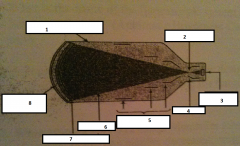
3.
|
output phosphor
|
|
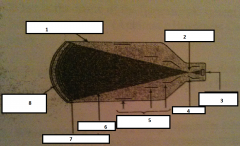
4.
|
anode
|
|
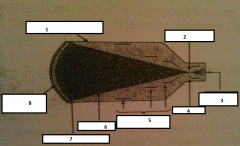
5.
|
electrostatic lenses
|
|
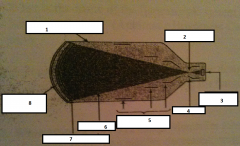
6.
|
electrons
|
|
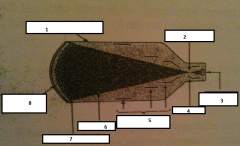
7.
|
photocathode
|
|
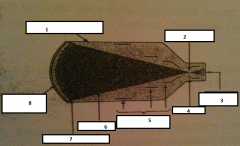
8.
|
input phosphor
|
|
|
What are several radiation safety features of fluoroscopic equipment that reduces unnecessary radiation to the patient and personnel?
|
1. 5 mA maximum
2. 12" min SID 3. distance between focal spot and table top 4. 10 R/min max exposure allowed at tabletop 5. dead-man foot pedal (switch) 6. automatic collimation 7. Bucky-slot cover to protect operator 8. 5 minute audible, cumulative timer 9, protective curtain (tower drape) 10. filtration |
|
|
What type of fluoroscopic image recording involves altering the pattern of magnetic flux on the recording medium?
|
videotape
|
|
|
What is the purpose of fluoroscopy?
|
to view dynamic (motion) anatomy, real time viewing
|
|
|
In a stationary fluoroscopic unit, where is the fluoroscopic x-ray tube located?
|
under the table
|
|
|
What is the normal tube current during fluoroscopy?
|
1-5 mA
|
|
|
What is photoemission?
|
The emission of electrons (photoelectrons) from the photocathode
|
|
|
At what stage of image intensified fluoroscopy is the number of photons the lowest?
|
upon entering the input phosphor
|
|
|
What is the name of the fluoroscopic system designed to maintain a constant image brightness?
|
ABC (automatic brightness control)
(controlled mainly by the fluoro mA) |
|
|
ABC is designed to compensate for changes in what?
|
patient positioning (when going for flat to oblique to lateral --- when patient thickness changes)
|
|
|
When using a 25/17/12 image intensifier tube, which number offers the largest field of view?
|
25 cm
As number decreases: mag of image increases larger number=larger FOV and less radiation to patient |
|
|
What happens to resolution when using a multifocus image intensifier tube in the magnification mode?
|
resolution improves
|
|
|
What component of the television monitor transfers the video signal into a visible image?
|
fluorescent screen
|
|
|
In digital fluoroscopy, which piece of equipment is the weakest link ( or produces the most noise/snow)?
|
TV camera
|
|
|
Where is the human eye is visual acuity the greatest?
|
where the cones are concentrated (at the fovea centralis)
|
|
|
What is the difference in what type of light stimulates the rods and cones of the eye?
|
rods- low light stimulation
cones- bright light stimulation |
|
|
What is the difference between photopic and scotopic vision?
|
photopic- higher light vision, cones, perceives color, more acute
scotopic- low light vision, rods, does not perceive color, 10 times less acute |
|
|
What is the purpose of the potential difference across the accelerating anode?
|
increases the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons as they travel to the anode (pushes photoelectrons)
|
|
|
What is flux gain?
|
the ratio of x-rays incident on the input phosphor to light photons exiting the output phosphor
|
|
|
What is brightness gain?
|
the ability of the image intesifier to increase the illumination level of the image; it is the product of minification gain and flux gain; brightness gain is typically 5000-30000 times
|
|
|
What is the kVp for UGI?
|
100-110
|
|
|
What is the kVp range for BE?
|
110-120
|
|
|
What is the kVp range for air contrast BE?
|
80-90
|
|
|
What is the kVp range for myelograms?
|
70-80
|
|
|
What is the kVp range for SB?
|
110-120
|
|
|
What is the kVp for gallbladder studies?
|
65-75
|
|
|
Light produced at the output phosphor of the II has been increased how many times in intensity since leaving the photocathode?
|
50-75
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the II fluoroscopy?
|
To view dynamic images with the same light intensity of radiographic viewing (because of the brightness gain of the image)
|
|
|
What is the difference of contrast perception and visual acuity?
|
contrast perception- the ability of the human eye to detect differences in brightness levels
visual acuity- the place in the human eye where objects are most clear; greatest at the fovea centralis |
|
|
How is an II tube typically identified?
|
by the diameter of the input phosphor
|
|
|
what is one of the major drawbacks of conventional fluoroscopy?
|
the low-light level of the image
|
|
|
Which of the following devices revolutionized fluoroscopy in the 1950s?
|
image intensifier
|
|
|
The input phosphor of second-generation image intensifiers is composed of what phosphor?
|
cesium iodide
|
|
|
What is the function of the input phosphor of an image intensifier?
|
to convert x-rays to light
|
|
|
What is the function of the photocathode of an image intensifier?
|
to convert light to electrons
|
|
|
The photocathode is:
|
-referred to as the photoemissive layer
- the cathode of the image intensifier |
|
|
What part of the image intensifier draws the electrons away from the photocathode?
|
accelerating anode
|
|
|
The output phosphor of an image intensifier:
|
-converts electrons to light
-is smaller in diameter than the input phosphor -is composed of zinc cadmium sulfide |
|
|
Vignetting is:
|
a fall-off in brightness at the periphery of the field
|
|
|
Cine:
|
-is the recording of the dynamic image on film
-requires pulsing of the x-ray beam |
|
|
Which of the following are major differences between cine and spot film cameras?
|
-film size, frame rate, patient dose
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a major disadvantage of spot-film cameras?
|
decreased film costs
|
|
|
Which of the following television tubes is most widely used for fluoroscopic imaging?
|
vidicon
|
|
|
When comparing mirror optics to a television system, which of the following is true?
|
Mirror optics provides better resolution, and television provides better contrast.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a method of recording the television image?
|
cine
|
|
|
Which of the following is a disadvantage of both television systems and spot-film cameras?
|
maintenance costs, decreased resolution
|
|
|
Which of the following imaging techniques places the greatest stress on the x-ray tube?
|
cine
|
|
|
Which of the following methods does NOT record the dynamic nature of fluoroscopy?
|
spot-film camera, spot-film device, multiformat camera, magnetic disk recorder
|
|
|
In a modern fluoroscope, the fluoroscopic x-ray tube:
|
can either be under or over the table.
|
|
|
The fluoroscope was invented by:
|
Thomas Edison
|
|
|
Compared with a radiographic examination, the primary purpose of a fluoroscopic examination is to visualize:
|
dynamic images
|
|
|
Fluoroscopy normally requires a tube current of:
|
1-5 mA
|
|
|
Compared with a radiography, the x-ray technique for fluoroscopy calls for which of the followinng?
|
lower mA
|
|
|
Automatic brightness stabilization (ABS) is designed to compensate for changes in which of the following?
|
patient composition- thickness of part
patient positioning- AP, lateral or oblique |
|
|
The Bucky slot cover of a fluoroscope is a:
|
protective device
|
|
|
Which of the following units of measurement is used to express fluoroscopic image brightness?
|
cd/m^2
|
|
|
Which eye structure is most sensitive to colors?
|
cones
|
|
|
What is the function of the iris?
|
control the light level
|
|
|
The cones are:
|
used for phototopic vision
|
|
|
The fovea centralis is:
|
part of the retina
|
|
|
Visual acuity is the ability to do what?
|
perceive fine detail
|
|
|
The rods are principally used for what?
|
dim vision
|
|
|
In general, during fluoroscopy as compared with radiography:
|
the mA is lower
|
|
|
Which of the following describes the fluoroscopic system designed to maintain constant image intensity?
|
automatic brightness stabilization (ABS)
|
|
|
Which of the following structures is responsible for the vision of dim objects?
|
rod
|
|
|
Which ocular structure immediately precedes the vitreous humor along the path of incident light?
|
lens
|
|
|
Which property is associated with rods but not with cones?
|
scotopic vision
|
|
|
Photoelectric emission:
|
is the emission of electrons from an illuminated surface
|
|
|
At what stage of image-intensified fluoroscopy is the number of the image-forming photons lowest?
|
entering the input phosphor
|
|
|
Image-intensifier brightness gain increases with increasing:
|
flux gain
|
|
|
when an image intensifier receives x-rays at the input phosphor, what is emitted at the output phosphor?
|
visible light
|
|
|
Which of the following is the input phosphor of image intensifiers?
|
cesium iodide
|
|
|
Which of the following is the output phosphor of image intensifiers?
|
zinc cadmium sulfide
|
|
|
The photocathode converts:
|
visible light into electrons
|
|
|
Which of the following is the component of the image intensifier responsible for focusing the electron beam?
|
electrostatic lens
|
|
|
The ability of image intensifier responsible to increase image illumination is called:
|
brightness gain
|
|
|
The minification gain of an image intensifier increases with increasing:
|
input phosphor size
|
|
|
Which of the following is a representative brightness gain for an image intensifier?
|
20,000
|
|
|
If an image intensifier is described as a 25/12 tube, the 25/12 refers to which of the following?
|
diameter of the input phophor in inches
|
|
|
When a multifocus image intensifier is operated in the magnification mode:
|
the electron focal point is closer to the input phosphor.
|
|
|
An image that displays vignetting:
|
is dim around the periphery
|
|
|
With a multifocus image intensifier in the magnification mode:
|
spatial resolution is improved
|
|
|
In a 10/7/5 image intensifier:
|
The field of view is largest in the 10 mode.
|
|
|
An image intensifier has a 5 cm output phosphor and a 45 cm input phosphor. The brightness gain is 10,000. The flux gain is approximately:
|
120
|
|
|
Place the following in proper sequence for image-intensified fluoroscope:
1. electric signal to light 2. electrons to light 3. light-to-electric signal 4. light to electrons 5. x-ray to light |
5,4,2,3,1
|
|
|
Which of the following applies to output phosphor?
|
light emitted
|
|
|
Vertical television resolution is limited principally by which of the following?
|
lines per frame
|
|
|
The electron beam in a television camera tube is produced by which of the following means?
|
thermionic emission
|
|
|
What is the cinefluorography component of image-intensifier fluoroscopy?
|
synchronized
|
|
|
What is the photoemissive component of image-intensified fluoroscopy?
|
electrons from light
|
|
|
Which of the following is photoconductive?
|
target
|
|
|
What is the principal disadvantage to coupling the television camera to the image intensifier by fiber optics?
|
photospot camera cannot be used
|
|
|
Which of the following refers to the image-intensifier input phosphor?
|
cesium iodide
|
|
|
Which is a critical component is optically coupling an image intensifier to a photospot camera?
|
objective lens
|
|
|
What is the most important component in a television monitor?
|
cathode ray tube
|
|
|
In an optical coupling arrangement, which is nearest the television camera?
|
camera lens
|
|
|
What is the component of the television monitor where the video signal is transformed into an image?
|
phosphor screen
|
|
|
What is the electron beam of the television camera tube?
|
modulated
|
|
|
One television frame is equivalent to which of the following?
|
two television fields
|
|
|
Fluoroscopic television operates at a frame rate of:
|
30 f/s
|
|
|
Horizontal television resolution is principally limited by which of the following?
|
bandpass
|
|
|
What is normally the weakest imaging link in television fluoroscopy?
|
television monitor
|
|
|
the common frame rates during cinefluorography are 15, 30, and 60 f/s because:
|
of the frequency of the power supply
|
|
|
When the electron beam of the CRT is blanked, it is:
|
in a vertical retrace
|
|
|
Which of the following is true about cineradiography?
|
The x-ray beam is off when the shutter is closed as a patient protective measure.
|
|
|
What is the television camera tube component of image-intensified fluoroscopy?
|
vidicon
|

