![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the vaginal fornix?
|
Pocketing of vagina - spermatazoa can hide here
|
|
|
What is the vestibular bulb?
|
Thickened area of CT
|
|
|
Which muscles are found at the exterior end of the vagina?
|
Constrictor vulvae
Constrictor vestibuli |
|
|
Ovary to uterus?
|
Ovary
Uterine tube Uterine horn Body of uterus |
|
|
Where does the suspensory ligament go from and to?
|
Ovary to transverse fascia near last rib in carnivores
|
|
|
What are the 3 broad ligaments?
|
Mesovarium
Mesosalpinx Mesometrium |
|
|
Which ligament descends from the ovary to the uterine tube?
|
Mesosalpinx
|
|
|
Which ligament suspends the ovaries?
|
Mesovarium
|
|
|
Where is the mesometrium found?
|
Attaches to uterus, cervix and cranial vagina
|
|
|
What is the ovarian bursa?
|
Extension of the mesovarium, pockets the ovary
|
|
|
What is the utero-ovarian ligament?
|
Between ovary and cranial uterine tube
|
|
|
What is the round ligament?
|
Passes from mid uterine horn to inguinal canal
|
|
|
Where is the intercornual ligament found?
|
Between uterine horns
Dorsal and ventral parts in the cow |
|
|
Describe how the ova travels from the ovary
|
Ova captured by fimbriae of infundibulum
Ova goes through infundibulum to uterine tube to isthmus, which is where it is fertilised |
|
|
What are the 3 parts of the uterine tube?
|
Infundibulum
Ampulla Isthmus |
|
|
What can knowledge of reproductive anatomy be applied to?
|
Rectal palpation
Ultrasound Spaying Placentation Vaginal smear Abnormalities AI |
|
|
Briefly describe the topography of reproductive organs
|
In pelvis, in lumbosacral region
Ventral to rectogenital pouch, dorsal to vesicogenital pouch |
|
|
Where are the ovaries positioned in the bi t ch?
|
Dorsal and caudal to kidneys
|
|
|
Describe the position of the uterus in the nongravid bi tch and in the pregnant one
|
Short and caudal
Extends cranially in pregnancy |
|
|
What blood vessels supply the reproductive organs in the bitch?
|
Ovarian artery -> uterine artery -> vaginal artery
Internal iliac artery |
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the sow's reproductive organs
|
Ovary - mobile, rounded with follicles
Sphincter at uterotubal junction Uterine horn - long, flexuous and freely movable Uterine body - short Cervix - long Upturned conical vulva |
|
|
What are 2 examples of abnormal genitalia in sows
|
Infantile vulva - reduced vulva, turned more upwards
Pseudohermaphroditism - enlarged clitoris, penis-like |
|
|
Describe the topography of the ovaries, uterine horn and cervix in the sow
|
Ovaries - suspended by mesovarium, ventrolateral to pelvic inlet
Uterine horn - suspended by broad ligaments, cranial to pelvic inlet Cervix - in abdominal cavity and pelvic inlet |
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the reproductive organs in the cow
|
Ovaries - firm, large corpus luteum
Uterine horn - short, double intercornual ligaments Uterine body - large cavity Labia round and clitoris long |
|
|
Where does the uterine uterus sit in the cow?
|
Non-gravid - in pelvic inlet
Gravid - extends cranially |
|
|
How do you tell the difference between ruminant uteri and sow/mare uteri?
|
Ruminants - obvious bumps - caruncles - implantation areas
Mare and sow - sow smooth but with little folds, mare more folded |
|
|
Difference between caruncles of breeds of sheep
|
Highland breeds - melanin in caruncles - dark
|
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the reproductive organs of the mare
|
Ovaries - follicles concealed by richly vascularised connective tissue
Specific ovulation fossa Well developed ovarian bursa Sphincter at uterotubal junction Large body of uterus Short cervix Large clitoris |
|
|
Describe the topography of the equine reproductive organs
|
Ovaries - dorsal part of abdomen, found cranioventral to lumbar 5 iliac wings
Uterus - suspended by broad ligament Cervix short Vagina mostly retroperitoneal |
|
|
In which animals is the uterine horn more fused?
|
Mare and cow
|
|
|
What is the difference between mare and sow cervix
|
Mare - short
Sow - long |
|
|
Why is it useful for the arterial and venous supply of the reproductive organs to be close together?
|
Allows exchange of hormones - hormones don't get into general circulation
|
|
|
What is Freemartinism?
|
Infertile female twin from mixed sex twins - common in cows
|
|
|
What is intersex?
|
Variation in sex characteristics: chromosomes, genitalia - individual cannot be identified as either male or female
|
|
|
What is a double uterus?
|
Double uterus due to congenital abnormalities, also sometimes double cervix and vagina
|
|
|
Name 4 common diseases associated with the reproductive organs
|
Hydrosalpinx
Prolapse Carcinoma UTIs |
|
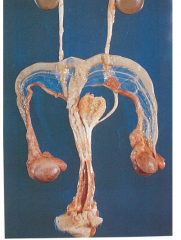
What condition is this?
|
Male pseudohermaphroditism - pseudo used because only testes present, male used because testes not ovaries (ALTHOUGH IN BOOKLET IT SAYS OVARIES PRESENT TOO SO W T F)
|

