![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 accessory sex glands?
|
Prostate
Ampulla Vesicular Bulbourethral |
|
|
What are 2 functions of the testes?
|
To produce sperm
To produce hormones |
|
|
What does the spermatic cord contain?
|
Ductus deferens
Testicular artery/vein Nerves and lymphatics Pampiniform plexus Mesoductus and mesorchium Surrounding vaginal tunic |
|
|
Which muscle does the cremaster muscle come from?
|
Internal abdominal oblique m.
|
|
|
What is the function of the ductus deferens?
|
Transports sperm to distal urethra for ejaculation by smooth muscle wall contraction
|
|
|
Where does the ductus deferens start come from?
|
Tail of epididymis
|
|
|
What is the pampiniform plexus?
|
A plexus of veins surrounding the tortuous testicular artery
|
|
|
Why do the testes live outside the body?
|
Because sperm cannot develop at core body temperature (except for elephants, dolphins etc.)
|
|
|
What are testiconda?
|
Animals with intra-abdominal testes
|
|
|
What structure do the testes descend through?
|
Inguinal canal
|
|
|
Where does the inguinal canal start and finish?
|
Start - deep inguinal ring - space at end of internal abdominal oblique m.
End - superficial inguinal ring - opening in aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique m. |
|
|
When do the testicles descend in cats and dogs?
|
Cats - 2-5 days after birth
Dogs - last few days of gestation and first few days after |
|
|
When do testicles descend in the horse?
|
Last few months ( after 9 months) of gestation and first few days after birth
|
|
|
When do testicles descend in the cow and sheep?
|
Cow - 3.5-4 months
Sheep - mid-gestation |
|
|
When do testicles descend in the pig?
|
After 85 days of gestation
|
|
|
Describe the gubernaculum's role in testicle descent
|
Structure that extends from gonad to potential scrotum and guides testicle to scrotum
Upper part degenerates; lower part remains as scrotal ligament |
|
|
What are the fascia layers from superficial to deep of the testes?
|
Skin
Dartos External spermatic fascia Cremaster muscle and fascia Internal spermatic fascia Parietal vaginal tunic Vaginal cavity Visceral vaginal tunic Tunica albuginea |
|
|
From which muscles do the ext. spermatic fascia, cremaster m. and int. spermatic fascia arise?
|
External spermatic fascia - external abdominal oblique m.
Cremaster muscle - internal abdominal oblique Internal spermatic fascia - transversus abdominis |
|
|
Difference between a closed and open castration?
|
Closed keeps vaginal tunic intact
|
|
|
Name the 3 gubernacular ligament remnants
|
Ligament of the tail of the epididymis - from epididymis tail to parietal vaginal tunic
Scrotal ligament - parietal vaginal tunic to scrotum Proper ligament - from testes to epididymis tail |
|
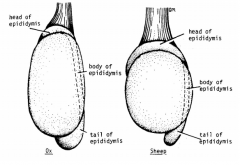
What do you call this axis of testicle?
|
Vertical long axis - found in ox and sheep
|
|
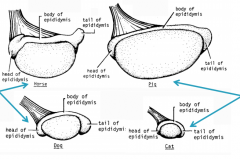
What is this axis called?
|
Horse and dog - horizontal
Pig and cat - tilted towards the anus |
|
|
What is the appearance of the testicular artery and from where does it arise?
|
Very convoluted distally
Abdominal aorta |
|
|
Where do the testicular veins leave?
|
Into caudal vena cava
Left testicular artery goes into left renal vein first |
|
|
What are the functions of this vascular complex?
|
Venous blood cools incoming arterial blood
Decreases arterial pulse Counter current exchange of small molecules e.g. testosterone |
|
|
What is the rete testis?
|
Where things from the seminiferous tubules drain into
|
|
|
What do the seminiferous tubules consist of?
|
Sertoli cells and gametes
|
|
|
What does the interstitial tissue consist of?
|
Leydig cells or interstitial cells
|
|
|
What is the function of Leydig cells?
|
Produce sex hormones (androgens)
e.g. testosterone |
|
|
What is the function of testosterone?
|
Essential for seminiferous tubule function
Causes secondary sexual characteristics |
|
|
What happens to testosterone once it's produced?
|
Aromatised to oestrogen and reduces to dihydrotestosterone (more potent)
|
|
|
Which hormone affects accessory sex gland function?
|
Dihydrotestosterone
|
|
|
Which cells aromatise testosterone to oestrogen?
|
Sertoli cells
|
|
|
Which hormone stimulates Leydig cells?
|
LH
|
|
|
How are sperm and fluid moved out of the seminiferous tubules?
|
Basal lamina surrounded by contractile myoid cells
|
|
|
Where do sperm cells develop motility?
|
In epididymis
|
|
|
What are the two cells of the seminiferous tubules?
|
Sertoli cells - support and nourish the developing sperm
Germinal cells - produce sperm |
|
|
What do the tight junctions between sertoli cells divide the developing sperm germinal cells into?
|
Basal and luminal compartments
|
|
|
What is this barrier called?
|
Sertoli barrier or blood-testis barrier
|
|
|
Which hormone influences sertoli cells?
|
FSH - for aromatisation of testosterone and nourishment of sperm
|
|
|
Where do sertoli cells transport testosterone to?
|
Lumen of tubule
|
|
|
What do sertoli cells produce that affects FSH?
|
Inhibin - negative feedback
|

