![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stages of Mitosis |
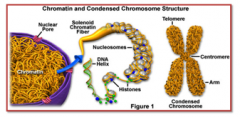
|
|
|
Mitotic (M) phase |
Phase which includes both mitosis and cytokenisis |
|
|
Interphase |
Non-Dividing phase in which chromosomes, cytoplasm, and organelles are duplicated & cell size usually increases |
|
|
Prophase |
chromatin condenses into chromosomes, nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear & spindle begin to form |
|
|
Metaphase |
chromosomes line up at equator of spindle |
|
|
Anaphase |
-Cohesin proteins and centromere are cleaved and chromosomes separate
-Daughter chromosomes move towards opposite poles |
|
|
Telophase |
-Chromosomes become less dense and visible
-Nucleoli and nuclear membrane reappear
-The spindle begins to breakdown (depolymerize) |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of cytoplasm to form 2 separate, but genetically identical daughter cells
In ANIMALS: Cleavage - process of cytokinesis in animal cells, characterized by pinching in of plasma membrane
PLANTS: Cell plate – membrane-bounded, flattened sac located at the equator of a dividing plant cell inside which the new cell wall forms during cytokinesis |
|
|
mitosis occurs in cancer cells. |
1. Cancer cells do not follow normal pathways that control cell division, dividing excessively while invading tissues
2. Cancer cells are immortal, dividing indefinitely if a continuous supply of nutrient exist
|
|
|
Asexual v. Sexual Reproduction |
Asexual reproduction – generation of offspring from a single parent, occurring without the fusion of gametes; in most cases, offspring are genetically identical to the parent
example: kamodo dragon |
|
|
Sexual reproduction |
generation of offspring in which gametes from two parents fuse and give rise to genetically unique offspring Maintains a constant chromosome # Creates genetic diversity in offspring
EX: Dogs |
|
|
Mitosis v. Meiosis |
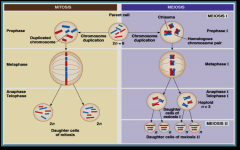
|
|
|
Mitosis v. Meiosis sexual cycle |

|
|
|
Monohybrid cross |
cross between 2 organisms that are heterozygous for the character being followed |
|
|
Dihybrid |
organism that is heterozygous with respect to two genes of interest |
|
|
Dihybrid cross |
cross between 2 organisms that are each heterozygous for both characters being followed |
|
|
Sex chromosomes |
chromosomes responsible for determining the sex of an individual and all the characteristics that accompany gender
Female = XX (homologous) Male = XY (not homologous) |
|
|
Gonads |
– male and female sex organs which, through meiosis, produce haploid gametes
Female = ovaries Male = testes |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
error in mitosis or meiosis in which members of a pair of homologous chro-mosomes or a pair of sister chromatids fail to properly separate from each other
ex: Down’s Syndrome |
|
|
Frederick Griffith (1928) |
discovered DNA’s ability to transform non-pathogenic bacteria cells into pathogenic bacteria cell |
|
|
Hershey & Chase (1952) |
found that when a phage infected a bacterium, only DNA enter-ed the bacterium, not protein |
|
|
Bacteriophage (phage) |
a virus that infects a bacterium; protein coat surrounding DNA |
|
|
Leading strand |
new complementary DNA continuously synthesized along the template strand towards the replication fork (5’ → 3’ direction) |
|
|
Lagging strand |
discontinuously synthesized DNA strand, elongating by Okazaki fragments away from the replication fork (5’ → 3’ direction) |
|
|
Nucleotide excision repair |
removes, then correctly replaces a damaged segment of DNA using the undamaged strand as a guide |
|
|
Semiconservative model – DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand (parent) and one new strand |
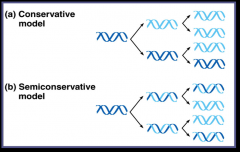
|
|
|
According to Watson & Crick:
-H-bonds are broken and the two strands of DNA unwind and separate
-Each original strand acts as a template to a new complementary strand
-Result is two semi-conserved pairs of chains |
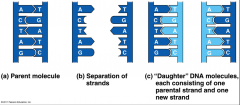
|

