![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
QbD, quaity by design |
> building qualit into a product and the processes used to manufacture the product |
|
|
QbD, building blocks |
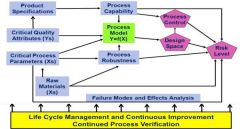
Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) that are the most important process output measurements linked to customer needs. Product specifications that define what a quality product is; a product that meets the stated needs of the customer. Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) that encompass the process input (API and excipient), control, and environmental factors that have major effects on the CQAs. Raw Materials Factors that include the stability and capability of raw material manufacturing processes that affect process robustness, process capability, and process stability. A Process Model, represented schematically as Y=f(X), where Y is the CQA and X represents the CPPs, provides a quantitative picture of the process based on fundamental and statistical relationships that predict the CQA results. Design Space that is the combinations of input variables and process parameters that provide assurance of quality product that meets specifications. Process and Measurement Capability that tracks process performance relative to CQA specifications and provides measurement repeatability and reproducibility regarding CQAs. Process and Measurement Robustness is the ability of the process and measurement system to perform when faced with uncontrolled variation in process, input, and environmental variables. Process and Measurement Control includes the use of control procedures, including statistical process control, to hold the process and the measurement system on target and within the desired variation. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) of the CPPs, including raw material variables, identifies how the process can fail and, after appropriate controls and fixes are in place, the areas of the process that remain at greatest risk of failing. Risk Level that is a function of the design space, FMEA results, and process and measurement capability, control, and robustness. Life Cycle management: Continuous improvement and continued process verification as specified in the FDA Process Validation Guidance (3) |
|
|
QbD, what's needed vs what's wanted |
Revisiting QbD increases clarityn and understanding, enabling easy ID of critical elements and develop strategy, plans, and roadmaps. |
|
|
QbD, holistic view |
... the central role of the dsign space, th elife cycle benefits of an effective process monitoring system that enables continued process verification, the value of process robustness and the importance of test metbhod repeatability, reproducibility and robustness. ... also aids technology transfer/build transition to operations |
|
|
QbD, process understanding |
... to successful process development, operation and improvement. A process is generally considered to be well understood when: > all critical sources of variability are identified and explained > variability is managed by the process > product quality attributes are be accurately and reliably predicted within the design space established fo rthe material sused, proces sparameters, and manufactuing and environmental conditions |
|
|
QbD, critical quality attributes |
Critical Quality Attributes (CQA) are chemical, physical, biological and microbiological attributes that can be defined, measured, and continually monitored to ensure final product outputs remain within acceptable quality limits. |
|
|
products = VOC, critical-to-quality |
The first 2 critical steps of the product-development process are to capture the VOC and convert it into a product's critical-to-quality characteristics (CTQC). Functional requirements are the CTQCs of a product. |

