![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
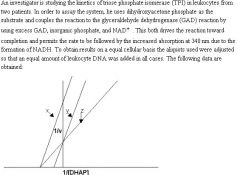
*ol 2119
Which of the following choices best explain these dat? |

Normal enzyme control: Line Z;
Mutation producing INCREASED Km: Line Y; Mutation DECREASING amount of functional enzyme: Line X |
|

*ol 083
|

overcooked food
|
|

m200028
|

She inherited two X-chromosomes, both carrying a defective G6PD gene.
rest of explanation: *She inherited two X- chromosomes, both carrying a defective G6PDH gene *rest of explanation: Choice B: If a normal woman inherits a single defective X-chromosome, the phenotype will NOT usually be expressed. Choice C: Inheriting an X-chromosome carrying a defected G6PD gene, which is translocated onto an autosome during meiosis, would be another mechanism that would account for expression of a disease phenotype by a heterozygous female in a recessive X-linked trait, but it would be VERY RARE. Choice D: Inheriting an X-chromosome carrying a defective G6PD gene may permit the phenotypic expression of a disease trait in a female carrying an X-linked recessive trait if there were incomplete inactivation of the chromosome. In such cases, the female would be expected to express the disease in an attenuated form. |
|

* ol309
|

*2-3 MONTHS
|
|
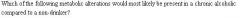
*OL 985
|

The ratio of NADH to NAD+ is INCREASED
|
|

*OL 2121
|

3.00 mM
|
|
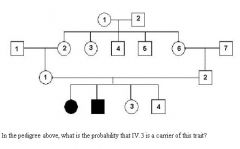
*ol192
|

2/3
|
|

*m00066
|

*Aminoacidopathy
|
|

*ol 1661
|

0%
|
|

*ol1140
|

*pyruvate kinase
|
|

*m200057
|

*Inactivation of tumor suppressor genes
|
|

*ol 2038
|

*methionine
|
|

*1158
|

*Acetoacetic acid
|
|

*ol1956
|

*CORRECT ANSWER:
LONG-CHAIN ACYL COA DEHYDROGENASE (LCAD) DEFICIENCY Choice E: Muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency, or McArdle disease, is also associated with muscle weakness and potential cardiomyopathy, but there is no associated hypoglycemia or hypoketosis. Muscle glycogen is NOT released as free glucose into the blood, and keton synthesis is a hepatic pathway assiciated with fatty acid oxidation in that tissue. A muscle biopsy of a patient with muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency would reveal glycogen deposits. There would be no increaswe in acyl carnitines. |
|

*ol 1673
|

*Desmoglein
|
|

*ol 1099
|

*PHENYLEPHRINE
|
|

*m200058
|

*Removal of introns as lariat structures
|
|

*ol 1652
|

50%; 50%
|
|

*ol 1647
|

*A high proportion of the X chromosomes carrying the mutation are active.
|
|

*ol 1650
|

*2/3
|

