![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the four major macromolecules of life? |
Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Lipids and Hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
Structure defines ___________. |
Function |
|
|
|
What is an isomer? Give an example. |
An isomer is a molecule with the same formula as another molecule but a different structure ie: glucose and fructose. |
|
|
|
Why is water so important to life? |
Water does not change forms relatively fast, and so exists mostly in liquid form. Its liquid form is better suited to harbour life due to its excellent solvent characteristics (hydration shell) and high specific heat capacity. It is less dense in its solid form, which allows it to float. The attraction between water molecules causes a phenomenon known as cohesion, which allows water to move against the force of gravity. |
Temperature |
|
|
What are the intermolecular and intramolecular forces studied in Biology? |
Hydrogen bonding, van Der Waals forces, ionic forces, covalent forces. |
|
|
|
What are the four steps of the scientific method? |
1. Characterisation 2. Hypothesis 3. Experimentation 4. Interpretation of Results |
|
|
|
A hypothesis must be _______ & ________. |
Falsifiable & testable |
|
|
|
An ________ variable is changed by the scientist. A _________ variable responds to changes in the ___________ variable. A controlled variable remains _________. |
Independent, dependent, independent & constant |
|
|
|
True or false: a light microscope is capable of viewing objects below a 100 nm in diametre. |
False; only electron microscopes |
|
|
|
The ________ is the basic unit of life. |
Cell |
|
|
|
What 4 elements make up 90% of matter in living organisms? |
Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon |
|
|
|
Why are organisms different from each other in terms of functions and appearances? |
Different structures, proportions and arrangements of atoms. |
|
|
|
What is an isotope? |
Atom with same number of protons but different number of neutrons |
|
|
|
What are radioisotopes and why are they used in medicine? |
1. Unstable isotopes that decay and release energy 2. Energy is then used to measure speed of chemical processes or movemeny of substance ie diagnostics |
|
|
|
What nuclear reactor produces 30-40% of radioisotopes globally? |
Chalk river reactor in Canada |
|
|
|
Electrons move around protons in regions called __________, which are grouped in ______. |
Orbitals, shells |
|
|
|
The unequal sharing of electrons creates a ________ ________ bond. |
Polar covalent |
|
|
|
Hydrogen bonding helps with what in proteins? |
Creating 3D structure |
|
|
|
What are van der Waals forces? |
They are forces that develop between nonpolar molecules through the constant motion of electrons. This causes zones of positive and negative charges. |
|
|
|
What are buffers? Name an example. |
Buffers control pH of our blood ie dissociation of carbonic acid |
|
|
|
Name all important biological functional groups. |
Hydroxyl (-OH) Carbonyl (-C=O) Carboxyl (-COOH) Amino (-NH2) Phosphate (-PO4^2-) Sulfhydryl (-SH) |
There are 6 1) (-SH) |
|
|
Which type of reaction synthesizes a polymer? Which one breaks down a polymer? |
1. Dehydration 2. Hydrolysis |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a-glucose and b-glucose? |
Their structures differentiate them from each other and give them different functions. They are enantiomers. A-glucose (starch) is digestible while b-glucose (cellulose) is not. |
|
|
|
The base monomer of a carbohydrate is a __________. Many of these in a chain create a ________. |
Monosaccharide; polysaccharide |
|
|
|
Glucose + glucose = 1 Glucose + fructose = 2 Glucose + galactose = 3 |
1. Maltose 2. Sucrose 3. Lactose |
|
|
|
Name the glycosidic linkages. |
Linear; branched; h-bonds; n-groups |
|
|
|
What are the different functions of proteins? |
Structural support Storage Transport Enzymes in reactions Cellular comms Movement |
|
|
|
What is the basic structure of an amino acid? |
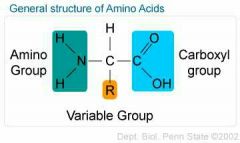
Amino group, side group and carboxyl group |
|
|
|
What is the base unit of a protein and what is it made of? |
Polypeptide; amino acids |
|
|
|
Name the nonpolar amino acids |
Alanine (Ala) Valine (Val) Leucine (Leu) Isoleucine (Ile) Glycine (Gly) Cysteine (Cys) Phenylalanine (Phe) Tryptophan (Trp) Methionine (Met) Proline (Pro) |
|
|
|
Name the uncharged polar amino acids |
Serine (Ser) Threonine (Thr) Tyrosine (Tyr) Asparagine (Asn) Glutamine (Gln) |
|
|
|
Name the negatively charge amino acids |
Aspartic acid (Asp) Glutamic acid (Glu) |
|
|
|
Name the positively charged amino acids |
Lysine (Lys) Arginine (Arg) Histidine (His) |
|
|
|
Describe the 4 protein structures |
Primary = linear sequence, not much info, R groups do not participate Secondary = Alpha helix or beta pleated sheets, H bonds between Nitrogen and Oxygen partial charges, R groups do not participate Tertiary = folding, R groups participate, structure is defined and so function is given, various bonds cause folding ie hydrogen, disulfide bridge, ionic, hydrophobic interaction etc. Quaternary = >2 polypeptides come together to create functional protein ie collagen. Can have cofactors such as heme to create protein ie hemoglobin |
|
|
|
What are the subdivisions of nucleic acids? |
DNA RNA rRNA tRNA mRNA |
|
|
|
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid and what is its structure? |
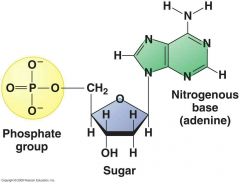
Nucleotide: nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, 1-3 phosphate groups |
|
|
|
What are the differences between RNA and DNA? Which nucleotides are used in energy transfer? |
DNA = desoxyribose, Thymine RNA = ribose, Uracil Adenine and Guanine |
|
|
|
What is the basic structure of DNA and RNA? How do you read them? |
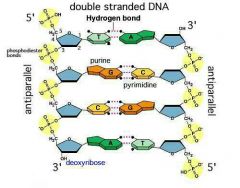
2 nucleotide chains, sugar-phosphate backbone; phosphodiester bonds, H bonds, nitro bonds
From 5' to 3' |
|
|
|
What allows us to predict the opposing strand of a DNA molecule? |
Complementary strands: G-C, A-T (DNA) or A-U (RNA) |
|
|
|
Describe the structure of a lipid. |
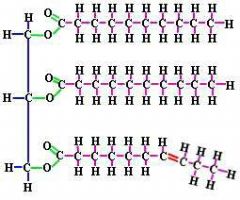
Nonpolar molecule with long hydrocarbon chains. Double bond causes a kink in chain. |
|
|
|
Name the three categories of lipids. |
Fats Phospholipids Steroids |
|
|
|
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Sat fats have no carbon double bonds (all bonds saturated) while unsat fats have one or more. This makes unsat fats less dense and therefore liquid at room temp. |
|
|
|
Describe basic structure of a fat. |
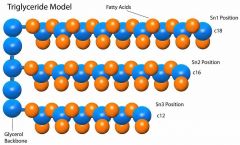
Glycerol + fatty acids + 3 hydrocarbon chains = triglyceride |
|
|
|
What is a phospholipid? |
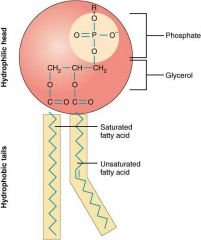
Lipid that has polar hydrophilic phosphate end and nonpolar hydrophobic fatty acid end. Two-chain structure with one chain having a double bond. |
|
|
|
What is a steroid? |
4 carbon ring structure with dual solubility. It is base form of cholesterol. Many hormones are sterol-based ie testosterone, estrogen, etc. |
|

