![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What percent of the circulation does the pulmonary circulation receive?
|
100%
ALL OF IT! |
|
|
What percent of CO goes through the bronchial circulation?
|
2%
|
|
|
What is the arterial source for the bronchial arteries?
|
Aorta
|
|
|
What is the drainage of the bronchial arteries?
|
1/3: Azygous vein
2/3: pulmonary capillares (broncho-pulmonary anastamoses) |
|
|
What is the most common source for PE's?
|
Deep veins of the legs:
-Femoral -Illiac -Pelvic Not so common: -Subclavian -RA/V |
|
|
What types of people get PE's?
|
Hospitalized old people
|
|
|
What are the components of Virchow's triad?
|
YOU SHOULD NEVER FORGET THIS!!!
Stasis Abnormal coagulation Tissue injury |
|
|
What are some common causes of stasis leading to PE?
|
Surgery (urologic, orthopedic)
Pregnancy (pelvic vein stasis) CHF Bed rest travel Prior thromboembolism Casts for fractures |
|
|
What are some common causes of abnormal coagulation leading to PE?
|
Alteration of female hormones (contraceptives, HRT, pregnancy)
Malignancies Mutations in clotting factors |
|
|
What are some common causes of tissue injury leading to PE?
|
Surgery
Trauma IV catheters prior thromboemboli |
|
|
What are the symptoms of a PE?
|
Not too terribly specific!
Here's a list, though: -Dyspnea -Pleuritic chest pain -Cough -Hemoptysis -Palpations -Syncope -Leg pain/swelling |
|
|
What are the signs of a PE?
|
Not specific!
Here's a list, though: -Tachypnea -Rales -Calf/thigh swelling (good predictor) -Calf/thigh pain (good predictor) |
|
|
What is Homan's sign? What condition is it commonly found in?
|
Calf pain on dorsiflexion of the fooot
PE |
|
|
What blood gas finding is classic for PE's?
|
Respiratory alkalosis due to increased RR secondary to V/Q mismatch
|
|
|
Why does hypoxemia occur with PE?
|
Blood going through places that there isn't ventilation (lower lobe has high Q. when PE, Q diverted to upper lobe, where V is lower)
Low of pulmonary surfactant in areas of PE Reduced mixed venous O2 contend due to decreased CO |
|
|
What is the physiologic response to PE?
|
Disproportionate increase in pulmonary vascular resistance: generalized constriction--> RHF--->decreased LV filling--> decreased CO--> hypotension, shock
|
|
|
Are EKG and CXR very helpful for making a diagnosis of PE?
|
No. they aren't sensitive or specific.
|
|
|
What is Westermark's sign? When is it seen?
|
Decreased vascular markings in an area of lungs.
PE |
|
|
What is Hampton's hump?
|
A wedge shaped infiltrate extending to the pleural surface
PE |
|
|
What is the "classic" PE finding on EKG?
|
S1, Q3, T3 pattern
|
|
|
What is the wells score?
|
Clinical probability model for PE
|
|
|
What are the most diagnostic clinical features on the Wells Model?
|
In order:
-Clinical signs of DVT -Excluding other causes -Immobilization -Tachycardia -Previously diagnosed PE/DVT |
|
|
What are good diagnostic studies for PE?
|
V/Q scan
CT angiography Pulmonary angiography - perform this last...it's invasive |
|
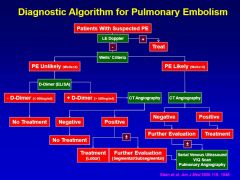
Just take a look at the diagnostic map for a PE and think about it.
|
WOULDJA LOOKIT THAT!
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EF8GhC-T_Mo |
|
|
What are ways that you can prevent PE's in patients?
|
Have them walk! (ambulation)
Compression stockings Prophylactic anticoagulations |
|
|
What is the treatment of a PE?
|
Supportive therapy
Heparin (reduces morality significantly) Thrombolytics IVC filter |
|
|
What is the long-term treatment of PE?
|
Bridge the patient to warfarin
|

