![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bronchiectasis |
Foul smelling purulent Recurrent pulmonary infections Train tracks on cxr Recurrent pneumonia Hemoptysis Crackles at bases
Non-CF- Hflu
CT gold standard Tx- acute exacerbations with abx... amoxicillin 10-14 days Chest physiotherapy Inhaled bronchodilator |
|
|
Strep pneumo |
Single rigor Rust colored sputum Lobar consolidation, pleural effusion, empyema Most common |
|
|
Hflu/mcat |
Smokers copd Patchy multi lobar consolidation |
|
|
Mycoplasma |
Sore throat Bullous myringitis Young healthy adults Summer and fall Patchy lower lobe infiltrates bronchipneumoniae |
|
|
Chlamydia pneu |
Long prodrome- sore throat/laryngitis Cpsittaci- bird **** |
|
|
Legionella |
Nonproductive cough Fever GI symptoms/diarrhea Contaminated water Air conditioning Lobar or patchy infiltrate, possible hilar lymphadenopathy |
|
|
Staph aureus |
Cap or hap Copd, smoker SNF IV drug abusers Immunosuppressed CF Patchy infiltrate and abscess/empyema |
|
|
Klebsiella |
Etoh Diabetes Fevers rigor Currant jelly sputum Upper lobes, cavitary lesions |
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
CF bronchiectasis Smells like grapes Lower lobes, cavitation |
|
|
Pneumocystic jirovecii |
Aids/immunosupressed Ca/chemo Weight loss Night sweats Underdeveloped countries Ground glass Pneumothorax ARDS |
|
|
Small pneumo tx |
Observation and supplemental oxygen |
|
|
Larger pneumo |
Catheter aspiration and placement of small bore chest tube (with suction) |
|
|
Tube thoracostomy |
Chest tube placement
Secondarypneumo Tension pneumo LargePneumo while on mechanical vent **empyemas should always be drained by thorocostomy (strep pneumo) |
|
|
Thorascopy or open thoracotomy |
Bilateral pneumothorax Recurrence Failure of expansion with chest tube |
|
|
Secondary pneumothorax causes |
Underlying or contributing disturbance in pulmonary function COPD Mechanical ventilation, needle aspiration, central IV catheter Severe, chronic asthma Cystic fibrosis Tb, HIV associated pneumocystits infection Interstitial lung disorders- sarcoidosis |
|
|
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax causes |
Without previous or chronic respiratory disorder Unrecognized form of lung disease Early 20s Ruptured blebs Smokers Family hx Marfan syndrome |
|
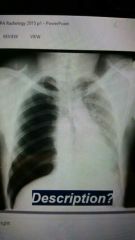
What is this? |
Tension pneumo Deep sulcus sign- diaphragm pushed down |
|
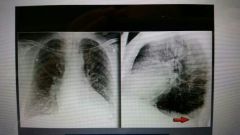
|
Pleural effusion |
|
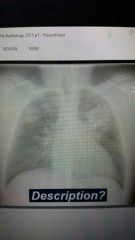
|
Tb- bilateral upper lobe infiltrates |
|
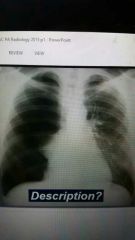
?? |
Pneumothorax |
|
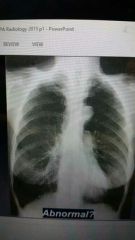
?? |
Hyperinflation due to emphysema |
|
|
Causes of exudative effusions |
Parapneumonic (empyema- drained via thoracostomy) Malignancy Secondary to PE, Tb, autoimmune ds (rheumatoid arthritis) |
|
|
Causes of transudative effusion |
CHF Cirrhosis Nephrotic syndrome Secondary PE |
|
|
Chylothorax |
Fluid triglycerides > 110 |
|
|
Lung PE pleural effusion |
Pleuritic chest pain Decreased breath sounds Dullness to percussion |
|
|
Empyema |
Cause of pleural effusion Pus Eloculated collection Not just fluid you can drain Gelatinous/consolidated Thick purulent appearing fluid Low pH Exudate, fibropurulent, organization Tx- drainage, chest tube/VAT/open/decortication intrapleural abx/thrombolytics |
|
|
Pleuritis tx |
ds Analgesics and antiinflammatory (indomethacin) Underlying dsAnalgesics and antiinflammatory (indomethacin)If bad- codeine If bad- codeine |
|
|
Classic asthma s/s |
Intermittent dyspnea Cough Wheezing Worse at night Precipitated by triggers (exercise, cold air, allergens) |
|
|
Status asthmaticus |
Severe bronchoconstriction not responding to bronchodilating drugs |
|
|
ICS |
Fluticasone Budesonide |
|
|
LABA example |
Salmeterol Formoterol |
|
|
Quick relief asthma |
1. Nebulizer saba (albuterol) Up to 2tx 20min apart of 2-6puffs 2. Anticholinergic (ipratropium bromide/atrovent) 3. Corticosteroid -prednisone or methylprednisolone 4. iv magnesium sulfate (2g) |
|
|
Intrinsic asthma causes |
Respiratory tract infection Asa, nsaids, beta blockers , methacoline |
|
|
Emphysema patho |
Increased pmn and macrophage elastase secretion leading to loss of elastic recoil, and surface area for gas exchange Loss of recoil --> air trapping Elastase breaks down elastin Usually a1anti-trypsin prevents elastase from breaking down excessive amounts of elastin but smoking eliminates a1at |
|
|
Why is emphysema obstructive? |
Because the lack of elastin in the resp bronchioles means there isn't a strong enough pressure to expire air which leads to air trapping and difficulty expiring air. |
|
|
Emphysema and asthma cxr |
Hyperinflation with flattened diaphragm |
|
|
Emphysema lung sounds |
Decreased breath sounds Hyperresonance (increased air) Expiratory wheezing |
|
|
V/Q chronic bronchitis |
Low v/q in areas of obstruction Increased shunting because of inadequate ventilation |
|
|
Chronic bronchitis mucosal metaplasia |
Columnar epithelium to squamous epithelium Squamous leads to loss of cilia and mucous qualities |
|
|
Pink puffers |
Dyspnea Low to nl pCO2 No peripheral edema Accessory muscle use Increases TLC |
|
|
Blue bloaters |
Sputum production Increased pCO2 overweight, peripheral edema, cyanosis Nl to slightly increased TLC |
|
|
Alpha1 AT |
Synthesized by hepatocytes Comorbid cirrhosis Serum protein electrophoresis |
|
|
Advair |
Fluticasone and salmeterol |
|
|
Chronic bronchitis xray |
Interstitial markings, prominent vessels, cardiomegaly |
|
|
First line for COPD |
Ipratropium bromide is preferred to a SABA in first line because of longer duration of action and absence of sfx |
|
|
Hospitalized COPD tx |
1. O2 2. Ipratropium bromide with saba 3. Steroids 4. Broad spectrum abx 5. Chest physiotherapy |
|
|
Pneumoconioses |
Lung rxns to mineral dust that results in alveolitis Inflammatory and immune response Coals workers Silicosis- small rounded opacities, increased incidence of Tb |
|
|
Asbestosis |
Insulating material, brake linings, cement pipes Localized pleural plaques Nodular Interstitial fibrosis Ferruginous body |
|
|
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
Farmers lung Pigeon breeders lung Type 3 Bibasilar crackles |
|
|
Sarcoidosis |
Systemic granulomatous disorder involving lung and hilar lymph nodes Non caseating granulomas Increased CD4 Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy Night sweats hemoptysis cough sob malaise Elevated serum angiotensin converting enzyme 2/3 have energy to skin Tb skin tests DX of exclusion Tx-steroid therapy |
|
|
Usual interstitial pneumonia |
1) Idiopathic ds by hx and who demonstrate inspiratory crackles on PE 2) restrictive physiology on PFT 3) progressive fibrosis over several years on cxr 4) diffuse, patchy fibrosis with pleural based honeycombing on high res CT Bronchoaveolar lavage Transbronchial bx Surgical lung bx Prednisone trial plus azathioprine x3-6months |
|
|
Acute bronchitis |
Cough lasting >5days Influenza A or B, parainfluenza, corona virus, rhinovirus, rsv Mycoplasma pneu, chlamydia and bordatella pertussis Procalcitonin- viral vs bacterial Tx- symptomatic , no abx |
|
|
Mycoplasma dx |
PCR |
|
|
Ventilator acquired pneumo bacteria |
Pseudomonas and klebsiella |
|
|
Tb organism |
Acid fast bacilli Caseating granulomas Nodular granulomatous- tubercle Ghon complex- hilar lymph node lesions plus primary lung lesion |
|
|
primary tb infection on lungs |
Inferior of upper lobe Superior of lower lobe |
|
|
Reinfection/reactivation Tb found... |
Apices |
|
|
Tb sputum exam |
3 samples at least 8hrs apart Bronchial washings or transbronchial lung biopsies
Cultures must be done for identification of drug susceptibility *DNA/RNA amplification- rapid DX of tb, high sensitivity and approved by fda to use instead of sputum smears |
|
|
Tb induration chart |

Rxns |
|
|
If INH resistant |
Rifamycing, pyrazinamide and ethambutol 6-9 mo |
|
|
If rifampin resistance |
Streptomycin, inh and pyrazinamide 9months Ethambutal, inh and ethambutol 12months |
|
|
Pyrazinamide resistant |
Inh and rifampin 9months |
|
|
Heparin test |
PTT |
|
|
Coumadin test |
PT/INR |
|
|
DVT gold standard |
Contrast venography |
|
|
PE gold standard/most common |
Gold- pulmonary angiography Common- helical CT with contrast If pregnant, kidney ds or allergic to contrast-- V/Q scan |
|
|
ARDS on cxr will show? |
Pulmonary edema |
|
|
Pertussis tx |
Whooping cough Culture for dx Macrolides- erythro |
|
|
Mallampati scores |
Class 1- everything and pillars Class 2- not pillars Class 3- base of uvula Class 4- nothing |

