![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the normal A-a gradient? What causes false-normal and increased gradient?
|
Normal: 5-15
False normal: Hyperventilation, high altitude Increased: PE, pulmonary edema, R to L shunts |
|
|
Which antibiotics are used to treat pharyngitis?
|
If streptococcal, Beta lactams
|
|
|
Which organisms cause sinusitis (4) and what is the treatment?
|
Viral
Strep pneumoniae H. influenza Moraxella catarrhalis Treatment: Amoxicillin |
|
|
First and most accurate tests for acute asthma exacerbation
|
First - Peak expiratory flow or ABG
Accurate - PFTs (decreased FEV1 with methacoline; can't do when patient is actively SOB) |
|
|
What determines the severity of an asthma exacerbation (2)?
|
Decreased PEF (FVC normalized to height and age)
ABG with increased A-a gradient |
|
|
Beclomethasone, fluticasone - drug class and side effects
|
Inhaled corticosteroids
Side effects: Dysphonia Oral candidiasis |
|
|
Side effects of systemic corticosteroids (6)
|
Osteoporosis
Cataracts Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia Adrenal suppression Fat redistribution, acne, hirsutism Thin skin, striae, easy bruising |
|
|
Initial treatment for acute asthma exacerbation
|
Oxygen
Albuterol Steroid bolus |
|
|
First and most accurate tests for COPD
|
First - CXR (increased AP diameter, air trapping, flattened diaphragm)
Most accurate - PFT (Increased TLC, decreased DLCO) |
|
|
EKG and echocardiogram findings in COPD
|
EKG
Right atrial and ventricular hypertrophy Afib or MAT Echo Right atrial and ventricular hypertrophy Pulmonary HTN |
|
|
Treatment for COPD that improves mortality and disease progression (3)
|
Smoking cessation
Oxygen therapy if pO2 <55 or O2 sat < 88% (pO2 cutoff is 60 in patients with pulmonary HTN, high HCT, or cardiomyopathy) Influenza and pneomococcal vaccines |
|
|
Treatment for COPD that only improves symptoms (5)
|
*Anticholinergics (ipratropium)
Short acting beta agonist (albuterol) Inhaled steroids Long acting beta agonists (salmeterol) Pulmonary rehab |
|
|
Pink puffer vs. blue bloater
|
Pink puffers: Emphysema because of pursed-lip breathing, dyspnea, and barrel chest
Blue bloaters: Chronic bronchitis bc cor pulmonale causes cyanosis and peripheral edema |
|
|
Which pneumonias present with dry cough and what are the CXR results?
|
Viral
Mycoplasma Pneumocystis jirovecci Chlamidophila CXR=bilateral interstitial infiltrates |
|
|
Empiric treatments for pneumonia
Healthy patients, no abx for 3 mos Comorbidities, or abx within 3 mos Inpatient |
Healthy patients, no abx for 3 mos: Macrolide (mycin) or doxycycline
Comorbidities, or abx within 3 mos Inpatient: Respiratory fluoroquinolon (floxacin) or ceftriaxone and azithromycin |
|
|
Exudate vs. transudate in pleural effusion
|
Transudate: CHF, hypoalbumin (cirrhosis), kidney disease
Exudate: Infection, cancer, PE, vasculitis - Protein fluid:serum > 0.5 - LDH fluid:serum > 0.6 - Pleural fluid LDH > 1.5 times upper limit of normal pH<7.2 and glucose <60 - Complicated parapneumatic, rheumatic disease, drug-induced lupus, TB, cancer |
|
|
Criteria for hospital admission in patient w/ pneumonia
|
CURB65
Confusion Uremia Respiratory distress BP low Age >65 |
|
|
Combination therapy for TB
|
RIPE
Rifampin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol |
|
|
Most accurate test for CF
|
Chloride sweat test
|
|
|
Treatment for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
|
Oral steroids (not inhaled), can use itraconazole for recurrent episodes
|
|
|
Treatment for hospital acquired pneumonia
|
Piperacillin/tazobactam
Carbapenems Cephalosporins |
|
|
Treatment for aspiration pneumonia (3)
|
Combine 3:
First drug: - Piperacillin/tazobactam -Carbapenem -Cephalosporin Second drug: -Aminoglycoside -Fluoroquinolone (cipro- or levo-floxacin) Third drug: -Vancomycin or linezolid |
|
|
How to test for TB in a patient with symptoms or abnormal CXR
|
Sputum acid fast stain (PPD and CXR not helpful)
|
|
|
What are the blood cell changes with glucocorticoids
|
Increased neutrophils - increasing release from bone marrow and mobilizing the marginated pool
(eosinophils and lymphocytes are decreased) |
|
|
Symptoms of theophylline toxicity
|
CNS - Headache, insomnia, seizures
GI - Nausea, vomiting |
|
|
Aspirin sensitivity syndrome
|
Nasal polyps, episodic bronchoconstriction
Pseudo-allergic reaction Treatment: Leukotriene receptor antagonist (Zifirlukast, ziluteon) |
|
|
Pancoast syndrome
|
Tumor at lung apex compresses the brachial plexus, causing shoulder pain radiating to the arm in an ulnar distribution
|
|
|
Treatment for ARDS
|
Mechanical ventilation with low tidal volume, FiO2<40%, and PEEP
|
|
|
Causes of ARDS
|
ARDS
Aspiration, acute pancreatitis, air or amniotic embolism Radiation Drug overdose, diffuse lung disease, drowning Shock, sepsis, smoke inhalation |
|
|
Most common type of lung cancer in non-smokers
|
Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
SVC synrdrome
|
Obstruction of venous return to SVC, causing head swelling and CNS symptoms
|
|
|
H/P of goodpasture's disease
|
Hemoptysis
Renal disease |
|
|
Diagnosis and treatment of Goodpasture's
|
Dx: Renal biopsy shoing linear anti-GBM IgG
Treatment: Plasmapheresis, corticosteroids, immunosupression |
|
|
Most common adverse effect of inhaled corticosteroids
|
Oral candidiasis (thrush)
|
|
|
Most common cancer associated with asbestosis
|
Bronchogenic carcinoma (next is mesothelioma)
|
|
|
Unique finding on imaging in asbestosis vs. other restrictive lung diseases
|
Pleural plaques/linear fibrosis
|
|
|
Most common source of PE
|
Proximal deep leg veins - Iliac, femoral, popliteal
|
|
|
H/P of sarcoidosis
|
Dyspnea, dry cough with dry rales on exam
Bilteral hilar lymphadenopathy and diffuse interstitial infiltrates Erythema nodosum Uveitis |
|
|
Initial and most accurate test for sarcoidosis
|
Initial - CXR
Most accurate - lymph node biopsy showing non-caseating granulomas (also have high ACE levels) |
|
|
Treatment for sarcoidosis
|
Prednisone (if symptomatic)
|
|
|
New onset left vs. right BBB?
|
New RBBB = Pulmonary embolism
LBBB = MI |
|
|
What condition presents with pleural based wedge shaped density of chest CT?
|
Pulmonary embolism
|
|
|
This chart -->
|
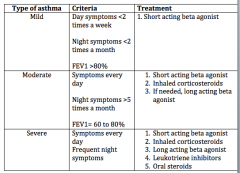
|
|
|
Definitive diagnostic test and treatment for legionella
|
Urine antigen testing or culture on charcoal agar
Treatment: Macrolide or fluoroquinolone |
|
|
Initial diagnostic tests for PE (3) and their findings
|
CXR - Usually normal, wedge shaped pleural infart or infarction of one lobe
EKG - Most common is non-specific ST-T wave changes, usually accompanied by sinus tachycardia ABG - High pH, low PCO2 |
|
|
Presentation of restrictive lung disease
|
Dyspnea on exertion
Fine rales or crackles Loud P2 Clubbing |
|
|
Initial and most accurate test for interstitial lung disease
|
Initial - CXR
Most accurate - lung biopsy |
|
|
Treatment for acute PE
|
Start warfarin and heparin, d/c heparin after 5 days if INR is therapeutic (2-3), then continue warfarin for 6 mos for 1st time clot, lifetime if second episode
|
|
|
What are the only 2 causes of hypoxemia that does not correct with supplemental oxygen?
|
Shunt (Intracardiac or ARDS)
|
|
|
What are the values of FEV1 and FEV1/FVC ratio:
Normal? Obstructive disease? Restrictive disease? |
Normal:
Between 80 and 120 Obstructive - FEV1: Decreased FEV1/FVC: Decreased Restrictive - FEV1: Decreased FEV1/FVC: Normal or increased |
|
|
Which lung cancer is associated with PTHrp
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Yellowish exudative pleural effusion with lots of lymphocytes, very high protein and glucose levels only slightly below blood glucose
|
Tuberculosis
|
|
|
Purulent exudative pleural effusion with very low glucose and lots of neutrophils
|
empyema
|
|
|
What does the ABG show in COPD vs. CHF
|
COPD: Respiratory acidosis with low PO2 and high PCO2
CHF: Respiratory alkalosis with low PO2 and low PCO2 |
|
|
What is the difference between malingering and factitious disorder?
|
Malingering want secondary gain
|

