![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Pulm AVMs |
|
no hints. quit being lazy/dumb |
|
|
Pulmonary Vasculitides- a list |
|
|
|
|
Granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis (Wegeners) |
|
|
|
|
Saddlenose Deformity |
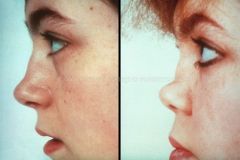
Differential: Wegeners Relapsing polychodritis leprosy |
|
|
|
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis w/ Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss Syndrome) |
|
|
|
|
Giant Cell Arteriitis |
|
|
|
|
Behcet Disease |
|
|
|
|
Takayasu Disease |
|
|
|
|
Goodpasture Syndrome |
|
|
|
|
Microscopic Polyangiitis |
|
|
|
|
Pulmonary HTN Types |
|
|
|
|
PAH |
|
|
|
|
PAH treatment |
CCB: only for patients w/ acute vasodilator response during RHC Prostanoids (epoprostenol, treprostineil,iloprost): supplements endogenous levels of prostacyclin which stimulates vasodilation and anti-smooth muscle proliferation Endothelin-1 Receptor Antagonists(Bosentan, Ambrisentan): blocks vasoconstrictor activity of endothelin (teratogenic and liver injury) PDE-5 inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil): prolongs effect of intrinsic vasodilator cyclic GMP by inhiniting hydrolysis of PDE-5 |
|
|
|
PFTs Obstructive |
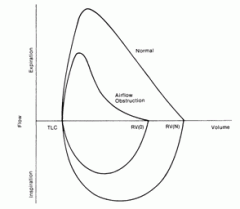
|
|
|
|
PFTs Restrictive |
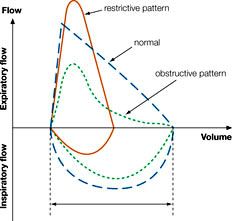
|
|
|
|
PFTs Graphs/Special Cases |
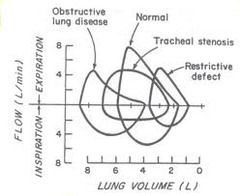
|
|
|
|
PFTs Graphs/Special Cases |
|
|

