![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what does HIPAA stand for and what is the purpose?
|
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
This was created to protect the patients personal medical information. |
|
|
what can be used to determine a pts identity?
|
birthdate, address, last four of social, id bracelet
|
|
|
what is an open ended question?
|
this type of question gets the pt to explain more than just yes or no. ex: what did you do today?
|
|
|
what should be included as part of an intervention?
|
type, amount, duration, and frequency
|
|
|
what should you be aware of about your environment when treating pts.?
|
Is it safe and clean, who else is around, and are you being a team player by helping others out.
|
|
|
how can you prepare your treatment area?
|
by cleaning your station and grabbing the equipment needed before handling your pt. Make sure you have sufficient room to treat.
|
|
|
if your hands are not visibly soiled , what should you use to sanitize?
|
alcohol based cleaning solution
|
|
|
define body mechanics?
|
these are the appropriate steps taken when lifting or handling a pt. Used to reduce stress on our musculoskeletal system.
|
|
|
what are the 5 cardinal rules of body mechanics?
|
1. widen your BOS
2.keep your COG in line with your BOS 3. no twisting- move feet 4. lift with legs 5. isometric contraction of trunk/abdominals |
|
|
what is a gait belt and what is it used for?
|
a belt that is used for safety and should always be on a pt. Used in case of falls or emergencies . to lower and guard.
FOR SAFETY! |
|
|
what is the difference between gait training and ambulation?
|
gait training- skill that is taught
ambulation- walking done on a day to day basis |
|
|
what position should you be in when guarding during gait?
|
stance is 45* positioned toward the pt on the involved side. Feet in stride
|
|
|
what should you do if a pt has LOB during gait?
|
pull them towards your BOS and slowly lower them to the ground using proper body mechanics
|
|
|
what is ergonomics?
|
work station modifications to help the pt improve their musculoskeletal postures.
|
|
|
when should you monitor vital signs?
|
before , during, and after treatment / exercise
|
|
|
list the 6 vital signs
|
1. HR
2. PR 3. Temp 4. Pain 5. BP 6. RR |
|
|
what is the difference between HR and PR?
|
HR- measured in auscultation
PR- measured distally |
|
|
list the trophic changes that are indicative of impaired circulation
|
blanching, atrophy, loss of hair, dry flaky skin, cooler temperature.
|
|
|
what is target HR and how do you determine it?
|
220- age = MHR
.60-.80 * MHR= target HR |
|
|
the current time is 7:00 pm, how would you right this in military time?
|
1900 hrs
|
|
|
you have a pt ready for PT and as you prepare to see the pt , what do you need to do first?
|
check chart/ eval notes from PT
prepare your area introduce yourself |
|
|
what do you need to look at in the medical record?
|
P.T. notes, nurses notes, lab results, order sections- imaging, meds
|
|
|
POC starts with PROM, AAROM, and bed mobility. What do you have to have to work with the pt.?
|
gait belt, sheet for draping, extra pillows
|
|
|
you walk into a pts room then what do you do?
|
verify the pt - chart, wrist, questions asked
check vitals explain what your going to do |
|
|
in regards to skin breakdown, what things are apt to cause this?
|
positioning, sheet wrinkles, moisture
|
|
|
pt is supine when you come into the room, what areas should you check for skin breakdown?
|
elbows, ishial tuberosity, calcaneus, back of head, back of knees
|
|
|
if you find problems with skin breakdown what steps should be taken?
|
document, describe size and redness, contact nurse
|
|
|
what are the steps in placing a pt in a side lying position.?
|
1. tell the pt what your doing
2. properly scoot them away from where your trying to put them 3. cross opposite leg 4. pull them towards you at their turning pts |
|
|
where will you teach the pt and family member to put pillows while the pt is in side lying ?
|
1. under head
2. in between legs at knees/ bent 3. forearms 4. extra pillow behind back to stabilize |
|
|
where would a pt be more at risk for pressure ulcers in side lying ?
|
greater trochanter, elbows, knees together, wrist.
|
|
|
why do we concern ourselves with draping?
|
modesty, privacy, temperature, wound cover
|
|
|
when should you check a pts skin in a new position?
|
5-10 min
|
|
|
how often should a pt be repositioned?
|
every 2 hrs
wheelchair- 10 mins , asking them to shift |
|
|
what are the different levels of assistance and how are they defined?
|
1. supervision- no assistance
2. (CGA) counter guard assistance- guard from falling 3. (SBA) stand by assistance- stand next when ambulating 4. total a: 0-24 max a: 25-49 mod a: 50- 74 min a: 75-100 |
|
|
what are the goals for positioning?
|
comfort,contractures , peripheral nerve impingement, CV system, lungs.
|
|
|
taking vital signs would also be called what?
|
systems review
|
|
|
what is the criteria for a goal?
|
pt centered, functional, measurable
|
|
|
what are the 4 interventions and there definitions?
|
1. Type: what you are going to do
2. Amount: reps, sets 3. Duration: how long and far 4. Frequency: the amount of times that day or week |
|
|
what is valsalva?
|
holding your breath. do not use because this can raise your BP.
|
|
|
what is the difference between HR and PR?
|
HR- measure taken over heart
PR- bpm, measured distally. Should be measured before , during, and after exercise |
|
|
what is basal HR?
|
HR after extended rest
|
|
|
what is resting HR?
|
HR taken at rest
|
|
|
how should a pts PR be taken?
|
should be done over the distal radial artery, never involve the thumb, and is to be taken for 60 sec.
|
|
|
what is the PR norms for an adult and child?
|
60-100bpm (adult)
80-100bpm (child) |
|
|
what is the difference between bradycardia and tachycardia?
|
bradycardia- PR is less than 60 bpm
tachycardia- PR rapid and higher than 100 bpm |
|
|
how do you find a persons max heart rate (MHR)?
|
220- age
|
|
|
what is the target heart rate (THR)?
|
target= .60- .80* MHR
|
|
|
what does mmHg stand for?
|
millimeters of mercury
|
|
|
what is systolic pressure?
|
it is blood exerted when the heart contracts
|
|
|
what is diastolic pressure?
|
blood exerted when the walls of the heart are not contracting.
|
|
|
what are Korotkoff sounds and what do they sound like?
|
1. clear tapping- systolic
2.murmurs 3.loud crisp tapping 4.thumping, muting 5. silence-diastolic |
|
|
where and how should a pts blood pressure be taken?
|
at the left upper medial arm, at the site of the brachial artery. normal is 120/80 mmHg and should always be documented by which arm you took it on.
|
|
|
what is BP exertion?
|
systolic pressure should increase during exercise and diastolic pressure should remain the same.
|
|
|
what is the normal temp of a healthy adult?
|
98.6 F
Afebrile- no fever, norm Febrile- temp above 100 F |
|
|
what are the different types of pain and what is considered a normal pain level?
|
norm is 0/10
burning, tingling, sharp, dull |
|
|
where would a pt most likely receive decubitus ulcers?
|
on bony prominences
|
|
|
how would you convert a pt from prone to supine?
|
on stomach, make sure theres room for roll, side lye, cross legs, use turning pts while bringing the pt towards yourself.
|
|
|
how should pillows and the body be positioned during sidelined, prone, and supine?
|
supine laying- pillows under head, knees , and not under heels
prone laying- pillow under trunk and lower legs with feet hanging over sidelying- pillow under head, between LEs, top UE supported with pillow. |
|
|
what are the different vital sign norms?
|
PR: 60-100 bpm (adult), 80-100bpm (child)
BP: 120/80 mmHg RR: 12-18 bpm (adult) , 20 bpm (child) Temp: 98.6F o2 sat: 100% Pain: 0/10 |
|
|
what is orthostatic hypotension?
|
it is decrease in blood flow to the brain and increase in blood pooling in the LEs. decrease in systolic pressure by 20 mmHg . sx: lightheadedness, blurred vision
|
|
|
what are the hemoglobin norms?
|
14-18 gm/dL (male)
12-16 gm/dL (female) 11.2-16.5 gm/dL (child) 16.5-19.5 gm/dL (newborn) low hemoglobin may indicate anemia |
|
|
what are the blood glucose norms?
|
100-250 mg/ dL
greater than 100 during exercise |
|
|
what are the different parts of a stethoscope?
|
chest piece , stem, binaural piece, earpiece, flexible tubing.
|
|
|
trendelenburg position
pelvis is higher than the head |

|
|
|
reverse trendelenburg
LEs are lower than the head |

|
|
|
Fowlers position
head is elevated- sitting up |
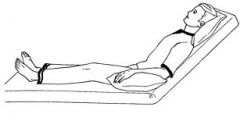
|
|
|
semi fowlers position
head less elevated than regular |
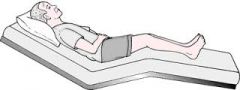
|

