![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by pain and progressive stiffness?
|
Ankylosing Spondylitis
|
|
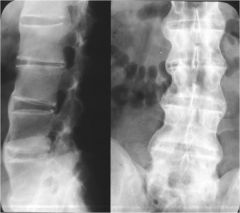
What is this?
|
Bamboo Spine
(Ankylosing Spondylitis) |
|
|
What is a forward translation of one vertebral body on another. It is most common in the lower lumbar spine?
|
Spondylolisthesis
|
|
|
What are the different classifications of spondylolisthesis?
|
Isthmic- basic lesion of pars interarticularis
Dysplastic- congenital Degenerative- arthritis Traumatic Pathologic- metabolic bone disease, tumor, or after surgery |
|
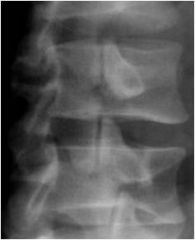
What is this?
|
Scotty Dog
Fracture of pars interarticularis- Spondylolysis |
|
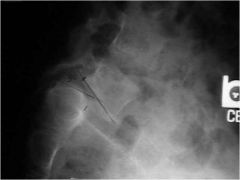
What is this?
|
Spondylolysthesis- slippage
|
|
|
About what percent of athletes have a radiological diagnosis of spondylolysis?
In a normal population? |
14%
4-6% |
|
|
What is the ratio of men to women who present with spondylolysis?
|
4.5:1
|
|
|
According to O'Sullivan et al, what is proven to decrease pain and increase function in patients with spondylolysis?
|
Lumbar stabilization exercise
|
|
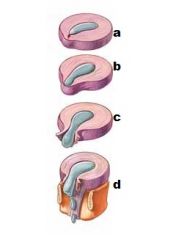
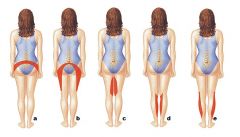
What are each letter?
|
a- disk degeneration
b- prolapse c- extrusion d- sequestration |
|
What is each letter?
|
a- L1
b- L2 c- L3 d- L4 e- L5 |
|
|
What are the 3 syndromes that classify disk herniation with a mechanical diagnosis?
|
Postural
Dysfunction Derangement |
|
|
What is the treatment for postural syndrome for disk herniation?
|
Patient education
Postural correction |
|
|
What is the treatment for dysfunction syndrome for disk herniation?
|
Patient education
Postural correction Stretching of contracted structures |
|
|
What is the treatment for derangement syndrome for disk herniation?
|
Reduction of derangement Maintenance of reduction
Rrecovery of function and prophylaxis |
|
|
Related to centralization, which deficits represent most distal symptoms?
|
Parasthesia
Neurological |
|
|
Is the centralization phenomenon as a prognostic factor for chronic low back pain and disability good for ruling in or out the condition?
|
Ruling in
High specificity |
|
|
What is a big difference between how we do a physical exam today and what the McKenzie Approach did?
|
The big difference is an increased emphasis on Repeated Movements & Sustained Postures
|
|
|
With a lateral shift, does the patient deviate toward or away from the symptoms?
|
Away
|
|
|
What causes a lateral shift?
|
Disc herniation
Muscle spasm Facet-joint impingement SI joint dysfunction |
|
|
What is the proper movement progression?
|
Flexion in Standing (FIS)
Repeated FIS (RFIS) Extension in Standing (EIS) Repeated EIS (REIS) Side Glide in Standing (SGIS) Repeated SGIS (RSGIS) |
|
|
What is the proper movement progression in an unloaded state?
|
Supine/Prone:
Flexion in lying (FIL) RFIL Extension in Lying (EIL) REIL |
|
|
What is the proper treatment progression?
|
Increase, worse - STOP
No effect/No worse -PROCEED WITH CAUTION Decrease/Centralize, better - GO! |
|
|
Patients with disc injuries may be at increased risk of re-injury with ________ early in the morning?
|
flexion
|
|
|
How do you progress flexion ROM?
|
Supine
Sitting Standing |
|
|
How do you progress extension treatment?
|
Prone
Prone in extension Extension in lying Extension in lying with patient overpressure (belts) |
|
|
What are the the general rules for clinicians regarding diagnostic imaging?
|
Shouldn't routinely obtain imaging in patients with nonspecific LBP
Should obtain imaging when serious underlying conditions are suspected on the basis of history and physical examination Should order imaging for patients with radiculopathy or stenosis only if the patient is a candidate for surgery |
|
|
What percentage of stress fractures pertaining to joggers?
|
1%
|
|
|
Why are femoral neck stress fractures difficult to diagnose?
|
Subtle
|
|
|
Which positions do you want to avoid with a THA?
|
Adduction
IR Hip Flexion > 90 |
|
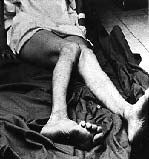
What is this position indicative of?
|
Posterior Hip Dislocation
|
|
|
What are physical therapy considerations for patient's who have hardware put in for femoral fractures?
|
Early and aggressive mobility of the total person
High risk for complications in older adults i.e. pneumonia, DVTs, etc. Must Avoid the “beginning of a downward spiral” |
|
|
What are the key points when treating THA and hip fractures?
|
Emerging Evidence Supportive of early and aggressive Physical Therapy intervention.
Rehab is often case/surgeon specific Call if questions/concerns |
|
|
The highest forces in the body are required to cause a fracture where?
|
Subtrochanteric Fracture
|
|
|
What is best for restoring symmetrical independent walking after a THA?
|
Treadmill training with partial weight bearing
|
|
|
What do phase I-IV of rehabilitation represent?
|
Phase I- Immediate Rehab
Phase II- Intermediate Rehab Phase III- Advanced Phase IV- Sport-specific training |
|
|
What are goals of phase I rehab following hip arthroscopy?
|
Protect integrity of repaired tissue
Restore ROM within restrictions Diminish pain and inflammation Prevent muscular inhibition |
|
|
What are goals of phase II rehab following hip arthroscopy?
|
Protect integrity of repaired tissue
Restore full ROM Restore normal gait Progressively increase muscle strength |
|
|
What are goals of phase III rehab following hip arthroscopy?
|
Restoration of muscular endurance and strength
Restoration of cardiovascular endurance Optimize neuromuscular control/balance/proprioception |
|
|
What are criteria for full return to competition following hip arthroscopy?
|
Full pain-free ROM
Hip strength > 85% of uninvolved side Ability to perform sport-specific drills at full speed without pain Completion of functional sports test |
|
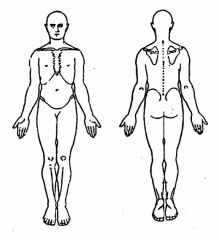
What are possible problems?
|
L3 dermatome
Groin Anterior or lateral thigh/ g. trochanter Knee |
|
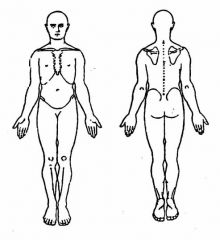
What are hypotheses for this person?
|
Non-musculoskeletal tissues
Joints under area of symptoms Joints referring to area of sx Contractile structures under area Other structures to be examined |
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for newborns?
|
Congenital dislocated hip
|
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for 2-8 years of age?
|
Avascular necrosis
|
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for 10-14 years of age?
|
Slipped epiphysis
|
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for 14-25 years of age?
|
Stress fracture, synovitis
|
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for 20-40 years of age?
|
Avascular necrosis, synovitis, rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for 45-60 years of age?
|
OA, synovitis
|
|
|
What are common hip pathologies for 65+ years of age?
|
Stress fracture, OA
|
|
|
Is hip OA higher in men or women?
|
Women
|
|
|
What is the prevalence of hip OA in 55-64 year olds?
|
3%
|
|
|
What is the prevalence of hip OA in 65+ year olds?
|
5-6%
|
|
|
What does hip OA usually lead to?
|
THA
|
|
|
What is the act or process of identifying or determining the nature and cause of a disease or injury through evaluation of patient history, examination, and review of laboratory data?
|
Diagnosis
|
|
|
What are traditional criteria for diagnosing hip OA?
|
Hip pain for > 25 of the past 30 days
And, at least 2 of the following criteria: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate <20 mm/1st hr Osteophytes on x-ray examination Obliteration of the joint space |
|
|
What is hip OA often referred to as?
|
DJD
|
|
|
If AM stiffness lasts for longer than 60 minutes, is the diagnosis hip OA?
|
No
|
|
|
What does Hoeksma (2004) say is the best prescription for PT for hip OA?
|
Long axis manipulation + stretching
|
|
|
What should be the first treatment choice when dealing with a patient who suffers from hip OA?
|
Manual Therapy
|
|
|
What often accompanies hip OA?
|
Bursitis
Tendonitis Tendinopathy |
|
|
What gait pattern is evident with patients who have greater trochanteric bursitis?
|
Trendelenberg
|
|
|
What is defined as pain in the tenon?
|
Tendinopathy
|
|
|
What are some causes of gluteus medius tendinosis?
|
Friction
Alteration in gait Repetitive microtrauma: steps and hyperadduction |
|
|
What is the triad of iliopsoas bursitis?
|
Mass
Pressure effects Advanced arthritis |
|
|
Which motions would reproduce pain caused by iliospoas bursitis?
|
Passive hip flexion
Passive hip IR Pain with resisted IR and ER |
|
|
What can cause iliopsoas bursitis?
|
Friction
Elevated intracapsular pressure Extensions of hip synovia |
|
|
How do you treat iliospoas bursitis?
|
NSAIDs, ice, physical agents
Activity modification Stretch hip flexors as tolerable Steroid injections, Aspiration |
|
|
What are the different grades of ankle sprains?
|
Grade I
Mild symptoms, no functional loss, local tenderness, mild swelling, no instability Grade II Moderate functional loss, diffuse swelling, mild echymosis, more diffuse tenderness, mild instability Grade III Significant functional loss, gross swelling, echymosis, multiple ligament tenderness, gross instability, possible fracture |
|
|
What percent of all ankle sprains are syndesmotic?
|
10-18%
|
|
|
How does a syndesmotic ankle sprain occur?
|
Forced external rotation of foot &
internal rotation of the leg Hyperdorsiflexion Hyperplantarflexion |
|
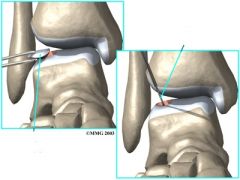
What is the impairment?
|
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Talus
|
|
|
What are the criteria for return to activity for ankle sprains?
|
Restoration of normal accessory & physiological ROM.
Restoration of muscle function, including strength and proprioception. Functional use of the injured part in full speed activities. |
|
|
What is a good intervention for subtalar joint dysfunction?
|

Supine subtalar (rearfoot) distraction manipulation
|
|
|
What is the best treatment for acute ankle sprain?
|
PRICES (protection, rest, ice, compression. elevation and
support) Minimize swelling with compression wrap, elevation, cryokinetic program and protected WB'ing if indicated. Functional treatment better than immobilization |
|
|
What is the best treatment for sub-acute ankle sprain?
|
Protection/Immobilization
–As symptoms subside, protect ligament with Aircast or splint. –Frict Massage and gentle joint mobilization to prevent adherence and restore normal mobility. –Flexibility, strength and proprioception program as early as tolerated. |
|
|
What is the best treatment for chronic ankle sprain?
|
Adhesions develop during healing phase and lack of reflex muscle protection due to proprioceptive deficit and faulty mechanoreceptor function.
–ntervention emphasis: Functional (proprioceptive) exercise activities and comprehensive biomechanical evaluation. |
|
|
What is pain and paraesthesia in the interdigital space (3-4) with a fibrous entrapment of the interdigital nerve.
May be referred to in any of the interdigital spaces. |
Morton's Neuroma
|
|
|
What is the best intervention for Morton's Neuroma?
|
Decompression of the space through modification of shoe wear, (wide toe box), correcting biomechanical stress (metatarsal pad or tube) to splay metatarsals, mobilization of the MT, instrumented soft tissue techniques.
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of Charcot Joint?
|
Diabetes
|
|
|
What are common causes of pain with running?
|
Knee valgus
Foot pronation (excessive and rapid) Hip IR and Adduction Glut Med weakness |

