![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which femoral condyle is C shaped?
|
Medial
|
|
|
Which femoral condyle is more rounded?
|
Lateral
|
|
|
What is the joint classification of the knee?
|
Synovial Hinge Joint
|
|
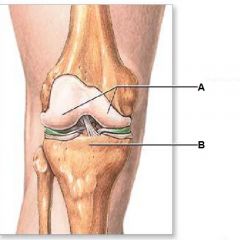
What is A?
|
Femoral Condyles
|
|
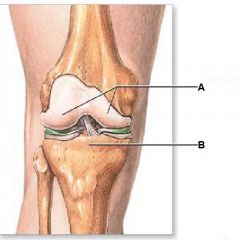
What is B?
|
Tibial Pateau
|
|
|
The distal femur is _________ medial to lateral and _________ superior to inferior.
|
Concave
Convex |
|
|
Which condyle is larger and longer?
|
Medial
|
|
|
What are the two layers of the knee joint capsule?
|
Fibrous
Synovial |
|
|
What are characteristics of hyaline cartilage at the knee joint?
|
Very thick on femur and tibia
Improved congruency due to compliance Improved ability to handle large forces |
|
|
Which meniscus is attached to the MCL?
|
Medial
|
|
|
Which meniscus is less movable and therefore more frequently injured?
|
Medial
|
|
|
Which meniscus is attached to the popliteus?
|
Lateral
|
|
|
What are some examples of foam roll and Static Stretch Techniques for feet turning out?
|
Gastrocnemius / Soleus
Bicept Femoris (short head) |
|
|
What are the two main pairs of ligaments?
|
ACL/PCL
MCL/LCL |
|
|
What motion does the ACL prevent?
|
Anterior translation of the tibia (tightest in extension)
|
|
|
What motion does the PCL prevent?
|
Posterior translation of the tibia (tight during flexion)
|
|
|
What is the function of the MCL?
|
Provides frontal plane stability
Resists valgus forces |
|
|
What is the function of the LCL?
|
Resists varus forces and lateral rotation?
|
|
|
What are functions and characteristics of the fat fad?
|
Protect anterior knee joint structures
Moves anterior with extension, moves posterior with flexion Highly innervated Can be very painful |
|
|
What is the tendency for rotation called?
|
Version
|
|
|
What is the normal version of the foot in the transverse plane?
|
0 Degrees
|
|
|
What is the normal tilt of the patella at rest?
|
Slight lateral titl
|
|
|
What is the open pack position of the knee?
|
25 Degrees Flexion
|
|
|
What is the closed pack position of the knee?
|
Full Extension
Tibial External Rotation |
|
|
What is the capsular pattern of the knee?
|
Flexion > Extension
|
|
|
What is normal end feel at the knee in flexion? Extension?
|
Flexion- Soft
Extension- Firm |
|
|
Name the normal ROM at the knee for the following:
Flexion/Extension Lateral Rotation Abduction |
Flexion/Extension- 140 Degrees
Lateral Rotation- 20 Degrees Abduction- 5 Degrees |
|
|
How many degrees of freedom does the knee have?
|
6
|
|
|
Which bone of the knee is concave? Convex?
|
Concave- Tibia
Convex- Femur |
|
|
If motion occurs in the sagittal plane, what direction does the roll occur in?
|
Anterior/Posterior
|
|
|
If motion occurs in the frontal plane, what direction does the roll occur in?
|
Superior/Inferior
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the patella?
|
Increase the moment arm or mechanical advantage of the quadriceps
|
|
|
How much does the patella translate on the femur?
|
5-6 cm
|
|
|
What are the influences of the Q angle on the knee?
|
The greater Q angle puts a larger medial stress on the knee and puts more stress on the ACL. If we have our knee in CKC, we put less shear force on the knee
|
|
|
Which structure pulls on the suprapatellar pouch?
|
Articularis Genu
|
|
|
What is the screw home mechanism?
|
Towards the end of knee flexion, the tibia medially rotates by way of the popliteus muscles.
|
|
|
Which muscles initiates flexion of the knee?
|
Popliteus
|
|
|
Which muscles cause internal rotation of the knee?
|
Semimembranosis
Semitendonosis Sartorius Gracilis |
|
|
Which muscles cause external rotation of the knee?
|
TFL
Biceps Femoris |
|
|
What is the mid range where the body is able to generate the most amount of force at the knee when performing knee extension?
|
50-80 Degrees
|
|
|
During free weights, the peak quad force is at which position?
|
Full extension
|
|
|
When dealing with pullies, constant force-magnitudes is dependent on what?
|
External Force
|
|
|
During CKC, force increases with what?
|
Knee Flexion
|
|
|
During isokinetic motion, peak force is attained at what range?
|
Mid range
|
|
|
Forced generated at the knee can reach how how?
|
9 times body weight
|
|
|
Walking causes how much force at the tibiofemoral joint? Jogging?
|
3x BW
12x BW |
|
|
During knee flexion, which direction does the patella move?
|
Distally
|
|
|
What mechanisms help prevent lateral trackining?
|
Large lateral condyle superiorly
Medial extensor retinaculum VMO |
|
|
Compressive and shear forces range from body weight with level walking to over 1100 lb while doing what?
|
Running
Jumping |
|
|
Increased Flexion = ?
|
Increase Compression
|
|
|
The dome of the talus from anterior-posterior is _____, while from medial-lateral is ______.
|
A-P: convex
M-L: concave |
|
|
The posterior facet of the calcaneous articulates with which structure?
|
Talus
|
|
|
Why is it important that the calcaneous is trabecular bone?
|
It allows for shock absorption
|
|
|
What are the keystones for the transverse arch of the foot?
|
Cuneiform bones
|
|
|
Which structures in the foot work as functional motion segment, often referred to as Rays?
|
Metatarsal and phalanges
|
|
|
What does the hindfoot include?
|
Calcaneus
Talus |
|
|
What is included in the midfoot?
|
Cuneiform
Navicular Cuboid |
|
|
What is included in the forefoot?
|
Metatarsals
Phalanges |
|
|
What are the 3 main functions of the ankle?
|
Shock absorption
Adapt WB activity to uneven ground Stable BOS for mobility |
|
|
What are motions at the ankle (tarsal)?
|
Plantar Flexion
Dorsiflexion Inversion Eversion Adduction Abduction |
|
|
Which joint is considered the proper ankle joint?
|
Talocrural
|
|
|
Varus position at the foot has the foot pointed _______. Valgus is pointed ______.
|
Varus: inward
Valgus: outward |
|
|
Which joint is referred to as the mortise joint?
|
Talocrural
|
|
|
What is normal plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the foot?
|
Plantar Flexion: 35-50 degrees
Dorsiflexion: 20 degrees |
|
|
The axis of motion at the ankle during plantar flexion and dorsiflexion is what?
|
From medial to lateral malleolus
|
|
|
Motion at the talocrural joint is considered _______.
|
Triplanar
|
|
|
What is the resting position of the ankle?
|
10 degree plantar flexion, midway between inversion and eversion
|
|
|
What is the closed pack position of the ankle?
|
Maximum dorsiflexion
|
|
|
When considering capsular pattern at the ankle, plantar flexion is ______ limited than dorsiflexion.
|
More
|
|
|
What motion does the ATFL limit?
|
Anterior glide of the talus
|
|
|
Is the lateral ligament stronger or weaker than the medial ligament?
|
Weaker
|
|
|
What are characteristics of the deltoid ligament?
|
Medial
Strong Medial malleolus to talus, calcaneus, and navicular Stabilizes during eversion |
|
|
Which ligament stabilizes the ankle during eversion?
|
Deltoid
|
|
|
Which bones comprise the subtalar joint?
|
Talus
Calcaneus |
|
|
What type of joint is the subtalar? How many joint capsules?
|
Synovial Joint
Two joint capsules (ant/post) |
|
|
What is normal inversion and eversion of the foot?
|
Inversion: 20 degrees
Eversion: 10 degrees |
|
|
Which motion at the ankle is directed medial-superior? Lateral-inferior?
|
Medial-superior: Inversion
Lateral-inferior: Eversion |
|
|
Which joint is referred to as the spring ligament of the talar head?
|
Talonavicular joint
|
|
|
DF/PF occur at which joint?
INV/EV? PRON/SUP? |
DF/PF: Talocrural
INV/EV: Subtalar and Transverse Tarsal PRON/SUP: All together |
|
|
Which motions occur at the MTP joints?
|
Flexion
Extension Abduction Adduction |
|
|
MTP 1 joint has how much ROM?
|
Flexion: 30-45 degrees
Extension: 50-70 degrees |
|
|
How many degrees of freedom does the MTP joint have?
|
2
|
|
|
What is the ROM of the IP joint of the hallux?
|
0-30 degrees
|
|
|
What are functions of the plantar fascia?
|
Maintain shape of foot
Support/stabilize skin and plantar surface of foot joints Dynamic in gait-stabilization of foot for pushing off the ground as it bears the weight of the body and is pulled taut |
|
|
What is the joint arthrokinematics of the subtalar joint?
|
Posterior part of the joint-view as concave talus moving on convex calcaneous
Anterior part-View as slightly convex talus moving on concave calcaneous |
|
|
What are the arthrokinematics of the talocrural joint?
|
Talus: Ant-Post: Convex
Talus: Med-Lat: Concave and Convex |
|
|
What condition has a high arch, is fairly rigid, and often is involved joint/bony injuries?
|
Pes Cavus
|
|
|
What condition is associated with flat foot, tends to be hypermobile, and is often involved with more soft tissue injuries?
|
Pes Planus
|
|
|
Which muscles has the largest cross-sectional area in the lower leg?
|
Soleus
|

