![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
learning can be described as _____ ?
|
learning is a permanent change in behavior as a result of an experience.
|
|
|
Classical Conditioning is associated primarily with which theorist?
|
Ivan Pavlov
|
|
|
Operant Conditioning is associated primarily with which theorist?
|
B.F. Skinner
|
|
|
Observational Conditioning is associated primarily with which theorist?
|
Albert Bandura
|
|
|
POSITIVE reinforcement _______________ the likelihood of a behavior.
|
INCREASES
|
|
|
NEGATIVE reinforcement _________________ the likelihood of a behavior.
|
INCREASES
|
|
|
DEFINE NS ?
SAME AS CS |
NATURAL STIMULUS,DOESNT ELICT RESPONSE PRIOR TO LEARNING
|
|
|
DEFINE UCS ?
|
UNCONDITIONED STIMULUS
|
|
|
DEFINE UCR ?
SAME AS CR |
UNCONDITIONED RESPONSE, REFLEXIVE RESPONSE TO UCS.
|
|
|
DEFINE CS ?
SAME AS NS |
CONDITIONED STIMULUS, PREVIOUSLY NS THAT NOW ELICTS THE CR.
|
|
|
DEFINE CR ?
SAME AS UCR |
CONDITIONED RESPONSE,LEARNED RESPONSE TO CS.
|
|
|
ORDER CLASSICAL CONDITIONING IN BEFORE,DURING,AFTER.
|
BEFORE
NS->UCS->UCR DURING CS + UCS->UCR AFTER CS->CR |
|
|
5 MAJOR CONDITIONING PROCESSES?
|
Acquisition,Extinction,Sponteneous Recovery,Stimulus Generalization, + Discrimination
|
|
|
Acquisition ?
|
initial stage of learning when a response is first established and gradually strengthened.
|
|
|
Extinction ?
|
when the occurrences of a conditioned response decrease or disappear. In classical conditioning, this happens when a conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
|
|
|
Spontaneous Recovery ?
|
the reappearance of the conditioned response after a rest period or period of lessened response. If the conditioned stimulus and unconditioned stimulus are no longer associated, extinction will occur very rapidly after a spontaneous recovery.
|
|
|
Stimulus Generalization ?
|
the tendency for the conditioned stimulus to evoke similar responses after the response has been conditioned.
|
|
|
Stimulus Discrimination ?
|
the ability to differentiate between a conditioned stimulus and other stimuli that have not been paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
|
|
|
3 major types of learning ?
|
classical,operant, and observational learning .
|
|
|
Thorn dike's Law of Effect ?
|
Rewarded behavior is likely to occur.
|
|
|
Operant conditioning (SHAPING)is based off what ?
|
thorn dikes law of effect.
|
|
|
Principles of reinforcement ?
|
POSITIVE (presenting something desirable,strengthening) vs. NEGATIVE (strengthens response by reducing/removing something averse)
PRIMARY(satisfies biological need ex: food for hunger) vs SECONDARY(gains power when paired with primary reinforcement ex: $) IMMEDIATE(typically superior to delayed reinforcement because it forms a stronger relationship between stimulus and response) vs DELAYED(ex:grades,paychecks) |
|
|
CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT ?
|
OCCURS EVERY SINGLE TIME,LEARNING OCCURS QUICKLY,EXTINCTION OF INFO. DOES TOO
|
|
|
PARTIAL REINFORCEMENT ?
|
SOMETIMES REINFORCED,SOMETIMES NOT REINFORCED. LEARNING OCCURS SLOWLY MORE RESISTANT TO EXTINCTION)
|
|
|
4 TYPES OF PARTIAL REINFORCEMENT ?
|
FIXED-RATIO :REINFORCE BEHAVIOR AFTER SET # OF RESPONSES EXAMPLE-BUY 6 GET 7 FREE
VARIABLE-RATIO : REINFORCE AFTER UNKNOWN # OF RESPONSES FIXED INTERVAL : FIRST RESPONSE AFTER FIXED TIME PERIOD EXAMPLE- PAYCHECKS VARIABLE-INTERVAL : VARIED TIME FRAME,REINFORCE AFTER INTERVAL = TIME RATIO = # OF RESPONSES FIXED = UNCHANGING VARIABLE = CHANGING |
|
|
PUNISHMENT ?
|
DECREASES STRENGTH OF RESPONSE
|
|
|
OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING/ VICARIOUS LEARNING ?
|
MODELING, IMITATING BEHAVIOR.
|
|
|
3 MEMORY PROCESSES OF THE INFORMATION PROCESSING MODEL ARE ?
|
ENCODING,STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL.
|
|
|
IMPLICIT VS EXPLICIT MEMORY ?
|
IMPLICIT- NON DECLARATIVE,MOTOR SKILLS,HABITS (CEREBELLUM)
EXPLICIT - DECLARATIVE MEMORY, EPISODIC -WHERE YOU HAVE LIVED,DIARY SEMANTIC - MENTAL DICTIONARY, MEANINGFUL INFO. TRIVIA HIPPOCAMPUS (LIMBIC SYSTEM) |
|
|
FACTORS THAT AFFECT MEMORY RETRIEVAL ?
|
INTERFERENCE
PROACTIVE (early learning disrupts later learning) VS. RETROACTIVE(new info. makes it more difficult to remember old info.) MOTIVATED FORGETTING(trying to move memory away) DECAY THEORY ENCODING FAILURE (info. not encoded properly) AND EBBINGHAUS' FORGETTING CURVE (rapid forgetting of info. over time) |
|
|
MISINFORMATION EFFECT ?
|
The misinformation effect occurs when people’s recollections of events are distorted by information given to them after the event occurred. The psychologist Elizabeth Loftus did influential research on the misinformation effect that showed that memory reconstructions can affect eyewitness testimony.
Example: A bank robber enters a crowded bank in the middle of the day, brandishing a gun. He shoots out the security cameras and terrifies everyone. He is taking money from a teller when one of two security guards approaches the robber, draws his own weapon, and shoots. Suddenly, another shot is fired from a different direction and the security guard falls to the ground, shot. Some of the customers see that the other security guard, who was approaching the robber from the other side, mistakenly shot his partner. Later, police ask the witnesses when the robber shot the guard, and they report that he shot after the guard fired on him. Even though they saw one guard shoot the other, they are |
|
|
CONTEXTUAL EFFECTS OF MEMORY ?
|
is a method of memory enhancement which uses visualization to organize and recall information.
|
|
|
SUPPRESSION VS REPRESSION ? FREUD
|
SUPPRESSION : trying to push memory away.
REPRESSION : memory forgetting happens automatically |
|
|
serial position effect ?
|
ORDER RECALLED IN
-cheese > 1ST -milk > 1ST -eggs > LEAST LIKELY -bread > LEAST LIKELY -apples > 2ND -water > 2ND |
|
|
MEMORY ?
|
STORE HOUSE FOR KNOWLEDGE CAN INVOLVE ALL YOUR SENSES.
|
|
|
AUTOMATIC VS. EFFORTFUL PROCESSING ?
|
AUTOMATIC IS WALKING TO CLASS NOW
EFFORTFUL PROCESSING REMEMBERING WALKING TO CLASS 1ST DAY OF CLASS, DIDNT KNOW MUCH |
|
|
3 ENCODING STRATEGIES ?
|
ENCODING MEANING-CONNECT WHAT WE KNOW TO WHAT WE ARE LEARNING
VISUALIZATION- HIGHLY EMOTIONAL MENTAL ORGANIZATION(chunking)- ACRONYMS & HIERARCHIES |
|
|
3 MEMORY SYSTEMS ?
|
1. SENSORY
photographic <- iCONIC VS ECHOIC MEMORY -> auditory 2. SHORT TERM MEMORY temporary,maintenance rehearsal (7+/.2) 3.LONG TERM MEMORY limitless capacoty requires elaborate rehearsal |
|
|
LEVELS OF PROCESSING MODEL ?
|
visual not remembered <-SHALLOW VS DEEP PROCESSING -> remembered auditory semantic
|
|
|
SYNAPTIC CHANGES/LONG TERM POTENTIAL
|
NEURAL BASIS OF MEMORY REPEATIVE ACTION POTENTIAL DRUGS,ALCOHOL,STRESS HORMONES.
|
|
|
STRESS & HORMONES IN MEMORY?
|
INCREASED.
|
|
|
HOW TO IMPROVE MEMORY ?
|
IDUNNO
|
|
|
4 STAGES OF SLEEP AND BRAIN WAVES PATTERNS ASSOCIATED WITH IT?
|
S1: THETHA (SMALL) RELAXED, ALPHAS(FALLING ALSSEP) LIGHT SLEEP
S2:K COMPLEX/SPINDLES S3: SLOW WAVES( DEEPER SLEEP) PARTIAL DELTA S4:FULL DELTA (HIGH FREQUENCY)WAVES (DEEPEST SLEEP) |
|
|
SLEEP DISORDER CHARACTERIZED BY SUDDEN ONSET OF SLEEP BEHAVIOR IS CALLED ?
|
PARASOMNIAS
|
|
|
INDIVIDUALS WHO SNORE,SNORT, AND GASP WHILE SLEEPING DUE TO INTERRUPTED BREATHING WOULD BE DIAGNOSED WITH ?
|
SLEEP APNEA
|
|
|
DRUG CATEGORIES AND 1 EXAMPLE ?
|
Depressants - ALCOHOL
OPIATES-HEROINE STIMULANTS- COCAINE HALLUCINOGENS- MARIJUANA |
|
|
CONSCIOUSNESS ?
|
AWARENESS OF PERCEPTIONS,THOUGHTS,FEELINGS, SENSATIONS + ENVIRONMENTS,
|
|
|
WILLIAM JAMES & CONSCIOUSNESS?
|
HIGH LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS > STUDYING
2ND LEVEL > DAY DREAMING 3RD >SLEEPING 4TH >AUTOMATIC PROCESSING ( ZONING OUT ) |
|
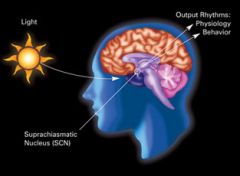
CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS ?
JET LAG/SHIFT WORK/DAYLIGHT SAVINGS TIME |
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental and behavioral changes that follow a roughly 24-hour cycle, responding primarily to light and darkness in an organism’s environment.
HIGHEST ALERT = 9 AM + 9PM HIGHEST TEMP. = 4PM LOWEST TEMP. = 4AM Circadian rhythms can influence sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, body temperature and other important bodily functions. Circadian rhythms are important in determining human sleep patterns. The body’s master clock, or SCN, controls the production of melatonin, a hormone that makes you sleepy. |
|
|
HOW MUCH OF OUR LIVES DO WE SPEND SLEEPING ?
|
1/3
|
|
|
NREM VS REM SLEEP ?
EUGENE ASERINSKY |
NON RAPID EYE MOVEMENT VS RAPID EYE MOVEMENT
R.E.M / ACTIVE SLEEP -> B/P, T, R, P (GO +) INTENSE BRAIN ACTIVITY,INTERNAL BODY AROUSAL,EXTERNAL BODY IS PARALYZED,EYES DART AROUND,MALES GET ERECTION IN R.E.M. |
|
|
SLEEP CYCLE ?
|
90 MINS, 5 CYCLES OF NREM + REM
|
|
|
LARKS VS OWLS ?
|
LARKS- MORNING PEOPLE
OWLS- NIGHT PEOPLE |
|
|
HOW MUCH SLEEP DO WE NEED ?
|
7+ HOURS
|
|
|
FUNCTIONS OF SLEEP ? 2 THEORIES
|
RESTORATIVE FUNCTION THEORY- AWAKENESS CAUSES WEAR + TEAR,SLEEPING RESTORES IT
ADAPTIVE OR EVOLUTIONARY THEORY-SLEEP EVOLVED FOR SAFETY REASONS BORBERLY- COMBO OF BOTH |
|
|
EFFECTS OF SLEEP DEPRIVATION ?
|
TIRED,FATIGUE,MINIMAL CONCENTRATION, MINOR HALLUCINATIONS,MICRO SLEEP.
|
|
|
CONTENT OF DREAMS
MANIFEST VS LATENT CONTENT ? |
MANIFEST- STORY LINE,FOCUSED ON THIS
LATENT-SYMBOLIZED, UNDERLYING MEANING |
|
|
PARASOMNIAS ?
EXAMPLES ? |
UNDESIRABLE PHYSICAL AROUSAL,BEHAVIORS, OR EVENTS DURING SLEEP OR SLEEP TRANSITIONS.
SLEEP WALKING (SOMNAMBULISM),SLEEP TERRORS,NIGHTMARES,SLEEP TALKING,SLEEP SEX, SLEEP RELATED EATING DISORDER(USUAL EATING BEHAVIOR WHILE SLEEPING), REM SLEEP BEHAVIOR DISORDER ( DOESN'T HAVE BODY PARALYZES DURING REM SLEEP,ACTS OUT DREAMS) |
|
|
DYSSOMNIAS ?
EXAMPLES ? |
DISRUPTIONS ION AMOUNT,QUALITY, OR TIMING OF SLEEP.
NARCOLEPSY(EXCESSIVE DAY TIME SLEEPING) SLEEP APNEA(BREATHING STOPS DURING SLEEP) INSOMNIA ( POOR QUALITY OF SLEEP CANT STAY OR GO TO SLEEP) RESTLESS LEG SYNDROME ( SPAMS,ACHES) |
|
|
ALTERED STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS ?
|
MEDITATION(YOGA,ZEN & TRANSCENDENTAL (FOCUSING ON BREATHING),HYPNOSIS(POWER OF SUGGESTION)
|
|
|
3 THEORIES OF HYPNOSIS ?
|
STATE THEORISTS-ALTERED STATE
-NEODISSOCATION THEORY/HIDDEN OBSERVER > SPLIT IN CONSCIOUSNESS (DOING/OBSERVING) PLANNING + MONITORING -THEORY OF DISSOCIATED CONTROL- AUTHENTIC ALTERED STATE,EXECUTIVE FUNCTION OF FRONTAL CORTEX IS WEAKENED. -NON STATE THEORISTS SOCIOCOGNITIVE THEORISTS PERSON IS MOTIVATED, BEHAVING AS IF HYPNOTIZED. |
|
|
+/- OF HALLUCINATIONS ?
|
+ = SEEING SMELLING TASTING SOMETHING NOT PRESENT
-= IMAGINING SOMETHING IS THERE BUT ACTUALLY ISNT |
|
|
DRUG REBOUND EFFECT ?
|
A rebound effect is what happens when the body tries to bring itself back into balance -- homeostasis after a drug has been taken by pulling in the opposite direction of the drug. One of the ironies of addiction is that the rebound effect causes the user to experience the very same effects they were hoping to escape through drug use.
|
|
|
ACTIVATION SYNTHESIS MODEL OF DREAMING ?
|
RANDOM FIRING OF NEURONS
|
|
|
FUNCTIONS OF R.E.M. SLEEP ?
|
HELPS MENTAL HOUSING CLEANING,ALCOHOL REBOUND
|
|
|
COMMON DREAMS ?
|
CHASING + FALLING .
|
|
|
3 COMPONENTS OF EMOTIONS ?
|
PHYSICAL-INSIDE OF BODY,PHYSCIAL AROUSAL
COGNITIVE-THOUGHTS BEHAVIORAL-EXTERNAL EXPRESSION |
|
|
4 THEORIES ON EMOTIONS ?
|
WKS.
|
|
|
3 COMPONENTS OF LOVE ?
|
PASSION > PHYSICAL/SEXUAL
INTIMACY > EMOTIONAL CONNECTION DECISION/COMMITMENT > LONG TERM PLANS |
|
|
MOTIVATION ?
|
BIOLOGICAL,EMOTIONAL,COGNITIVE + SOCIAL FORCES WHICH DIRECT OUR BEHAVIOR.
|
|
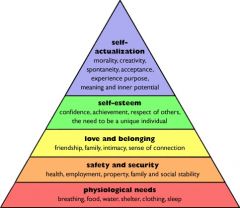
MASLOW HIERARCHY OF NEEDS ?
|
CHART
|

