![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
157 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sensation |
The process of by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receieve and represent stimulus energies from our environment. |
|
|
|
Perception |
The process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. |
|
|
|
Bottom-up Processing |
Analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brains integration of of sensory information. |
|
|
|
Top-down processing |
Information process guided by higher level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and perceptions. |
|
|
|
Transduction |
Transforming stimulus into neural impulses our brain can interpret: recieve, transform, and deliver. |
|
|
|
Sensation perception process |
1. Physical stimulus 2. Sensation 3.Transduction 4. Perception |
|
|
|
Absolute threshold |
The minimum amount of stimulus needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time |
Least amount of salt added to a gallon of water to taste a difference ex |
|
|
Difference thresholds |
The minimum difference between 2 stimuli required for detection 50% of the time. We experience the difference as just noticeable. |
Two buckets of paint ex |
|
|
Signal Detection Theory |
A theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus. It assumes there is no absolute threshold and that detection depends on a person's experience, expectations, motivation, and alertness. |
Quality control jobs, grading, retail jobs. |
|
|
Cornea |
Light enters here; protects the eye and bends light to provide focus. |
|
|
|
Pupil |
A small, adjustable opening. |
|
|
|
Iris |
A colored muscle that controls the size of the pupil by dilating or constricting to light intensity. |
|
|
|
Lens |
Focuses incoming light rays into an image in the retina. |
|
|
|
Optic nerve |
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain. |
|
|
|
Retina |
The light sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones, plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information. |
|
|
|
Visual cortex |
Located in the occipital lobe, in the rear of your brain; processes neural messages from the eye. |
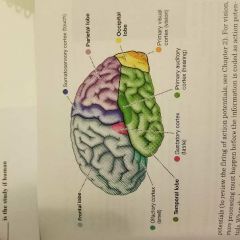
|
|
|
Gustatory |
Taste : Sweet, bitter, salty, sour, umami |
|
|
|
Olfactory |
Smell |
|
|
|
Olfactory cilia |
Fine, hair-like receptor cells; odor molecules bind to these receptors activating an electrical pulse to the Olfactory Bulb |
|
|
|
Olfactory Bulb |
Filters olfactory information to various parts of the brain. |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Produces hormones related to thirst, hunger, sex, moods. |
|
|
|
Amygdala |
Emotion related memory formation. |
|
|
|
Vision Sensation-Perception process |
1. Physical Stimulus: Light waves reflected on an image pass through the cornea and enter the eye through the pupil. The lens focuses light on the retina. 2. Sensation: Sensory receptors, called rods and cones, detect the light waves. 3. Transduction: Rods and cones convert light waves into signals. Those signals are processed by the ganglion cells, which generate action potentials that are sent to the brain by the optic nerve. 4. Perception: Signals from each visual field are processed on one side of each retina. The signals travel along the optic nerve through the thalamus and are processed in the visual cortex. |
|
|
|
Learning |
The process of acquiring through experience new and relatively enduring information or behaviors. |
|
|
|
Non-associative learning |
Learning about a stimulus in the external world. |
|
|
|
Associative learning |
Learning that certain events occur together. |
|
|
|
Cognitive learning |
The acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language. |
|
|
|
Habituation |
Exposure that leads to a decreased response to a stimulus. |
Non-associative learning |
|
|
Sensitization |
Exposure that leads to an increased response to a stimulus. |
Non-associative learning |
|
|
Stimulus |
Any event or situation that triggers a response |
Associative learning concept |
|
|
Response |
Any reaction to stimulus. |
Associative learning concept |
|
|
Classical conditioning |
A type of learning in which one learns to link 2 or more stimuli and anticipate events. |
|
|
|
Operant conditioning |
A type of learning in which behavior is strengthen if followed by a reinforcement or diminished if followed by a punisher. |
Associative learning |
|
|
Neural stimulus |
A stimulus the elicits no response. Can be anything. |
Classical conditioning comcepts |
|
|
Unconditioned Response |
An unlearned, naturally occurring reaction. Reflexes or automatic bodily functions. |
Classical conditioning concept |
|
|
Unconditioned stimulus |
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response. Sight or smell of food, touch. |
Classical conditioning concept |
|
|
Conditioned Response |
A learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus. |
Classical conditioning concept |
|
|
Conditioned Stimulus |
An originally irrelevant stimulus, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response. |
Classical conditioning concept |
|
|
Law of effect |
Behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. |
Operant conditioning concept |
|
|
Reinforcement |
Any even that strengthens the behavior it follows. |
Operant conditioning concept |
|
|
Shaping |
A procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior towards closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior. |
|
|
|
Positive reinforcement |
Increasing behavior by presenting positive reinforcers. |
Operant conditioning concept |
|
|
Negative reinforcement |
Increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli (Not punishment) |
Operant conditioning concept |
|
|
Primary reinforcer |
An innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. |
Operant conditioning concept |
|
|
Conditioned reinforcer |
A stimulus that gains it's reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. |
Operant conditioning concept |
|
|
Continuous reinforcement |
Reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs. Produces faster acquisition, and quicker extinction. |
Reinforcement schedule |
|
|
Intermittent reinforcement |
Reinforcing a response part of the time. Produces slower acquisition and slower extinction. |
Reinforcement schedule |
|
|
Fixed-ratio reinforcement |
A reinforcement schedual that reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses. (Buy 10 get 11th free) |
Reinforcement schedule |
|
|
Variable-ratio |
A reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses (slot machines) |
Reinforcement schedule |
|
|
Fixed-interval |
A reinforcement schedule thay reinforces a response only after a specified amount of time elapsed. |
Reinforcement schedule |
|
|
Variable-interval |
A reinforcement schedual tbat reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals. |
Reinforcement schedule |
|
|
Memory |
The persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information. |
|
|
|
Recall |
Retrieving information that is not currently in your conscious awareness, but was learned at an earlier time. |
Fill in the blank test questions |
|
|
Recognition |
Identifying items previously learned. |
Multiple choice questions |
|
|
Relearning |
Learning something more quickly when you learn it a second or later time. |
Studying for a comprehensive final exam |
|
|
Encoding |
Getting information into our brain |
|
|
|
Storage |
The retention of encoded information over time. |
|
|
|
Retrieval |
The process of getting information out of memory storage. |
|
|
|
Sensory memory |
The immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system. |
|
|
|
Short-term memory |
Activated memory that holds a few items briefly ( 7 digits of a phone number while dialing) before the information is stored or forgotten |
|
|
|
Long-term memory |
The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences. |
|
|
|
Working memory |
A newer understanding of short-term memory that focuses on conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual-spatial information, and information retrieved from long-term memory. |
Contemporary memory concepts |
|
|
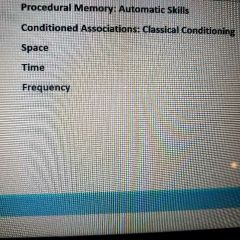
Automatic processing |
Unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, frequency, and well learned information, such as word meanings. |
Contemporary memory concept |
|
|
Explicit memory: Memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare". |
Building memories (Encoding) |
|
|
|
Effortful processing |
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort. (Reading, learning multiplication tables, studying for psych quiz. |
Building memories (Encoding) |
|
|
Implicit memories (automatic processing) |
Retention independent of conscious reflection. (Space, time , frequency) |
Building memories (Encoding) |
|

|
|
|
|
|
Capacity of short-term and working memory |
7 digits, 6 letters, 5 words. |
|
|
|
Chunking |
Organizing items into familiar, manageable units. |
Effort processing strategies |
|
|
Mnemonics |
Memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices. |
Effort processing strategies |
|
|
Hierarchies |
Organizing information from top to bottom, or bottom to top. |
Effort processing strategies |
|
|
Spacing effect |
The tendency for distributed study or practice or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice. |
Effort processing strategies |
|
|
Testing effect |
Enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply re-reading information. |
Effort processing strategies |
|
|
Explicit-memory system |
Frontal lobes Hippocampus |
Memory storage |
|
|
Implicit-Memory system |
The cerebellum Basal ganglia |
Memory storage |
|
|
Emotions and memory |
The amygdala |
Memory storage |
|
|
Priming |
The activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory. (Sensory cues) |
Memory retrieval |
|
|
Context-dependant memory |
Memory retrieval primed location, time of day, and other context-specific factors |
Memory retrieval |
|
|
Mood-congruent memory |
The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's good or bad mood. |
Memory retrival |
|
|
Serial position effect |
Our tendency to recall the best the last and the first items on a list. |
Memory retrieval |
|
|
Anterograde amnesia |
The inability to form new memories; past memory are still intact. |
Forgetting |
|
|
Retrograde amnesia |
The inability to retrieve information from one's past. |
Forgetting |
|
|
Encoding failure |
Not noticing or not paying attention |
Forgetting |
|
|
Storage decay |
Forgetting is initially rapid, then levels off with time. |
|
|
|
Proactive interference |
When prior learning disrupts your recall of new information. (If your fb password interferes with your ability to retrieve your new qvcc email pass) |
Retrieval failure |
|
|
Retroactive interference |
When new learning disrupts recall of new information (someone singing new lyrics to the tune of an old song) |
Retrieval failure |
|
|
Repression |
In psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories. |
Memory construction errors |
|
|
Misinformation effect |
Exposed to misleading information, we tend to misremember. |
Memory construction errors |
|
|
Source amnesia |
Attributing to the wrong source an event we have experience, heard about, read about, or imagined. |
Memory construction errors |
|
|
Déjà vu |
The eerie sense that "I have experienced this before." Cues from the current situation may subconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience. |
Memory construction errors |
|
|
Cognition |
The mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating. |
Thinking comcepts |
|
|
Concepts |
A mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, and people. |
Thinking concepts |
|
|
Prototypes |
The mental image of the best example of a category, used as a quick and easy method for sorting items |
Thinking concepts |
|
|
Algorithms |
Step by step procedures that guarantee a solution |
Problem solving |
|
|
Heuristics |
A simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems more efficiently. |
Problem solving |
|
|
Insight |
A sudden realization of a problem' s solution; contrasts with strategy-based solutions. |
Problem solving |
|
|
Confirmation bias |
A tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence. |
Problem solving |
|
|
Mental set |
A tendency to approach the problem with a mindset of what has worked previously. |
Problem solving |
|
|
Intuition |
An effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought. |
Decisions and judgement |
|
|
Availability heuristic |
Estimating the likelihood of events based off their availability in memory. |
Decisions and judgement |
|
|
Overconfidence |
The tendency to overestimate the accuracy or out knowledge and judgement. |
Descisions and judgement |
|
|
Belief perseverance |
Clinging to ones initial beliefs after the basis of those beliefs have been discredited. |
Descisions and judgement |
|
|
Framing |
The way an issue is posed shapes decision making and judgments about the issue. |
Decisions and judgement |
|
|
Creativity |
The ability to produce novel and valuable ideas |
Creative thinking |
|
|
Convergent thinking |
Narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution. |
Creative thinking |
|
|
Divergent thinking |
Expands the number of possible solutions. |
Creative thinking |
|
|
Expertise |
1.Well developed knowledge base. |
Sternberg's 5 components of creativity |
|
|
Imaginative thinking |
2. The ability to see novel patterns and relationships |
Sternberg's 5 components of creativity |
|
|
Ventursome personality |
3. The ability to tolerate ambiguity, new experiences and risk. |
Sternberg's 5 components of creativity |
|
|
Intrinsic motivation |
4. Driven by interest, challenge, and satisfaction. |
Sternberg's 5 components of creativity |
|
|
Creative environment |
5. Sparks, supports, and refine creative ideas. |
Sternberg's 5 components of creativity |
|
|
Language |
Our spoken, written, or signed words and the way we combine them to communicate meaning. |
|
|
|
Phonemes |
The smallest unit of distinctive sound in language, ex. Ch, sh, a, l. |
|
|
|
Morphemes |
The smallest units that carry meaning. Ex pre-, ed, a, l. |
|
|
|
Grammar |
Rules that enable us to communicate with one another. |
|
|
|
Intelligence |
1. Qualities that enable a person to succeed in their own time and in their own culture. 2. The ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use new knowledge to adapt to new situations. |
|
|
|
Spearman's general intelligence factor |
Abilities tend to cluster. |
|
|
|
Sternberg's 3 intelligences |
Analytical: traditional academic problem solving. Creative: innovation, new ideas. Practical: street smarts, handling everyday tasks. |
|
|
|
Emotional intelligence |
Perceiving emotions (recognizing them in faves, music, and stories) Understanding emotions (predicting them, how they change, and blend.) Managing emotions: knowing how to express a range of emotions in varied situations. ) Using emotions. |
|
|
|
Aptitude |
Ability to learn |
|
|
|
Achievement |
What people have already learned |
|
|
|
Mental age |
The level of skill typically associated with chronological age. |
|
|
|
Chronological age |
Literally how old you are. |
|
|
|
IQ |
Mental age/chronological age ×100 |
|
|
|
Stereotype threat |
The fear or apprehension of confirming negative bias and opinions about ones own group. |
|
|
|
Central nervous system |
The brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system |
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body. 1. Somatic nervous system 2. Autonomic nervous system - sympathetic nervous system and parasympathertic nervous system. |
|
|
|
Neurons |
Neural information building blocks; nerve cells. |
|
|
|
Dendrites |
Neurons bushy, branching extensions that recieve messages and conduct impulses towards the cell body. |
|
|
|
Axons |
The neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons, muscles, or glands. |
|
|
|
Myelin sheath |
A fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; enables faster transmission of neural impulses. |
|
|
|
Action potential |
A brief electrical charge that travels down its axon when stimulated by sensory or chemical signals. |
|
|
|
Threshold |
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. |
|
|
|
Synapse |
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrites of the cell body of the reviving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap, or cleft. |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters |
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons |
|
|
|
Acetylcholine |
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory. |
|
|
|
Dopamine |
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. |
|
|
|
Serotonin |
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. |
|
|
|
Norepinephrine |
Helps control alertness and arousal |
|
|
|
Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
(GABA) a major inhibitory neurotransmitter. |
|
|
|
Glutamate |
An excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory |
|
|
|
Endocrine system |
Regulates chemical reactions in cells and therefore control functions of the organs, tissue, and other cells. |
|
|
|
Hormones |
Chemical messengers secreted by glands. |
|
|
|
Adrenal glands |
Triggers the body's fight or flight response. |
|
|
|
Parts of the human brain |
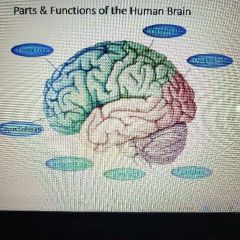
|
|
|
|
Frontal lobe |
Found under your forehead. Center of reasoning, planning, some parts of speech, movement (motor cortex), emotions, and problem solving. |
|
|
|
Parietal lobe |
Found on the top of your head. Receives sensory input from the skin (touch, temperature, pressure, and pain) |
|
|
|
Temporal lobe |
Found on the sides of your head above your ears. Functions include speech perception, hearing, and some types of memory. |
|
|
|
Occipital lobe |
Found at the back of your head. Receives input from the eyes. Often referred to as the visual cortex. |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
Found at the back of your head under the cerebrum. Means little brain. Responsible for movement, balance,and posture. Often takes over learned activities (like riding a bike) |
|
|
|
Brainstem |
Most basic part of your brain. Controls functions essential to life (breathing, digesting, eliminating waste, sleeping, maintaining body temperature) Maintains life without "thinking" |
|
|
|
Limbic system |
Limbic lobe, amygdala, hippocampal formation and associated with structures. |
|
|
|
Limbic lobe |
Feeding behavior. Fight or flight responses Aggression Expressions of emotions Expressions off autonomic, behavioral and endocrine aspects of the sexual response. |
|
|
|
Neruplasticity |
The brains ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience. |
|
|
|
Maslow's hierarchy of needs |
1. Physiological- breathing, food, water, sex, sleep, homeostasis, excretion. 2. Safety- security of the body, of employment, of resources, of morality, of the family, of the health, of property. 3. Love/belonging- friendship, family, sexual intimacy. 4. Esteem- self-esteem, confident, achievement, respect of others, respect by others. 5. Self-actualization - morality, creativity, spontaneity, problem solving, lack of prejudice, acceptance of facts. |
|
|
|
P.E.R.M.A |
Pleasure (positive emotion) Engagement (being absorbed) Relationship (positive) Meaning (purpose, coherence) Accomplishment (excellence, mastery) |
|
|
|
Sources of happiness |
Sonja Lyubomirsky- 10% circumstance, 50% intent, 40% genetics |
|

