![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Consciousness |
An organism aware of internal events and of the external environment |
Awareness |
|
|
Alternate state of consciousness. |
A mental state other than ordinary, waking consciousness that occurs during sleep dreaming psychoactive drug use and hypnosis. |
ASC |
|
|
Circadian rhythm |
A consistent pattern of cyclical bodily activities governed by an internal biological clock that generally occurs on a 24 to 25 hour cycle. |
Circa (about) Dies (day) |
|
|
What controls,Circadian rhythms. |
Circadian rhythm are regularly by a part of hypothalamus called the superachiasmatic nucleus. |
SCN |
|
|
Sleep deprivation |
Disrupted Circadian rhythms |
|
|
|
Rapid eye movement |
The 5th stage of sleep marked by rapid eye movements high frequency brain ways paralysis is a of large muscle and often dreaming |
REM |
|
|
How many cycles of sleep |
5, 1st one last about 90 minutes |
Stages |
|
|
Stages |
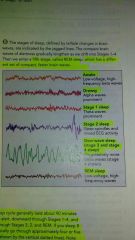
Awake, Drowsy, stage 1, Stage 2, Slow-wave Sleep 3-4, REM |
|
|
|
Non rapid eye movement. |
Stages one through 4 of sleep during which a sleeper does not show rapid eye movements. |
NREM |
|
|
Adaptation on protection theory of sleep. |
The theory that sleep involved to conserve energy and provide protection from predators. |
Animals/ hibernate? |
|
|
Repair restoration theory of sleep |
The theory that sleeps allow organisms to repair or recuperate from depleting daily waking activities. |
Human injurys |
|
|
Growth development theory of sleep |
But that deep sleep states for is correlated with physical development, including changes in structure and organization of the brain, infants spend more time in Stage 4 of sleep than adults. |
Grow while sleeping |
|
|
Learning memory theory of sleep |
The theory that sleep is important for learning and for consolidation, storage and Maintenance of memories |
Memories and learning |
|
|
3 dream theories |
With fulfillment view, Latin content, manifest content. |
Freud's theory |
|
|
Wish fulfillment view |
The Freudian believe that dreams provide an outlet for unacceptable desires |
Desires |
|
|
Latent content of dreams |
According to Freud, a dreams unconscious hidden meaning transformed into symbols I within the dreams, manifest content |
Story line |
|
|
Manifest content of dreams |
Dream analysis the surface or remembered story line, which contains symbols that mass the dreams latent content. |
True meaning behind storyline |
|
|
Activation-synthesis hypothesis of dreams |
The perspective that dreams are by products of random stimulation of the brain cells, which the brain attempts to combine or into coherent patterns known as dreams. |
Synthesis |
|
|
Cognitive view of dream |
To respective that dreams are a type of information processing that helps interpret daily experiences and organize them into memories. |
memory card |
|
|
Insomnia |
They sleep disorder characterized by persistent problems falling asleep, staying asleep or waking too early |
|
|
|
Sleep wake disorders. |

|
|
|
|
Narcolepsy |
The sudden and irresistible compulsion to sleep during the day time |
Narco means numbness. |
|
|
Sleep Apnea |
They sleep. This order of upper reportorial system that causes a repeat interruption of breathing during sleep, it also leads to loud snoring or poor quality sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness. |
Snoring |
|
|
Nightmares |
Anxiety arousing dreams that generally occur near the end of sleep cycle during rem sleep. |
Scary |
|
|
Sleep terrors |
Abrupt awakening from non rapid eye movement sleep accompanied by intense physiological arousal and feelings of panic. |
War flashes |
|
|
Psychoactive drug |
A chemical that changes mental processes and conscious awareness mood and or perception. |
Mind changing drugs |
|
|
AgOnist drugs |
A drug that binds to receptor and triggers a response in the cell which mimics or enhances a neurotransmitter |
Mimics |
|
|
Antagonist Drug |
A drug that binds to a receptor and triggers a response in the cell which blocks a neurotransmitter |
Blocks |
|
|
Hypnosis |
An alternate state of consciousness characterized by deep relaxation and a trans like state of heightened suggestibility and intense focus. |
Deep sleep |

