![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
tx for delusional disorder
|
1. psychotherpy is first line
2. antipsychotics are not helpful unless severe psychosis/delusion and there's a potential for harm |
|
|
ddx NMS vs:
1. anticholinergic syndrome 2. malignant hyperthermia 3. CNS infection |
1. anticholinergic syndrome (from overdose) doesn't have rigidity and elevated CPK
2. malignant hyperthermia occurs after inhaling anesthetic agents e.g. surgery procedure 3. CNS finection would have lab finding on lumbar puncture, may have elevated CPK if seizures occur |
|
|
time period criteria :
1. PTSD 2. Acute stress disorder 3. GAD 4. Adjustment disorder |
1. 1 month
2. < 1 month 3. 6 months 4. sx within 3 months of stressor; sx resolves in 6 months |
|
|
organic cause vs psychiatric disorder
|
ALWAYS R/O ORGANIC CAUSES; e.g. likely dx is cardiovascular disease over panic attack
e.g. kid taking amphetamines has seizures ==> most likely dx is epilepsy and not amphetamine toxicosis |
|
|
tx of severe mania in bipolar w/ additional sx of depression and suicide
|
1. lorazepam to keep the patient calm
2. valproic acid: can be loaded rapidly to achieve therapeutic blood levels in 3-5 days |
|
|
psychodynamic psychotherapy
|
intensive, long-term therapy helpful for people who wish to better understand the nature of their relationship with others
|
|
|
what do the following test:
1. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children 2. Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale 3. Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory 2 (MMPI-2) 4. Goodenough Draw-a-Person Test 5. Kohs Block test 6. Peabody-Vocabulary Test |
1. IQ
2. IQ 3. personality structure 4. Visual motor coordination 5. Visual motor coordination 6. Assess language barrier |
|
|
What other disorders are associated with Tourette?
|
- OCD and ADHD
- note: these may always be comorbid with Tourette or separate entities - but dx with tourette even if pt presents with sx of OCD as well |
|
|
With antipsychotic is associated with QT prolongation?
|
Pimozide
|
|
|
hepatic encephalopathy sx
|
*** asterixis (characteristic, but not specific)
- tremors, increased deep tendon reflexes, altered sensorium - physical stigmata (reflects changes in liver function): ecchymosis, peripheral edema, ascites formation, palmar erythema, spider angiomas - psychiatric sx: personality change, mood swings, changes in cognitive ability - acute decompensation: depression, catatonia, psychosis, delirium |
|
|
HIV-associated dementia sx
|
- can present in many ways: motor abnormalities, cognitive decline, behavioral changes
- typical behavioral changes: apathy, social withdrawal - neurologic abnormalities: weakness, imbalance, ataxia |
|
|
hyperthyroidism sx
|
- psychiatric sx: depressive, hypomanic, cognitive deficits
- neurologic: tremor, lid lag, brisk deep tendon reflexes, proximal myopathy, muscle wasting, myalgias - other: hot flashes, increased sensitivity to heat |
|
|
SLE sx
|
- psychiatric: "lupus psychosis," schizophrenia-like syndromes, affective disorders, psychotic symptoms, delirium, personality changes, anxiety, emotional lability
- cognitive impairment - only last hours to days associated with flares of the illness - neurologic: seizures, stroke, cranial nerve abnormalities, HA |
|
|
sx of delirium due to hypoglycemia
|
- acute confusional state (e.g. refusal to give blood)
|
|
|
signs of hypoglycemia
|
- tachycardia, tremor, hypertension, seizures
|
|
|
Beck's triad
|
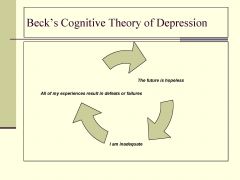
- used to dx MDD
- includes: feeling ineffectual, believing the world is always hostile, knowing that things will never change |
|
|
drug property associated with greater withdrawal sx
|
shorter half life
|
|
|
drug property associated with greater addiction potential
|
shorter the half life, the quicker the high, and the quicker the addiction potential
|
|
|
types of delusions:
1. mood congruent 2. mood-incongruent 3. bizarre delusions 4. somatic delusions 5. ego-syntonic delusions 6. ego-dystonic delusions |
1. delusions compatible with state of mind e.g. pt feels guilty and he has delusions of punishment
2. delusions are not compatible with mood, e.g. pt has delusions of grandeur 3. no way the delusions can be true 4. related to bodily functions 5.delusions are acceptable and pleasant to the pt; e.g. king of the world 6. delusions are unacceptable and unpleasant |
|
|
narcolepsy vs idiopathic hypersomnolence
|
multiple naps in narcolepsy are much refreshing, versus idiopathic hypersomnolence in which naps are long and unrefreshing
|
|
|
hypnagogic hallucinations
|
hallucinations when going to sleep
|

