![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CNS dopamimergic pathways
|
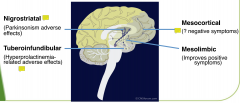
|
|
|
What do all antipsychotics do?
What is special about second generation antipsychotics? |
D2 blockade
D2 bloackade isn't primary action, can be seritonin or histamine |
|
|
the Antipsychotic granddaddy
|
clozapine (clozaril)
most effective dosing int. 25, maintainance 200-500 max 800. hs-tid reserved for refractory schizophrenia takes 4-6 months to reach effect dose |
|
|
Describe the course of treatment effects of antipsychotics
|
1st week - hyperactivity, hositility, agitation, and aggression
first few weeks - self-care, hygiene 4-8 weeks - delusions and hallucinations months - negative symptoms |
|
|
What is the mechanism of atypicals?
What are they trying to avoid? |
low affinity to, and fast dissociation from the D2 receptor
EPS - Parkinsonism - bradykinesia, stiffness, and tremor. akinesia (inability to initiate movement) and akathisia (inability to remain motionless). |
|
|
Anticholinergic side effects
|
hot as a hare (increased body temp)
dry as a bone (dry mouth, dry eyes, decreased sweating) blind as a bat (mydriasis (dilated pupils)) red as a beet (flushing) mad as a hatter (delirium) |
|
|
The worst side effect of antipsychotics
|
Tardive dyskinesia - irreversible involuntary movement disorder resulting form long term exposure to D2 blocking agents
risk 4-5% per year with first generation antipsychotics 1% with second generation involves face (lip smacking puckering, tongue contusions, puffing, frowning) hands and arms (choreoathetoid movements), feet, trunk (writhing movements) |
|
|
what is Neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
|
an adverse effect associated with all antipsychotics
clinical features: hyperthermia, autonomic instability, altered mental status, muscular hypertonicity (rhabdomyolysis) Management: stop antipsychotic, supportive measures (often in the ICU), monitor vitals |
|
|
other adverse effects of antipsychotics
|
postural hypotension
hyperprolactinemia (amenorrhea, galactorrhea, sexual dysfunction, gynecomastia) tachycardia, long QT hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, DM |
|
|
What are the common co-medications for antipsychotics?
what are the primarily used for |
benzos - agitation, akathisia, anxiety, insomnia, tremor
anticholinergics - balance between dopamine and cholinergic activity in the nigrostriatal pathway beta blockers - akathsia and tremor all basically trying to mop up the adverse effects of antipsychotics |

