![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
430 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Overachievement in one area to offset real or perceived deficiencies in another area
Napoleon complex: diminutive man becoming emperor Nurse with low self esteem works double shifts so her supervisor will like her. |
Compensation
|
|
|
Expression of an emotional conflict through the development of a physical symptom, usually sensorimotor in nature.
Teenager forbidden to see X-rated movies is tempted to do so by friends and develops blindness, and the teenager is unconcerned about the loss of sight |
Conversion
|
|
|
Failure to acknowledge an unbearable condition; failure to admit the reality of a situation of how one enables the problem to continue.
Diabetic person eating chocolate candy Spending money freely when broke Waiting 3 days to seek help for severe abdominal pain |
Denial
|
|
|
Ventilation of intense feelings toward persons less threatening than the one who aroused those feelings.
Person who is mad at the boss yells at his/her spouse Child who is harassed by a bully at school mistreats a younger sibling |
Displacement
|
|
|
Dealing with emotional conflict by a temporary alteration in consciousness or identity
Amnesia that prevents recall of yesterday’s auto accident Adult remembers nothing of childhood sexual abuse |
Disossciation
|
|
|
Immobilization of a portion of the personality resulting from unsuccessful completion of tasks in a developmental stage
Never learning to delay gratification Lack of a clear sense of identity as an adult |
Fixation
|
|
|
: Modeling actions and opinions of influential others while searching for identity, or aspiring to reach a personal, social, or occupational goal
Nursing student becoming a CCU nurse because this is the specialty of an instructor she admires |
Identification
|
|
|
Separation of the emotions of a painful event or situation from the facts involved; acknowledging the facts but not the emotions.
Person shows no emotions when discussing a serious car accident |
Intellectualization
|
|
|
Unconscious blaming of unacceptable inclinations or thoughts on an external object
Man who has thought about same-gender sexual relationship, but never had one, beats a man who is gay Person with many prejudices loudly identifies others as bigots |
Projection
|
|
|
Excusing own behavior to avoid guilt, responsibility, conflict, anxiety, or loss of self respect
Student blames failure on teacher being mean Man says he beats his wife because she does not listen to him |
Rationalization
|
|
|
Acting the opposite of what one thinks or feels
Women who never wanted to have children becomes a super mom Person who despises the boss tells everyone what a great boss she is |
Reaction Formation
|
|
|
Moving back to a previous developmental stage to feel safe or have needs met
Five year old asks for a bottle when new baby brother is being fed Man pouts like a 4 year old if he is not the center of girlfriend’s attention |
Regression
|
|
|
Excluding emotionally painful or anxiety provoking thoughts and feelings from conscious awareness
Women has no memory of the mugging she suffered yesterday Women has no memory before age 7 when she was removed from abusive parents |
Repression
|
|
|
Overt or covert antagonism toward remembering or processing anxiety producing information
Nurse is too busy with tasks to spend time talking to a dying patient Person attends court ordered tx for alcoholism but refuses to participate |
Resistance
|
|
|
Substituting a socially acceptable activity for an impulse that is unacceptable
Person who has quit smoking sucks on hard candy when the urge to smoke arises Person goes for a 15 minute walk when tempted to eat junk food. |
Sublimation
|
|
|
Components of a therapeutic relationship
|
•Trust: Behaviors such as caring, interest, understanding, consistency, honesty, promise keeping, listening, congruence (words & actions match)
•Genuine interest: Self comfort, self awareness of strengths and limitations, clear focus •Empathy: Putting oneself in client’s shoes, client and nurse giving “gift of self”, Different from sympathy (feelings of concern or compassion; focus shifting to nurse’s feelings) •Acceptance: No judgments; set boundaries •Positive regard: Unconditional nonjudgmental attitude |
|
|
Uses aspects of personality, experience, values, feelings, intelligence, needs, coping skills, perceptions to establish relationships beneficial to clients (Developed by H. Peplau)
|
Therapeutic use of self
|
|
|
tool to learn about oneself
4 quadrants: open/public self, blind/unaware self, hidden/private self, unknown •Goal: To move qualities from quadrants 2, 3, 4, into quadrant 1 |
Johari Window
|
|
|
Establishing a Therapeutic relationship: Peplau’s model of 3 phases, overlapping & interlocking of phases
|
•Orientation
•Working •Termination |
|
|
Meeting nurse, client
Establishment of roles Discuss purpose and parameters of future meetings Clarification of expectations Identification of clients problems Nurse/client contract/confidentiality, duty to warn/self disclosure |
Orientation phase
|
|
|
Problem identification: issues or concerns identified by client; examination of clients feelings & responses
Exploitation: examination of feelings & responses; development of better coping skills, more positive self image, behavior change, independence Possible transference/counter transference: the client treats the nurse like someone they know |
Working Phase
|
|
|
Begins when clients problems are resolved
Ends when relationship is ended Deals with feelings of anger or abandonment that may occur; client may feel termination as impending loss |
Termination Phase
|
|
|
Behaviors diminishing therapeutic relationships
|
Inappropriate boundaries: relationship becomes social or intimate
Feelings of sympathy: encouraging client dependency Nonacceptance: of client, avoidance |
|
|
Teacher: coping, problem solving, medication regimin, community resources
Caregiver: therapeutic relationship, physical care Advocate: ensuring privacy & dignity, informed consent, access to services, safety from abuse & exploitation Parent surrogate |
Therapeutic roles of a nurse in a relationship
|
|
|
Exchange of information
literal words spoken |
Verbal communication
|
|
|
pocess all messages used to give meaning congruent or incongruent messages
|
Non verbal communication
|
|
|
Boundaries for therapeutic communication most comfortable distance is
|
when nurse and client are 3-6 feet apart
|
|
|
Therapeutic communication
Touch five types |
Functional/professional
Social/polite Friendship/warmth Love/intimacy Sexual/arousal |
|
|
This focuses on the clients needs the goals are to est a therapeutic relationship, identify client concerns, assess client perceptions, facilitate client expression of emotions, teach client and family necessary self care skills
|
Therapeutic Communication
|
|
|
This concentrates exclusively on what the client says
|
Active listening
|
|
|
Watching nonverbal actions as the speaker communicates
|
Active observation
|
|
|
The nurse needs to use_________ not abstract messages
|
concrete
|
|
|
Which one of the following would be a nontherapeutic communication technique
reassuring reflecting focusing exploring |
Reassuring: is a non therapeutic technique because it attempts to dispel the clients feelings
|
|
|
_______, ________, and _________ have an effect on coping with ilness
|
Age, growth, and development
|
|
|
Clients of the Russian culture often welcome the use of medications for tx of mental illness
|
False: use home remedies first and are often reluctant to take medications
|
|
|
In culture aspect_______ is best source of info
|
Client
|
|
|
The nurse should have general cultural knowledge in________, _______ __________, and ________
|
preferences, health practices, and beliefs
|
|
|
Self awareness issues with culture
|
Be genuine and caring, ask how you can help with spiritual, religious or health practices, recognize own feelings or prejudices, remember the clients response to illness is complex and unique
|
|
|
A behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern (Clinically significant)
|
Mental Disorder
|
|
|
Difficult to define
No single universal definition Many components influenced by factors Dynamic, ever changing state |
Mental Health
|
|
|
Influencing factors for mental health (3)
|
Individual (personal)
Interpersonal (relationship) Social/cultural (environemental) |
|
|
Taxonomy of American Psychiatric Association
|
DSM-IV-R
|
|
|
DSM-IV-R Classification
Major psychiatric disorders except mental retardation, personality disorders |
AXIS I
|
|
|
DSM-IV-R Classification
Mental retardation and personality disorders |
AXIS II
|
|
|
DSM-IV-R Classification
Current medical conditions potentially relevant |
AXIS III
|
|
|
DSM-IV-R Classification
Psychosocial and environmental problems |
AXIS IV
|
|
|
Dont dx before dealing with a medical/physical problem because?
|
The mental dx will never go away
|
|
|
Aristotle and imbalances of the four humors
|
Blood, water, yellow & black bile
|
|
|
Creation of asylums
|
Period of enlightenment (1790's)
|
|
|
The definition of mental health is standardized and universally accepted T/F?
|
False: There is no single definition of mental health, which has many components and is influenced by a myriad of factors
|
|
|
Development of psychotropic drugs
|
1950's
|
|
|
Deinstitutionalization
Legislation for disability income (SSI) Changes in commitment laws |
Community mental health movement
|
|
|
More than ____% of americans 18 and older have diagnosable mental disorder
|
26%
|
|
|
Mental health is an economic burden that exceeds all types of _______?
|
Cancer
|
|
|
There is a revolving door effect due to ________?
|
deinstitutionalization
|
|
|
cachinnate
|
to laugh loudly
|
|
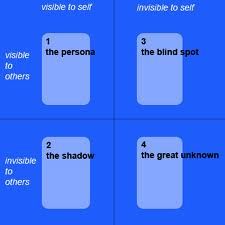
What does the image depict; define it
|
Quadrant 1: Open/public self—qualities one knows about oneself and others also know
Quadrant 2: Blind/unaware self—qualities known only to others Quadrant 3: Hidden/private self—qualities known only to oneself Quadrant 4: Unknown—an empty quadrant to symbolize qualities as yet undiscovered by oneself or others |
|
|
Purposes of this are:
Standardize nomenclature, language Identify defining characteristics or symptoms Assist in identifying underlying causes |
DSM-IV-R
|
|
|
This seeks innate desires
Is pleasure seeking Agressive Sexual impulses |
ID
|
|
|
This has morals
Is ethical Likes values and is parental |
Superego
|
|
|
This is mature, and has adaptive behavior
|
Ego
|
|
|
Major site of tension and gratification is the mouth, lips, and tongue; includes biting and sucking activities.
Id present at birth Ego develops gradually from rudimentary structure present at birth. |
ORAL
Birth to 18 months |
|
|
Anus and surrounding area are major source of interest.
Acquisition of voluntary sphincter control (toilet training) |
ANAL
18-36 months |
|
|
Genital focus of interest, stimulation, and excitement
Penis is organ of interest for both sexes. Masturbation is common. Penis envy (wish to possess penis) seen in girls; oedipal complex (wish to marry opposite-sex parent and be rid of same-sex parent) seen in boys and girls. |
PHALLIC/oedipal
3-5 years |
|
|
Resolution of oedipal complex
Sexual drive channeled into socially appropriate activities such as school work and sports Formation of the superego Final stage of psychosexual development |
LATENCY
5-11 or 13 years |
|
|
Begins with puberty and the biologic capacity for orgasm; involves the capacity for true intimacy
|
GENITAL
11-13 years |
|
|
Viewing the world as safe and reliable; relationships as nurturing, stable, and dependable (Erikson)
|
Trust vs. mistrust
Infant |
|
|
Achieving a sense of control and free will (Erikson)
|
Autonomy vs. shame
Toddler |
|
|
Beginning development of a conscience; learning to manage conflict and anxiety (Erikson)
|
Initiative vs. guilt
Pre-school |
|
|
Emerging confidence in own abilities; taking pleasure in accomplishments (Erikson)
|
Industry vs. inferiority
School age |
|
|
Formulating a sense of self and belonging (Erikson)
|
Identity vs. role confusion
Adolescence |
|
|
Forming adult, loving relationships and meaningful attachments to others (Erikson)
|
Intimacy vs. isolation
Young adult |
|
|
Being creative and productive; establishing the next generation (Erikson)
|
Generativity vs. stagnation
Middle adult |
|
|
Accepting responsibility for one's self and life (Erikson)
|
Ego integrity vs. despair
Maturity |
|
|
involves clients' interactions with one another, including practicing interpersonal relationship skills, giving one another feedback about behavior, and working cooperatively as a group to solve day-to-day problems.
|
Milieu Therapy
|
|
|
First American psychiatric nurse
|
Linda Richards
|
|
|
First training site for nurses to work with the mentally ill
|
McLean Hospital
|
|
|
First psychiatric nursing textbook
|
Nursing Mental Diseases
Publishes in 1920 |
|
|
First school of nursing to include a psyschiatric nursing course
|
Johns Hopkins (1913)
|
|
|
Required schools to include psychiatric nursing experience
|
National League for Nursing (NLN)
|
|
|
Developed the Therapeutic nurse-client relationship, interpersonal dimension (foundation for current practice)
|
H. Peplau
|
|
|
Basic level functions for an RN
|
Counseling
Milieu therapy Self care activities Psychobiologic interventions Health teaching Case management Health promotion, maintenance |
|
|
Advanced degree nurse functions
|
Psychotherapy
Prescriptive authority for drugs Consultation, liaison Evaluation |
|
|
Student concerns and psychiatric mental health
|
Saying the wrong thing
Knowing what to do Being rejected or not talking to the student Asking personal questions Hanling bizarre, inappropriate, or sexually aggressive behavior Handling feeling unsafe Seeing someone they know on unit Dealing with similar problems or backgrounds |
|
|
is the process by which the nurse gains recognition of his or her own feelings, beliefs,
and attitudes. |
Self Awareness
|
|
|
This takes a long time and is lengthy, expensive and practiced on a limited basis today
|
Psychoanalysis
|
|
|
Developed 8 stages of psychosocial development
|
Erik Erikson
|
|
|
This is very important in looking at interpersonal relationships
|
Therapeutic milieu or community
|
|
|
Developed hierarchy of needs
|
Abraham Maslow
|
|
|
Basic physiologic
Safety and security Love and belonging Self esteem Self actualization |
Hierarchy of Needs
|
|
|
Client centered therapy (focus on clients role)
Unconditional positive regard, genuineness, empathetic understanding was developed by whom? |
Carl Rogers
|
|
|
This focuses on behaviors and behavior changes not how the mind works
|
Behaviorism
|
|
|
Classical condiditong developed by
|
Ivan Pavlov
|
|
|
Operant conditioning
All behavior is learned Behavior with consequences (reward or punishment) Recurrance of rewarded behavior Developed by whom? |
B.F. Skinner
|
|
|
Behavior modification
Token economy (used alot on adolescent unit) Systemic desensitization Are all types of? |
Treatment modalities
|
|
|
True or False
Abraham Maslow was the 1st theorist to focus on clients role? |
False
Carl Rogers |
|
|
Overall belief of this theory is deviations occur when the person is out of touch with self or environment
|
Existential Theories
|
|
|
Consists of 11 irrational beliefs leading to unhappiness
|
Rational emotive therapy
Albert Ellis |
|
|
Consists of life with meaning; therapy as search for that meaning. Takes a long time
|
Logo therapy
Viktor Frankl |
|
|
Emphasis on self awareness
Identification of thoughts, feelings in the here and now |
Gestalt Therapy
Frederick "Fritz" Perls |
|
|
Focus on person's behavior and how that behavior keeps person from achieving life goals
|
Reality Therapy
William Glasser |
|
|
Name the 4 stages of Crisis Intervention
|
Exposure to stressor
Increased anxiety when usual coping ineffective Increased efforts to cope Disequilibrium, significant distress |
|
|
Categories of crisis are (3)
|
Maturational
Situational Adventitious |
|
|
Duration for crisis is usually
|
4 to 6 weeks
|
|
|
Outcome for crisis
|
Resolution to functioning at pre crisis level, higher level or lower level
|
|
|
Name the 2 crisis intervention techniques
|
Directive interventions: Assess health status, promote problem solving
Supportive Interventions: Deal with person's needs for empathetic understanding |
|
|
Which of the following includes the concept of automatic thoughts?
A. Cognitive therapy B. Rational therapy C. Logotherapy D. Gestalt therapy |
B. Rational emotive therapy, focuses on 11 irrational beliefs and automatic thoughts
|
|
|
One of the most important skills a nurse can develop
Crucial to the success of interventions with clients requiring psychiatric care |
Therapeutic Relationship
|
|
|
Components of therapeutic relationship are (5)
|
Trust
Genuine Interest Empathy Acceptance Positive Regard |
|
|
Behaviors such as
Caring Understanding Consistency Honesty Promise keeping Iistening all facilitate this component of the therapeutic relationship |
Trust
|
|
|
Self comfort
Self awareness of strengths and limitations Clear focus all facilitate this component of the therapeutic relationship |
Genuine interest
|
|
|
Putting oneself in clients shoes
Different from sympathy all facilitate this component of the therapeutic relationship |
Empathy
|
|
|
No judgements; set boundaries
all facilitate this component of the therapeutic relationship |
Acceptance
|
|
|
Unconditional nonjudgemental attitude
all facilitate this component of the therapeutic relationship |
Positive Regard
|
|
|
Values (sense of right and wrong, code of conduct for living)
Values clairification: choosing, prioritizing, acting Beliefs Attitudes are all part of |
Self awareness
|
|
|
True or False
A nurse displays empathy by showing feelings of concern or compassion? |
False
Empathy is putting oneself into the clients shoes Sympathy is showing feelings of compassion or concern |
|
|
Name the patterns of knowing (4)
|
Empirical (learned from nursing science)
Personal (life experiences) Ethical (moral nursing knowledge of right and wrong) Aesthetic (nursing 6th sense) |
|
|
Fifth pattern of knowing
|
Unknowing: the nurse admits lack of knowledge or understanding of clients world
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of relationships
|
Social
Intimate Therapeutic |
|
|
True or False
A social relationship involves superficial communication for the purposes of friendship to task accomplishment |
True
A social relationship occurs for friendship, socialization, companionship or task achievement. It involves superficial communication with shifting roles |
|
|
Establishing a therapeutic relationship is met in 3 phases what are they and who developed them?
|
Orientation
Working Termination H. Peplau |
|
|
This part of the therapeutic relationship begins when the nurse and client meet and ends when the client begins to identify problems to examine. During this phase, the nurse establishes roles, the purpose of meeting, and the parameters of subsequent meetings; identifies the client's problems; and clarifies expectations.
|
Orientation Phase
|
|
|
This part of the therapeutic relationship is usually divided into two subphases: During problem identification, the client identifies the issues or concerns causing problems. During exploitation, the nurse guides the client to examine feelings and responses and to develop better coping skills and a more positive self-image; this encourages behavior change and develops independence. (Note that Peplau's use of the word exploitation had a very different meaning than current usage, which involves unfairly
using or taking advantage of a person or situation. For that reason, this phase is better conceptualized as intense exploration and elaboration on earlier themes that the client discussed.) |
Working Phase
|
|
|
is the final stage in the nurse–client relationship. It begins when the problems are resolved, and it ends when the relationship is ended. Both nurse and client usually have feelings about ending the relationship; the client especially may feel the termination as an impending loss. Often clients try to avoid termination by acting angry or as if the problem has not been resolved.
|
Termination Phase
|
|
|
if the client has had negative experiences with authority figures, such as a parent or teachers or principals, he or she may display similar reactions of negativity and resistance to the nurse, who also is viewed as an authority.
|
Transference
|
|
|
when the nurse responds to the client based on personal unconscious needs and conflicts; this is called
|
Countertransference
|
|
|
Name the 3 behaviors that diminish therapeutic relationships.
|
Inappropriate boundaries(relationship becomes social or intimate)
Feelings of sympathy (encouraging client dependency) Nonacceptance of client, avoidance |
|
|
During the working phase of the nurse-client relationship, which one of the following would occur?
A. Expectations are clairified B. Nurse-client contract is est C. Feeling of loss are addressed D. Client feelings are examied |
D. Clients feelings are examined.
During the working phase the client identifies issues or concerns and his/her feelings and responses are examined. |
|
|
1. Building trust is important in
A. The orientation phase of the relationship B. The problem identification subphase of the relationship C. All phases of the relationship D. The exploitation subphase of the relationship |
A. Orientation phase
|
|
|
Abstract standards that provide a person with his or her code of conduct are
A. Values B. Attitudes C. Beliefs D. Personal philosophy |
A. Values
|
|
|
Ideas that one holds as true are
A. Values B. Attitudes C. Beliefs D. Personal philosophy |
C. Beliefs
|
|
|
The emotional frame of reference by which one sees the world is created by
A. Values B. Attitudes C. Beliefs D. Personal philosophy |
B. Attitudes
|
|
|
_________________ The nurse reviews the client's medication regimen.
(Patterns of knowing) |
Empirical
|
|
|
_________________ The nurse notices that the client is in a dark cluttered room. Knowing the importance of environment, the nurse begins to open the drapes.
(Patterns of knowing) |
Aesthetic
|
|
|
_________________ The nurse's grandmother also suffered from dementia, so the client's behavior does not surprise her.
(Patterns of knowing) |
Personal
|
|
|
_________________ As report is given, the nurse realizes client confidentiality has been breached.
(Patterns of knowing) |
Ethical
|
|
|
The Department of Health and Human Services estimates that of the 200,000 chronically homeless persons in the United States, the prevalence of mental illness and substance abuse is
A. 25% B. 40% C. 70% D. 85% |
B. 40%
|
|
|
Hospitals established by Dorothea Dix were designed to provide which of the following?
A. Asylum B. Confinement C. Therapeutic milieu D. Public safety |
A. Asylum
|
|
|
Hildegard Peplau is best known for her writing about which of the following?
A. Community-based care B. Humane treatment C. Psychopharmacology D. Therapeutic nurse–client relationship |
D. Therapeutic nurse-client relationship
|
|
|
How many adults in the United States who need mental health services actually receive care?
A. 1 in 2 B. 1 in 3 C. 1 in 4 D. 1 in 5 |
C. 1 in 4
|
|
|
Name the five types of touch
|
Functional/professional
Social/Polite Friendship/warmth Love/Intimacy Sexual/lovers |
|
|
Name the 4 therapeutic roles of the nurse in the therapeutic relationship
|
Teacher
Caregiver Advocate Parent surrogate |
|
|
When words and actions match this is defined as
|
congruence
|
|
|
When words and actions do not match this is defined as
|
incongruent
|
|
|
True or False
Assertive communication focuses on identifying negative feelings? |
False
Assertive communication focuses on the expression of positive or negative feelings or ideas in an open, honest, direct manner |
|
|
0-18 inches
|
Intimate zone
This amount of space is comfortable for parents with young children, people who mutually desire personal contact, or people whispering. Invasion of this intimate zone by anyone else is threatening and produces anxiety. |
|
|
18-36 inches
|
Personal zone
This distance is comfortable between family and friends who are talking. |
|
|
4-12 feet
|
Social zone
This distance is acceptable for communication in social, work, and business settings. |
|
|
12-25 feet
|
Public zone
This is an acceptable distance between a speaker and an audience, small groups, and other informal functions |
|
|
The study of distance zones between people during communication is called
|
Proxemics
|
|
|
clear statements of intent, such as “I want to die.” The message is clear that the client is thinking of suicide or self-harm.
|
Overt cue
|
|
|
are vague or hidden messages that need interpretation and exploration—for example, if a client says, “Nothing can help me.” The nurse is unsure, but it sounds as if the client might be saying he feels so hopeless and helpless that he plans to commit suicide.
|
Covert
|
|
|
Client: “I had an accident.”
Nurse: “Tell me about your accident.” This is an example of which therapeutic communication technique? A. Making observations B. Offering self C. General lead D. Reflection |
C. General lead
|
|
|
“Earlier today you said you were concerned that your son was still upset with you. When I stopped by your room about an hour ago, you and your son seemed relaxed and smiling as you spoke to each other. How did things go between the two of you?”
This is an example of which therapeutic communication technique? A. Consensual validation B. Encouraging comparison C. Accepting D. General lead |
A. Consensual validation
|
|
|
“Why do you always complain about the night nurse? She is a nice woman and a fine nurse and has five kids to support. You're wrong when you say she is noisy and uncaring.”
This example reflects which nontherapeutic technique? A. Requesting an explanation B. Defending C. Disagreeing D. Advising |
B. Defending
|
|
|
“How does Jerry make you upset?” is a nontherapeutic communication technique because it
A. Gives a literal response B. Indicates an external source of the emotion C. Interprets what the client is saying D. Is just another stereotyped comment |
B. Indicates external source of emotion
|
|
|
Client: “I was so upset about my sister ignoring my pain when I broke my leg.”
Nurse: “When are you going to your next diabetes education program?” This is a nontherapeutic response because the nurse has A. Used testing to evaluate the client's insight B. Changed the topic C. Exhibited an egocentric focus D. Advised the client what to do |
B. Changed the topic
|
|
|
When the client says, “I met Joe at the dance last week,” what is the best way for the nurse to ask the client to describe her relationship with Joe?
A. “Joe who?” B. “Tell me about Joe.” C. “Tell me about you and Joe.” D. “Joe, you mean that blond guy with the dark blue eyes?” |
C. Tell me about you and Joe
|
|
|
Which of the following is a concrete message?
A. “Help me put this pile of books on Marsha's desk.” B. “Get this out of here.” C. “When is she coming home?” D. “They said it is too early to get in.” |
A. “Help me put this pile of books on Marsha's desk.”
|
|
|
Indicating reception
|
Accepting
|
|
|
Allowing the client to take the initiative in introducing the topic
|
Broad opening
|
|
|
Searching for mutual understanding, for accord in the meaning of the words
|
Consensual validation
|
|
|
Asking that similarities and differences be noted
|
Encouraging compairison
|
|
|
Asking the client to verbalize what he/she perceives
|
Encouraging description of perceptions
|
|
|
Asking the client to appraise the quality of his/her experiences
|
Encouraging expression
|
|
|
Delving further into a subject or idea
|
Exploring
|
|
|
Concentrating on a single point
|
Focusing
|
|
|
Asking the client to consider kinds of behavior likely to be appropriate in future situations
|
Formulating a plan of action
|
|
|
Giving encouragement to continue
|
General lead
|
|
|
Making available the facts that the client needs
|
Giving information
|
|
|
Telling the client what to do
|
Advising
|
|
|
Indicating accord with the client
|
Agreeing
|
|
|
Misjudging the degree of the clients discomfort
|
Belittling feelings expressed
|
|
|
Demanding proof from the client
|
Challenging
|
|
|
Attempting to protect someone/something from verbal attack
|
Defending
|
|
|
Opposing the clients ideas
|
Disagreeing
|
|
|
Denouncing the clients behavior or ideas
|
Disapproving
|
|
|
Sanctioning the clients behavior or ideas
|
Giving approval
|
|
|
Responding to a figurative comment as though it were a statement of fact
|
Giving literal responses
|
|
|
Attributing the source of thoughts, feelings, and behavoir to others or to outside influences
|
Indicating the existence of an external source
|
|
|
Asking to make conscious that which is unconscious; telling the client the meaning of his/her experience
|
Interpreting
|
|
|
Changing the subject
|
Introducing an unrelated topic
|
|
|
Offering meaningless cliches or trite comments
|
Making stereotyped comments
|
|
|
Persistent questioning of the client
|
Probing
|
|
|
Indicating there is no reason for anxiety or other feeling of discomfort
|
Reassuring
|
|
|
Refusing to consider showing contempt for the clients ideas or behaviors
|
Rejecting
|
|
|
Asking the client to provide reasons for thoughts, feelings, behaviors or events
|
Requesting an explanation
|
|
|
Appraising the clients degree of insight
|
Testing
|
|
|
Refusing to admit that a problem exists
|
Using denial
|
|
|
Rapid assessment
Stabilize symptoms D/C planning Short stays |
Inpatient hospital treatment
|
|
|
Inpatient hospital treatment also has longer stays for?
|
Severe, persistent mental illness requiring acute care services
|
|
|
Day tx programs
Eight broad categories of roles Has to be D/C from hospital a doctor orders this |
Partial hospitilization program
|
|
|
Vary in structure,level of supervision, services provided
Homes, apts, adult foster care, respite, crisis housing |
Residental settings
|
|
|
Evolves around consumer household, group living situation, may transition
|
Residental setting
|
|
|
Peer support
Bridging staff |
Transitional care
|
|
|
Board and care homes are an example of a partial hospitalization program T/F?
|
False; a board care home is an example of a residential tx setting
|
|
|
Emphasis is on recovery, growth, independence, control symptoms
|
Psychiatric rehab programs
|
|
|
Four guaranteed rights of members
Physician client relationship is the key Focus on health not illness |
Clubhouse model
|
|
|
Problem solving orientation
Direct provision of service Services intense no time constraints |
Assertive community Treatment (ACT)
|
|
|
In the clubhouse model the relationship between clients is most important T/F?
|
False; the physician client relationship is the most important
|
|
|
Spend more time in jail and shelters
Have less family contact Face greater barriers to employment PATH program ACCESS demonstration project |
Homeless Mentally Ill
|
|
|
13% have mental illness
Lack of adequate community support Barriers to succesful community integration |
Prisoners
|
|
|
A doctor who specalizes in mental illness is a
|
Psychiatrist
|
|
|
Interpersonal skills
Humanity Knowledge base Communication skills Team work skills Risk assessment and mgmt These are all characteristics of a? |
Interdisciplinary Team
|
|
|
Which of the following disciplines would most likely would be included as part of the interdisciplinary team?
A PA B Physical therapist C Pharmacist D Dietician |
C Pharmacist: would be a part of the team when med mgmt is complex
|
|
|
Stresses education
|
Primary prevention
|
|
|
Early identification of mental health problems
|
Secondary prevention
|
|
|
Monitoring, coordinating psychiatric rehab services
Clinical practice issues such as substance abuse, domestic violence, child abuse, greif, depression and many others |
Terriary prevention
|
|
|
Frustration of working w pts having persistent and severe mental illness
Empowering pts to make their own decisions |
Self awareness issues
|
|
|
Have an effect on coping w illness
Expression of illness Erikson's stages Adult developmental tasks |
Age, growth and development
|
|
|
Need for lower doses
|
Slower metabolism
|
|
|
is a person's ability to respond in a healthy manner to stressful circumstances or risky situations
|
Resillience
|
|
|
is demonstrated in one's ability to manage daily activities and is a personal characteristic acquired through interactions with others.
|
Resourcefulnes
|
|
|
involves the inner core of a person's being and his or her beliefs about the meaning of life and the purpose for living. It may include belief in God or a higher power, the practice of religion, cultural beliefs and practices, and a relationship with the environment.
|
Spirituality
|
|
|
has the most influence on a person's health beliefs and behaviors.
|
Culture
|
|
|
has a strong influence on a person's health. It may determine whether or not the person has
P.140 insurance, adequate access to health care, or the ability to afford prescribed treatment. |
Socioeconomic status
|
|
|
is a belief that a person's abilities and efforts can influence the events in her or his life. A person's sense of self-efficacy is an important factor in coping with stress and illness
|
Self-efficacy
|
|
|
is a person's ability to resist illness when under stress
|
Hardiness
|
|
|
The _________a person is, the better he or she can cope with stress or illness.
|
healthier
|
|
|
Communication
Physical distance or space Social organization Time orientation Environmental control Biologic variations Are all factors in a ________ assessment |
Cultural
|
|
|
Cultural factors include hardiness and resilience T/F?
|
False; cultural factors include clients belifs about health and illness
|
|
|
the client is the best source for this information
|
culture
|
|
|
The nurse must seek information about the pts
|
culture
|
|
|
Genreal knowledge about culture and ask pt questions about_______,_______ and ________
|
Preferences, health, and beliefs
|
|
|
The nurse must always maintain a _____ and ______ attitude
|
genuine and caring
|
|
|
The nurse should ask the pt of a different culture what
|
How may I help you
|
|
|
The nurse must recognize what about herself when dealing with different cultures
|
prejudices
|
|
|
Each pts response to illness is
|
unique and complex
|
|
|
________ assessment requires active pt participation
|
psychosocial
|
|
|
5 factors that can influence assessment:
|
Participation/feedback
Health status Experiences/misconceptions Ability to understand Nurse's attitude/approach |
|
|
During the assessment the______ needs to be comfortable, quiet, private, safe, few distrations,
|
environment
|
|
|
During interview the pts permission is necessary for_______ input
|
Family/friends
|
|
|
What type of questions are you asking in the interview?
|
Open ended
|
|
|
When interviewing a pt the nurse should select an area that is quiet and isolated from others T/F?
|
False; the nurse should interview the pt in an environment that is comfortable, private and safe for both the client and the nurse. The nurse should not choose an isolated location
|
|
|
This term is used for how the pt feels
|
Mood
|
|
|
THis is the term for the pts expression
|
Affect
|
|
|
These two things should match
|
Mood and affect
|
|
|
repeated purposeless behaviors often indicative of anxiety, such as drumming fingers, twisting locks of hair, or tapping the foot
|
Automatisms
|
|
|
overall slowed movements is called
|
psychomotor retardation
|
|
|
maintenance of posture or position over time even when it is awkward or uncomfortable is called
|
waxy flexibility
|
|
|
Invented words that have meaning only to the pt
|
neoglisms
|
|
|
This affect shows little or a slow-to-respond facial expression
|
Blunted
|
|
|
This affect displays a full range of emotional expressions
|
Broad
|
|
|
This affect shows no facial expression
|
Flat
|
|
|
This affect displays a facial expression that is incongruent with mood or situation; often silly or giddy regardless of circumstances
|
Inappropriate
|
|
|
This affect displays one type of expression, usually serious or somber
|
Restricted
|
|
|
_______ can be described as happy, sad, depressed, euphoric, anxious, or angry.
|
mood
|
|
|
When the client exhibits unpredictable and rapid mood swings from depressed and crying to euphoria with no apparent stimuli, the mood is called ________
|
labile
|
|
|
Refers to how the client thinks
|
thought process
|
|
|
This is what the client actually says
|
thought content
|
|
|
content is ______ and process is ________
|
what and how
|
|
|
a client eventually answers a question but only after giving excessive unnecessary detail
|
Circumstantial thinkingq
|
|
|
A fixed false belief not based in reality
|
Delusion
|
|
|
excessive amount and reate of speech composed of fragmented or unrelated ideas
|
Flight of ideas
|
|
|
client's inaccurate interpretation that general events are personally directed to him or her, such as hearing a speech on the news and believing the message had personal meaning
|
Ideas of reference
|
|
|
disorganized thinking that jumps from one idea to another with little or no evident relation between the thoughts
|
loose associations
|
|
|
wandering off the topic and never providing the info requested
|
Tangenital thinking
|
|
|
stopping abruptly in the middle of a sentence or train of thought; sometimes unable to continue the idea
|
thought blocking
|
|
|
a delusional belief that others can hear or know what the client is thinking
|
thought broadcasting
|
|
|
a delusional belief that others are putting ideas or thoughts into the client's head—that is, the ideas are not those of the client
|
thought insertion
|
|
|
a delusional belief that others are taking the client's thoughts away and the client is powerless to stop it
|
thought withdrawal
|
|
|
flow of unconnected words that convey no meaning to the listener
|
word salad
|
|
|
When a client makes specific threats or has a plan to harm another person, health care providers are legally obligated to warn the person who is the target of the threats or plan. The legal term for this is
|
duty to warn
|
|
|
recognition of person, place and time
|
orientation
|
|
|
is not synonymous with confusion
|
disorientation
|
|
|
which is to make associations or interpretations about a situation or comment.
|
abstract thinking
|
|
|
children and schizophrenics dont have the ability to
|
think abstractly
|
|
|
When the client continually gives literal translations, this is evidence of
|
concrete thinking
|
|
|
false sensory perceptions or perceptual experiences that do not really exist. __________ can involve the five senses and bodily sensations.
|
hallucinations
|
|
|
refers to the ability to interpret one's environment and situation correctly and to adapt one's behavior and decisions accordingly
|
judgement
|
|
|
is the ability to understand the true nature of one's situation and accept some personal responsibility for that situation
|
insight
|
|
|
is the way one views oneself in terms of personal worth and dignity.
|
self concept
|
|
|
which one of the following would the nurse include when assessing a pts self concept
A Roles B Support systems C Personal qualities D Abstract thinking |
C Personal qualities; assessment of self concept includes info about the pts personal view of self, description of self, his/her personal qualities
|
|
|
Axis V (5) is the
|
GAF
|
|
|
Personality tests measure a pts cognitive abilities T/F?
|
False; they reflect the pts personality in areas such as self concept, impulse control, reality testing, and major defenses
|
|
|
history, general appearance and motor behavior, mood and affect, thought process and content, sensorium and intellectual process, judgment and insight, self-concept, roles and relationships, and physiologic and self-care considerations are all part of .
|
a thorough psychosocial assessment
|
|
|
Which of the following is an example of an open-ended question?
A. Who is the current president of the United States? B. What concerns you most about your health? C. What is your address? D. Have you lost any weight recently? |
B what concerns you most about your health
|
|
|
2. Which of the following is an example of a closed-ended question?
A. How have you been feeling lately? B. How is your relationship with your wife? C. Have you had any health problems recently? D. Where are you employed? |
D where are you employed
|
|
|
Which of the following is not included in the assessment of sensorium and intellectual processes?
A. Concentration B. Memory C. Judgment D. Orientation |
C Judgement
|
|
|
Assessment data about the client's speech patterns are categorized in which of the following areas?
A. History B. General appearance and motor behavior C. Sensorium and intellectual processes D. Self-concept |
B general appearance and motor behavior
|
|
|
When the nurse is assessing whether or not the client's ideas are logical and make sense, the nurse is examining which of the following?
A. Thought content B. Thought process C. Memory D. Sensorium |
B thought process
|
|
|
The client's belief that a news broadcast has special meaning for him or her is an example of
A. Abstract thinking B. Flight of ideas C. Ideas of reference D. Thought broadcasting |
C Ideas of reference
|
|
|
The client who believes everyone is out to get him or her is experiencing a(n)
A. Delusion B. Hallucination C. Idea of reference D. Loose association |
A Delusion
|
|
|
To assess the client's ability to concentrate, the nurse would instruct the client to do which of the following?
A. Explain what “a rolling stone gathers no moss” means. B. Name the last three presidents. C. Repeat the days of the week backward. D. Tell what a typical day is like. |
C repeat the days of the week backward
|
|
|
Repeated purposeless behaviors often indicating anxiety
|
automatisms
|
|
|
the belief that others can read one's thoughts
|
thought broadcasting
|
|
|
generally slowed body movements
|
psychomotor retardation
|
|
|
flow of unconnected words that have no meaning
|
word salad
|
|
|
Clients receiving mental health care retain all civil rights afforded to all people except the right to
|
leave the hospital in the case of involuntary commitment
|
|
|
developed Principles for the Provision of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Treatment Services.
|
American psychiatric association (APA)
|
|
|
Civil
Laws are determined by each state Pts held without consent Held for 48-72 hours |
Involuntary hospitalization
|
|
|
Clients receiving mental health care retain all civil rights afforded to all people except the right to
|
leave the hospital in the case of involuntary commitment
|
|
|
Clients receiving mental health care retain all civil rights afforded to all people except the right to
|
leave the hospital in the case of involuntary commitment
|
|
|
Right to request D/C at any time. Released unless a danger to self or others
|
Voluntary hospitalization
|
|
|
developed Principles for the Provision of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Treatment Services.
|
American psychiatric association (APA)
|
|
|
Conditional release or outpatient commitment. Continued participation in tx on INVOLUNTARY basis after release from hospital
|
Mandatory outpatient treatment
|
|
|
developed Principles for the Provision of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Treatment Services.
|
American psychiatric association (APA)
|
|
|
Civil
Laws are determined by each state Pts held without consent Held for 48-72 hours |
Involuntary hospitalization
|
|
|
Examples include taking prescriped meds, keeping appts, follow-up, attending specific tx programs
|
mandatory outpatient treatment
|
|
|
Civil
Laws are determined by each state Pts held without consent Held for 48-72 hours |
Involuntary hospitalization
|
|
|
Right to request D/C at any time. Released unless a danger to self or others
|
Voluntary hospitalization
|
|
|
Legal guardianship; seperate from civil commitment for hospitalization.
People who are gravely disabled; are found to be incompetent; cannot provide food, clothing, and shelter for themselves even when resources exist; and cannot act in their own best interests may require appointment of a____________ |
Conservator
|
|
|
Right to request D/C at any time. Released unless a danger to self or others
|
Voluntary hospitalization
|
|
|
Conditional release or outpatient commitment. Continued participation in tx on INVOLUNTARY basis after release from hospital
|
Mandatory outpatient treatment
|
|
|
Conditional release or outpatient commitment. Continued participation in tx on INVOLUNTARY basis after release from hospital
|
Mandatory outpatient treatment
|
|
|
Examples include taking prescriped meds, keeping appts, follow-up, attending specific tx programs
|
mandatory outpatient treatment
|
|
|
Mental health pts who are hospitalized voluntarily give up their right to leave the hospital T/F?
|
False; they retain all the civil rights afforded to any person including the right to leave the hospital
|
|
|
Free of restraint/seclusion
|
Least restrictive environment
|
|
|
Legal guardianship; seperate from civil commitment for hospitalization.
People who are gravely disabled; are found to be incompetent; cannot provide food, clothing, and shelter for themselves even when resources exist; and cannot act in their own best interests may require appointment of a____________ |
Conservator
|
|
|
Examples include taking prescriped meds, keeping appts, follow-up, attending specific tx programs
|
mandatory outpatient treatment
|
|
|
is the direct application of physical force to a person, without his or her permission, to restrict his or her freedom of movement.
|
Restraint
|
|
|
Mental health pts who are hospitalized voluntarily give up their right to leave the hospital T/F?
|
False; they retain all the civil rights afforded to any person including the right to leave the hospital
|
|
|
Legal guardianship; seperate from civil commitment for hospitalization.
People who are gravely disabled; are found to be incompetent; cannot provide food, clothing, and shelter for themselves even when resources exist; and cannot act in their own best interests may require appointment of a____________ |
Conservator
|
|
|
Free of restraint/seclusion
|
Least restrictive environment
|
|
|
Mental health pts who are hospitalized voluntarily give up their right to leave the hospital T/F?
|
False; they retain all the civil rights afforded to any person including the right to leave the hospital
|
|
|
is the direct application of physical force to a person, without his or her permission, to restrict his or her freedom of movement.
|
Restraint
|
|
|
Free of restraint/seclusion
|
Least restrictive environment
|
|
|
is the direct application of physical force to a person, without his or her permission, to restrict his or her freedom of movement.
|
Restraint
|
|
|
is the involuntary confinement of a person in a specially constructed, locked room equipped with a security window or camera for direct visual monitoring.
|
Seclusion
|
|
|
face to face eval in 1 hr;
every eight hrs.( every 4 for children) Dr order every 4 hrs, every 2 for children Document assessment every 1-2 hrs close supervision Debriefing session within 24 hrs after release from seclusion or restraint |
Short term use of restraints and seclusion
|
|
|
The protection and privacy of personal health information is regulated by the federal government through the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996
|
Confidentiality
|
|
|
this term has a legal meaning but no medical definition.
|
Insanity
|
|
|
The argument that a person accused of a crime is not guilty because that person cannot control his or her actions or cannot understand the wrongfulness of the act is known as the
|
M'Naghten rule
|
|
|
__________states have abolished the insanity defense
|
four
|
|
|
A nurse is req to maintain pt confidentality unless the pt threatens a specific individual or group T/F?
|
True; In cases where a pt threatens a third party the nurse has a duty to warn that third party
|
|
|
meaning the care they provide to clients meets set expectations and is what any nurse in a similar situation would do.
|
Standards of care
|
|
|
is a wrongful act that results in injury, loss, or damage; may be either unintentional or intentional.
|
Tort
|
|
|
is an unintentional tort that involves causing harm by failing to do what a reasonable and prudent person would do in similar circumstances.
|
Negligence
|
|
|
is a type of negligence that refers specifically to professionals such as nurses and physicians
|
Malpractice
|
|
|
A legally recognized relationship (i.e., physician to client, nurse to client) existed. The nurse had a duty to the client, meaning that the nurse was acting in the capacity of a nurse.
|
Duty
|
|
|
The nurse (or physician) failed to conform to standards of care, thereby breaching or failing the existing duty. The nurse did not act as a reasonable, prudent nurse would have acted in similar circumstances.
|
Breech of duty
|
|
|
The client suffered some type of loss, damage, or injury.
|
Injury or damage
|
|
|
The breach of duty was the direct cause of the loss, damage, or injury. In other words, the loss, damage, or injury would not have occurred if the nurse had acted in a reasonable, prudent manner
|
Causation
|
|
|
involves any action that causes a person to fear being touched in a way that is offensive, insulting, or physically injurious without consent or authority.
|
Assault
|
|
|
involves harmful or unwarranted contact with a client; actual harm or injury may or may not have occurred.
|
Battery
|
|
|
is defined as the unjustifiable detention of a client such as the inappropriate use of restraint or seclusion.
|
False imprisonment
|
|
|
A nurse is required to maintain client confidentiality unless the pt threatens a specifically identified individual or group T/F?
|
True; In cases where a pt threatens an identifiable 3rd party, the nurse has a duty to warn that 3rd party
|
|
|
This is the responsibility for providing safe, competent, legal, ethical care
|
Nursing liability
|
|
|
Meeting standards of care developed from code of ethics, scope and standards of practice, state nurse practice acts, agency policies and procedures, civil and criminal laws
|
Nursing liability
|
|
|
Unintentional torts are
|
Negligence
Malpractice |
|
|
Elements to prove malpractice
|
Duty
breech of duty injury or damage Causation |
|
|
Assualt
Battery False imprrisonment |
Intentional torts
|
|
|
3 elements to prove liability
|
Willful voluntary act
Intention to bring about consequences or injury Act as a substantial factor in injury or consequences |
|
|
which of the following would be considered an unintentional tort?
A.Malpractice B.Assualt C. Battery D.False imprisonment |
A. Malpractice; is an unintentional tort
|
|
|
This is a branch of philosphy dealing with values of human conduct (rightness and wrongness of actions) and goodness or badness of motives and ends in such actions
|
Ethics
|
|
|
Components of ethical decision making are these 6 things
|
Gather info
Clairfy values Identify options Identify legal considerations, practical restraints Building consensus for decision reached Renewing analyzing decision |
|
|
Pervasive alterations in emotions manifested by depression, mania or both
|
Mood disorders
|
|
|
Interference with life; long term sadness, agitation, or elation
|
Mood disorders
|
|
|
These are the most psychiatric dx associated with suicide. (depression is one of the most important risk factors for it)
|
Mood disorders
|
|
|
Categories of mood disorders
|
Major depressive disorder
Bipolar disorder Related disorders |
|
|
Related disorders include
|
Dysthymic disorder
Cyclothymic disorder Substance induced mood disorder; mood disorder due to general medical condition Seasonal affective disorder Postpartum blues, depression, psychosis |
|
|
Genetic
Neurochemical Neuroendocrine are all what kind of theories? |
Biologic
|
|
|
Freud
Bibring Jacobson Mania are all what kind of theories? |
Psychodynamic
|
|
|
Masking of depression by other behaviors considered age appropriate include
|
School phobia
Hyperactivity Learning disorders Failing grades Antisocial behaviors Substance abuse gangs risk behaviors eating disorders compulsive behaviors |
|
|
Major manifestation among cultures that avoid verbalizing feelings
|
Somatic complaints
|
|
|
Depression is most commonly associated with suicide T/F?
|
True; depression is considered the most common dx that results in suicide
|
|
|
Incidence women to men is 2:1
Decreases with age in women; increases with age in men; highest in single, divorced people |
Major depressive disorder
|
|
|
For a pt to be dx with a major depressive disorder they must have been having symptoms for at least?
|
2 weeks or longer
|
|
|
Sad mood, lack of interest in life and at least four other symptoms to meet criteria for this type of dx
|
Major depressive disorder
|
|
|
A pt with major depressive disorder may experience some or all of the following:
|
Changes in appetite, weight, sleep or psychomotor activity
Decreased energy; feels worthless or guilty Difficulty thinking, concentrating or making decisions, recurrent thoughts of death or suicide, plans or attempts |
|
|
Major depressive disorder can range from?
|
Mild to severe
|
|
|
Psychopharmacology classes of drugs for major depressive disorder
|
SSRI's
Cyclic antidepressants Atypical antidepressants MAOI's |
|
|
Another tx for major depressive disorder
|
ECT
|
|
|
Interpersonal therapy
Behavior therapy Cognitive therapy are all types of _________ therapy |
psycho
|
|
|
Assessment for major depressive disorder includes?
|
Hx
appearance Mood Thought processes, content Sensorium Judgement Self concept Roles, relationships Physiologic, self care considerations Depression |
|
|
Clients with depression often exhibit anhedonia T/F?
|
True; anhedonia refers to the loss of any sense of pleasure from activities that a person formerly enjoyed. This is a manifestation of depression
|
|
|
Interventions for major depressive disorder
|
Provide safety
Promote therapeutic relationship Promote ADL's Using therapeutic communication Managing meds Client, family teaching |
|
|
THis disorder has extreme mood swings from mania to depression
|
Bipolar Disorder
|
|
|
This disorder is second only to major depression as cause of worldwide disability
|
Bipolar Disorder
|
|
|
Onset of this disorder usually occurs in the early 20's
|
Bipolar Disorder
|
|
|
Manic episodes begin suddenly, last from a few weeks to several months
|
Bipolar Disorder
|
|
|
Psychopharmacology for bipolar disorder
|
Antimanic: Lithium
Anticonvulsants: mood stabilizers Agents helpful inreducing manic behavior and protecting against depressive cycles |
|
|
This is useful in midly depressive or normal portion bipolar cycle. Not useful during manic stage
|
Psychotherapy
|
|
|
Which of the following would be most appropriate for the tx of mania associated with bipolar disorder?
A. Lithium B. Fluoxetine C. Citalopram D. Venalfaxine |
A. Lithium; is an antimanic agent which would be most appropriate for tx a manic client with bipolar disorder
|
|
|
Interventions for bipolar disorder
|
Provide for safety
Meet psysiologic needs provide therapeutic communication Promote appropriate behaviors Manage meds Provide client family teaching |
|
|
Intentional act of killing oneself
|
Suicide
|
|
|
Thinking about killing oneself
|
Suicidal ideation
|
|
|
The first____years after an attempt represent the highest risk period, especially the first ___ months.
|
2 years
3 months |
|
|
Those with a ________ who committed suicide are at increased risk for suicide: the closer the relationship, the greater the risk.
|
relative
|
|
|
Examples of outcomes for a suicidal person include the following:
|
The client will be safe from harming self or others.
The client will engage in a therapeutic relationship. The client will establish a no-suicide contract. The client will create a list of positive attributes. The client will generate, test, and evaluate realistic plans to address underlying issues. |
|
|
Suicide is the ultimate rejection of
|
family and friends
|
|
|
Family members of the person who comitted suicide may feel?
|
Guilt
Shame Anger |
|
|
The nurses response to the pt talking about suicide
|
Need for positive unconditional regard
Avoidance of pt blame Nonjudgemental approach/tone Belief that one person can make a difference in anothe's life Possible devistation of staff if pt commits suicide |
|
|
When dealing with a pt who is suicidal the nurse needs to assume a dependent role
|
False; when dealing with a pt who is suicidal the nurse must take an authoritative role
|
|
|
Depression among the elderly is increased when?
|
elders are medically ill
|
|
|
Elder considerations for suicide
|
Psychotic features common
Increased intolerance to meds ECT more commonly used |
|
|
Suicide is increased among the?
|
Elderly
|
|
|
Nurses as first HCP to recognize behaviors consistent with?
|
mood disorders
|
|
|
This disorder requires a referral to psychiatrist or psychiatric advanced practice nurse for tx
|
Bipolar disorder
|
|
|
Screening for early detection of risk factors
|
Family strife
Parental alcoholism or mental illness Hx of fighting Access to weapons in the home |
|
|
refers to the subjective emotions and affect that are a normal response to the experience of loss
|
Greif
|
|
|
refers to the process by which a person experiences the grief. It involves not only the content (what a person thinks, says, and feels) but also the process (how a person thinks, says, and feels).
|
Grieving/bereavement
|
|
|
is when people facing an imminent loss begin to grapple with the very real possibility of the loss or death in the near future
|
Anticipatory grieving
|
|
|
is the outward expression of grief. Rituals of mourning include having a wake, sitting Shiva, holding religious ceremonies, and arranging funerals.
|
Mourning
|
|
|
Types of losses (5)
|
Psyiologic
Safety Loss of security,belonging Loss of self-esteem Loss R/T self actualization |
|
|
Kubler-Ross's five stages of grieving
|
Denial
Anger Barganing Depression Acceptance |
|
|
Bowlby's 4 phases of grieving
|
Experiencing numbness and denying the loss
Emotionally yearning for the lost loved one and protesting the permanence of the loss Experiencing cognitive disorganization and emotional despair with difficulty functioning in the everyday world Reorganizing and reintegrating the sense of self to pull life back together |
|
|
The 1st stage of grieving according to kubler ross is anger T/F?
|
False; according to kubler ross the 1st stage of grieving is denial followed by anger
|
|
|
Rando's 6 "R's"
|
Recognize
React Recollect and re-experience Relinquish Readjust Reinvest |
|
|
Worden's tasks
|
Accept reality of loss
Work thru pain of grief Adjust to changed environment due to loss Emotionally relocate loss and move on |
|
|
Dimensions of grieving
|
Cognitive responses
Emotional responses Spiritual responses Behavioral responses Physiologic responses |
|
|
is grief over a loss that is not or cannot be acknowledged openly, mourned publicly, or supported socially.
|
Disenfranchised grief
|
|
|
Three categories of circumstances can result in disenfranchised grief:
|
A relationship has no legitimacy.
The loss itself is not recognized. The griever is not recognized |
|
|
Grief process more complex due to absence of usual support for grieving, healing
Experienced by nurses when need to grieve not recognized |
Disenfranchised grief
|
|
|
Person devoid of emotion; grieving for prolonged periods; expressions of grief seems disproportinate to event
|
Complicated grieving
|
|
|
Low self-esteem
Low trust in others A previous psychiatric disorder Previous suicide threats or attempts Absent or unhelpful family members An ambivalent, dependent, or insecure attachment to the deceased person |
Complicated grieving
|
|
|
Risk factors leading to vunerability
|
Death of a spouse or child
Death of a parent (early childhood or adolescence Sudden, unexpected, untimely death Multiple deaths Death by suicide or murder |
|
|
While observing for client responses in the dimensions of grieving, the nurse explores three critical components in assessment:
|
Adequate perception regarding the loss
Adequate support while grieving for the loss Adequate coping behaviors during the process |
|
|
Nurses often experience complicated greif
|
False; although it is possible for anyone to experience complicated greif, a nurse would be more likely to experience disenfranchised grief when his/her need to grieve is not recognized
|
|
|
1. Which of the following accurately lists Bowlby's phases of the grieving process?
A. Denial, anger, depression, bargaining, acceptance B. Shock, outcry, and denial; intrusion of thought, distractions, and obsessive reviewing of the loss; confiding in others to emote and cognitively restructure an account of the loss C. Numbness and denial of the loss, emotional yearning for the loved one and protesting permanence of the loss, cognitive disorganization and emotional despair, reorganizing and reintegrating a sense of self D. Reeling, feeling, dealing, healing |
C. Numbness and denial of the loss, emotional yearning for the loved one and protesting permanence of the loss, cognitive disorganization and emotional despair, reorganizing and reintegrating a sense of self
|
|
|
2. Which of the following give cues to the nurse that a client may be grieving for a loss?
A. Sad affect, anger, anxiety, and sudden changes in mood B. Thoughts, feelings, behavior, and physiologic complaints C. Hallucinations, panic level of anxiety, and sense of impending doom D. Complaints of abdominal pain, diarrhea, and loss of appetite |
B. Thoughts, feelings, behavior, and physiologic complaints
|
|
|
3. Situations that are considered risk factors for complicated grief are
A. Inadequate support and old age B. Childbirth, marriage, and divorce C. Death of a spouse or child, death by suicide, and sudden and unexpected death D. Inadequate perception of the grieving crisis |
C. Death of a spouse or child, death by suicide, and sudden and unexpected death
|
|
|
Physiologic responses of complicated grieving include
A. Tearfulness when recalling significant memories of the lost one B. Impaired appetite, weight loss, lack of energy, palpitations C. Depression, panic disorders, chronic grief D. Impaired immune system, increased serum prolactin level, increased mortality rate from heart disease |
D. Impaired immune system, increased serum prolactin level, increased mortality rate from heart disease
|
|
|
Critical factors for successful integration of loss during the grieving process are
A. The client's adequate perception, adequate support, and adequate coping B. The nurse's trustworthiness and healthy attitudes about grief C. Accurate assessment and intervention by the nurse or helping person D. The client's predictable and steady movement from one stage of the process to the next |
A. The client's adequate perception, adequate support, and adequate coping
|
|
|
__________________ “I have this insatiable yearning to be with him.”
Dimensions of grieving |
Emotional dimension
|
|
|
__________________ Irritability and hostility toward others
Dimensions of grieving |
Behavioral dimension
|
|
|
__________________ “I thought a priest would certainly understand my need for support at this time. Why didn't he ask how I was feeling when I told him my husband was having surgery?”
Dimensions of grieving |
Cognitive dimension
|
|
|
__________________ “Why has God done this to me?”
Dimensions of grieving |
Spiritual dimension
|
|
|
__________________ “I've lost my appetite, and I just can't seem to get to sleep at night when I go to bed.”
Dimensions of grieving |
Physiologic dimension
|
|
|
The nurse observes that a client with bipolar disorder is pacing in the hall, talking loudly and rapidly, and using elaborate hand gestures. The nurse concludes that the client is demonstrating which of the following?
A. Aggression B. Anger C. Anxiety D. Psychomotor agitation |
D. Psychomotor agitation
|
|
|
A client with bipolar disorder begins taking lithium carbonate (lithium), 300 mg four times a day. After 3 days of therapy, the client says, “My hands are shaking.” The best response by the nurse is
A. “Fine motor tremors are an early effect of lithium therapy that usually subsides in a few weeks.” B. “It is nothing to worry about unless it continues for the next month.” C. “Tremors can be an early sign of toxicity, but we'll keep monitoring your lithium level to make sure you're okay.” D. “You can expect tremors with lithium. You seem very concerned about such a small tremor.” |
A. “Fine motor tremors are an early effect of lithium therapy that usually subsides in a few weeks.”
|
|
|
What are the most common types of side effects from SSRIs?
A. Dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth B. Convulsions, respiratory difficulties C. Diarrhea, weight gain D. Jaundice, agranulocytosis |
A. Dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth
|
|
|
The nurse observes that a client with depression sat at a table with two other clients during lunch. The best feedback the nurse could give the client is
A. “Do you feel better after talking with others during lunch?” B. “I'm so happy to see you interacting with other clients.” C. “I see you were sitting with others at lunch today.” D. “You must feel much better than you were a few days ago.” |
C. “I see you were sitting with others at lunch today.”
|
|
|
Which of the following typifies the speech of a person in the acute phase of mania?
A. Flight of ideas B. Psychomotor retardation C. Hesitant D. Mutism |
A. Flight of ideas
|
|
|
What is the rationale for a person taking lithium to have enough water and salt in his or her diet?
A. Salt and water are necessary to dilute lithium to avoid toxicity. B. Water and salt convert lithium into a usable solute. C. Lithium is metabolized in the liver, necessitating increased water and salt. D. Lithium is a salt that has greater affinity for receptor sites than sodium chloride. |
D. Lithium is a salt that has greater affinity for receptor sites than sodium chloride
|
|
|
Identify the serum lithium level for maintenance and safety.
A. 0.1 to 1.0 mEq/L B. 0.5 to 1.5 mEq/L C. 10 to 50 mEq/L D. 50 to 100 mEq/L |
B. 0.5 to 1.5 mEq/L
|
|
|
A client says to the nurse, “You are the best nurse I've ever met. I want you to remember me.” What is an appropriate response by the nurse?
A. “Thank you. I think you are special too.” B. “I suspect you want something from me. What is it?” C. “You probably say that to all your nurses.” D. “Are you thinking of suicide?” |
D. “Are you thinking of suicide?”
|
|
|
A client with mania begins dancing around the day room. When she twirled her skirt in front of the male clients, it was obvious she had no underpants on. The nurse distracts her and takes her to her room to put on underpants. The nurse acted as she did to
A. Minimize the client's embarrassment about her present behavior. B. Keep her from dancing with other clients. C. Avoid embarrassing the male clients who are watching. |
A. Minimize the client's embarrassment about her present behavior
|
|
|
Identify four areas that must be included in a patient teaching plan for a client starting lithium treatment.
|
Proper medication administration, salt and water needs, symptoms of lithium toxicity, need for periodic serum lithium monitoring
|
|
|
Identify four client statements that might indicate a subtle message about suicidal ideation.
|
“You've been a good friend;” “I can't do this anymore;” “This is where I keep my important papers;” and “I'd like you to have my chess set, the one you always admired.”
|

