![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
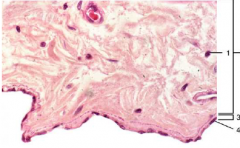
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
DESCRIPTION: a single layer of flat cells; centrally located nucleus
LOCATION: lines heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, air sacs of lungs, glomerular capsule of kidneys, and inner surface of tympanic membrane, forms epithelial layer of serous membranes FUNCTION: filtration, diffusion, osmosis, and secretion in serous membranes. |
|
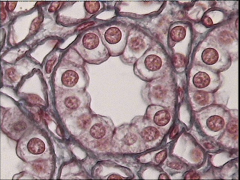
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
Description: single layer of cube-shaped cells; centrally located nucleus
Location: covers surface of ovary, lines anterior surface of capsule of the lens of the eye, forms the pigmented epithelium at the posterior surface of the eye, lines kidney tubules and smaller ducts of many glands, and makes up the secreting portion of some glands FUNCTION: secretion and absorption |
|
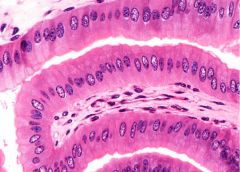
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
DESCRIPTION: single layer of column-like cells with nuclei near base of cells; contains goblet cells and cells with microvilli in some locations
LOCATION: lines the gastrointestinal tract, ducts of many glands, and gallbladder FUNCTION: secretion and absorption |
|
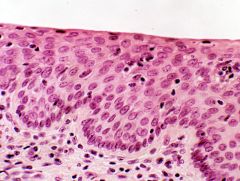
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
DESCRIPTION: several layers of cells; cuboidal to columnar shape in deep layers; squamous cells form the apical layer and several layers deep to it; cells from the basal layer replace surface cells as they are lost
LOCATION: keratinized variety forms superficial layers of skin, nonkeratinized variety lines wet surfaces, such as lining of the mouth, esophagus, part of larynx, part of pharynx, and vagina, and covers the tongue FUNCTION: protection |
|
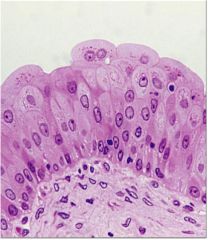
Transitional Epithelium
|
DESCRIPTION: appearance is variable; shape of cells in apical layer ranges from squamous (when stretched) to cuboidal (when relaxed)
LOCATION: lines urinary bladder and portions of uterus and urethra FUNCTION: permits distention (allows stretching) |
|
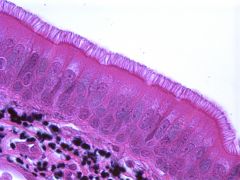
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
DESCRIPTION: not a true stratified tissue; nuclei of cells are at different levels; all cells are attached to basement membrane, but not all reach the apical surface
LOCATION: lines the airways of most upper respiratory tract (ciliated); lines larger ducts of many glands, epididymis, and part of male urethra (nonciliated) FUNCTION: secretion and movement of mucus by ciliary action (ciliated); absorption and protection (nonciliated) |
|
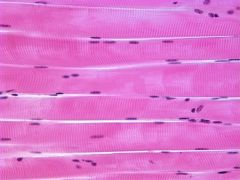
Skeletal Muscle
|
DESCRIPTION: long, cylindrical, striated fibers with many peripherally located nuclei; voluntary control
LOCATION: usually attached to bones by tendons FUNCTION: motion, posture, heat production, and protection |
|
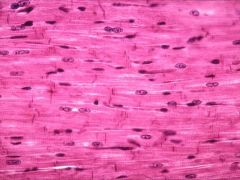
Cardiac Muscle
|
DESCRIPTION: branched striated fibers with one or two centrally located nuclei; contains intercalated discs; involuntary control
LOCATION: heart wall FUNCTION: pumps blood to all parts of the body |
|
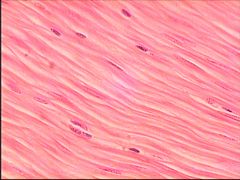
Smooth Muscle
|
DESCRIPTION: spindle-shaped (thickest in middle and tapering at both ends), nonstriated fibers with one centrally located nucleus; involuntary control
LOCATION: iris of the eyes, walls of hollow internal structures FUNCTION: motion (constriction of blood vessels and airways, propulsion of foods through GI tract, contraction of urinary bladder and gallbladder) |
|
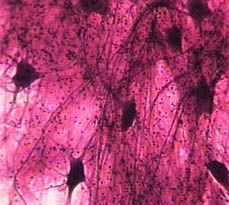
Nervous Tissue
|
DESCRIPTION: consists of neurons and neuroglia; neurons consist of a cell body and processes extending from the cell body (multiple dendrites and a single axon); neuroglia do not generate or conduct nerve impulses but have other important supporting functions
LOCATION: nervous system FUNCTION: exhibits sensitivity to various types of stimuli, converts stimuli into nerve impulses, and conducts nerve impulses to other neurons, muscle fibers, or glands |
|
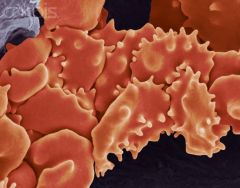
Crenation
|
the shriveling of a cell due to the presence of a hypertonic solution
|
|
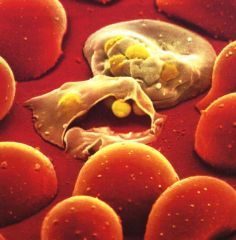
Hemolysis
|
the bursting of a cell due to the presence of a hypotonic solution
|

