![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endosymbiont theory |
mitcochondria and plastids were formally prokaryotes that began living within larger cells. |
|
|
serial enodsymbiosis |
theory that plastids evolved after mitochondria in eukaryotes |
|
|
phototrophs |
use energy from light to acquire carbon from carbon dioxide |
|
|
heterotrophs |
absorb organic molecules or ingest larger food particles
|
|
|
mixotrophs |
combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition |
|
|
primary endosymbiosis |
formation of a chloroplast from an endosymbiotic cyanobacterium within a eukaryotic host |
|
|
archaeplastida |
group that includes green and red algae |
|
|
secondary endosymbiosis |
plastid aquisition events occurred on several diffferent occasions via an endosymbiosis between red or green algae with a non-photosynthetic eukaryote host |
|
|
processes in evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes |
1) loss of cell wall 2) infolding of plasma membrane and elaboration of internal membrane structure 3) development of cytoskeleton 4) endosymbiosis of bacteria |
|
|
membrane infolding |
host cell infolded its membrane to help contain the two prokaryote cells. Membrane did not dissolve, this is why eukaryotes have a membrane around mitochondria and chloroplasts. Continued infolding may have resulted in endomembrane system |
|
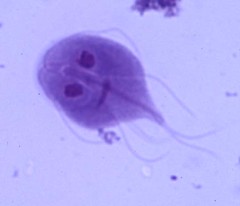
|
Giardia: -Supergroup excavata -Group diplomonada -lacks peroxisomes, chloroplasts and mitochondria -anaerobic -coenocytic-> 2 nuclei -4 flagella |
|
|
Dinoflagellate chromosome and cell cycle oddities |
-chromosomes are numerous -chromosomes remain condensed throughout the cell cycle, even during interphase -nuclear envelope persists during mitosis |
|
|
Apicomplexans |
ex. plasmodium-> malaria -all descendent from algae -used to have chloroplasts-> now have apicoplasts - |
|
|
Oomycetes |
-have same filamentous growth habit with fungi but arose due to convergent evolution-> analagous -have 2 flagella -have cellulose in their cell walls -diploid nuclei in hyphae -ecological roles= decomposers, plant pathogens |
|
|
phytophthora infestans |
-Oomycete -cause of the late blight of potatoes and the irish potato famine |
|
|
plasmopara viticola |
-Oomycete -cause of downey mildew of grape, France |
|
|
Diatoms |
-responsible for 40-50% of marine photosynthesis and 20-25% of planets photosynthesis -cells surrounded by two silica shells |
|
|
What processes led to the development of eukaryotes from prokaryotes? |
1) invagination of the cell wall 2) development of the cytoskeleton 3) endosymbiosis of mitochondria and plastid |
|
|
Differences between spore and gamete |
-spore is specialized for dispersal and unfavourable conditions -spore does not fuse with another cell -spore can undergo mitosis, gamete does NOT |
|
|
Brown algae life cycle |
-sporophyte generation is dominant -sporophyte and gametophyte look very different |
|

|
Euglena supergroup excavata group euglenazoa |
|
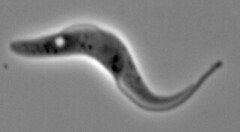
|
supergroup excavata african sleeping sickness |
|
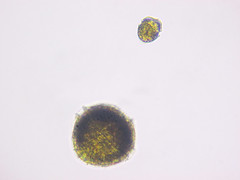
|
peridinium supergroup chromalveolata group alveolata subgroup dinoflagellata **red tide -2 flagella |
|
|
malaria |
supergroup chromalveolata group alveolata subgroup apicomplexa vector: anopheles mosquito |
|
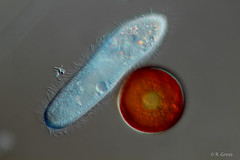
|
paramecium supergroup chromalveolata group alveolata subgroup ciliophora -have cilia -food vacuoles -contractile vacuoles -food follows route through the cytoplasm where it is digested by enzymes and then is released through the anal pore |
|

|
supergroup chromalveolata group stramenopila subgroup bacillatiophyta -marine and freshwater phytoplankton -unicellular |
|

|
brown algae subgroup phaeophyta -multicellular |
|

|
saprolegnia ferax subgroup oomycota -water moulds -important decomposers |
|
|
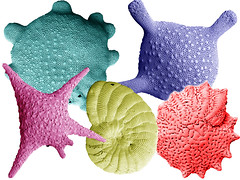
supergroup rhizaria foraminifera shells -contain calcium carbonate |
|

|
group radiolaria -shells composed of silica |
|
|
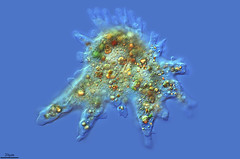
amoeba supergroup unikonta subgroup gymnamoeba |
|

|
supergroup archaeplastida group chlorophyta chlamydomonas -flagellated green algae -unicellular |
|
|
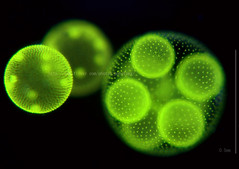
supergroup archaeplastida volvox -colonial form of green algae -2 flagella |

