![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How proteins are made? |
●to make a protein a specific gene is transcribed to make a molecule of pre-mRNA, whole gene is transcribed ●In eukaryotes pre-mRNA is then spliced to form mRNA which is a copy of the economy sections of the gene only ●mRNA is then translated to produce polypeptides |
|
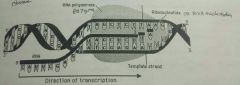
Transcription (in nucleus) |
●1 gene unwinds due to H bonds between complementary Base pairs being broken ●Complementary free RNA nucleotides bind to exposed bases on template strand (eg A-U & C-G) ●sugar phosphate backbone between free RNA nucleotides is joined using RNA POLYMERASE ●both intron & exon of gene transcribed to make pre-mRNA ●Transcription stops at stop triplet such as TAG (on coding strand) ●this marks the end of the gene & causes disengagement of RNA POLYMERASE ●gene transcribed repeatedly to make many pre-mRNA at 1 time ●●most genes transcribed to make pre-mRNA but some genes are transcribed to make rRNA & tRNA |
|
|
Splicing mRNA (In Nucleus) |

●In eukaryotic nuclei,pre-mRNA is spliced, the non-coding sections (transcribed from introns) are cut out & the coding sections ( transcribed from exons) are edited together to form mRNA (exons only) ●Prokaryotic DNA & Mitochondrial &Chloroplast DNA do not have introns so mRNA does not need splicing |
|
|
Translation (In Cytoplasm) |
■■mRNA leaves the nucleus through nuclear pores and binds to a ribosome (which contain rRNA) 1.Ribosome binds to the first 2 codon on the mRNA A tRNA carrying a methionine amino acid comes to the ribosome The anticodon on tRNA binds to the complementary codon on the mRNA 2.A 2nd tRNA binds to next codon,carrying a specific amino acid (in this case Tyr) 3. 2 amino acids undergo a condensation reaction and a peptide bond forms between them 4. 1st tRNA leaves the ribosome & picks up another amino acid Ribosome moves along the mRNA to cover the next codon Anticodon of another tRNA,again carrying a specific amino acid binds to next codon Amino acid binds to the growing polypeptide chain 5. When ribosome reaches stop codon it disengages from the mRNA There are no tRNA with anticodons complementary to stop codons |
|
|
ATP and Translation |
ATP is required to provide energy for the bond formation between an amino acid and tRNA molecule,allowing tRNA to carry an amino acid to the ribosomes during translation ●●adding a metabolic inhibitor (stops ATP production and respiration) will stop this process tRNA binds to specific amino acid determined by its anticodon this is helped by a specific enzyme |

