![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T/F The rate of prostate cancer dx far exceeds deaths |
T |
|
|
What percent of prostate cancer is dx at primary stage |
80% |
|
|
T/F there is a 100% survival for pts dx at age localized and regional prostate cancer |
T; 28% at distant and 77% at unstaged |
|
|
5 Risk factors for developing prostate cancer for men |
Age - (E/T ratio) Race/Ethnic background Diet Androgen levels Genetics |
|
|
* What is the median age of dx of prostate cancer |
66 |
|
|
What is the median age of death caused by prostate cancer |
80 - long life-cycle |
|
|
What group is most likely to develop prostate cancer? Least likely? |
Blacks - most, followed by non-hispanics American Indian - least |
|
|
What group is most likely to die from prostate cancer |
Blacks Access/Dx rate Maybe biological |
|
|
What dietary factor most contributes to developing prostate cancer |
Fat |
|
|
What 6 dietary factors decrease chances of developing prostate cancer |
|
|
|
T/F Family history plays a role in prostate cancer |
T |
|
|
T/F There are distinct and global associations between prostate cancer and MYC promoters and SNPs |
F; no global associations |
|
|
3 Drivers of prostate cancer (_____ Activation) |
Androgen Receptor Signaling (98-99% pCA) IGF-1/PTEN Pathway ETS Activation |
|
|
T/F pCA is primarily pt mutations and less genetic rearrangements |
F; pCA is PRIMARILY Genetic Rearrangements |
|
|
60% of pCA have _____ Fusions, while the rest are ______ |
ERG; rest are SPOP, FOXA1, IDH1 |
|
|
Most of the pCA are involved with ______ activation or ____ defects |
AR pathway activation DNA Repair Defects |
|
|
*After examining 333 primary pCA _____ were associated with m______ a______ |
74% Molecular Abnormality |
|
|
Give an example of epigenetic heterogeneity in pCA |
hypermethylated IDH1 mutant subset |
|
|
Defects in what 3 pathways are involved with pCA |
P13K MAPK DNA Repair |
|
|
T/F Primary tumors have higher mutations than mets |
F (in terms of fraction of genome and per megabase) |
|
|
Name Gene most disregulated for each cause of pCA
|
|
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for the conversion of T --> DHT |
5 - alpha - reductase (use 5-a-r inhibitors therapeutically ) |
|
|
Name the 5-a-r i |
Finasteride |
|
|
In a study of 18,000 pts over the age of 55, with Digital Rectal Exam and Prostate Specific Ag test, what percentage benefitted from Finasteride |
25%, with minimal-high morbidity in placebo |
|
|
T/F Of those from study pts who underwent Finasteride txt, 1/5 of the pts who developed cancer had more aggressive form (Gleason score of 8-10) |
T |
|
|
****In the REDUCE Trial, Dutasteride was associated with a _____ reduction in pCA cases compared to placebo |
23% |
|
|
T/F Dutasteride did NOT increase the prevalence of high-grade disease |
T |
|
|
What do we need to keep in mind regarding 5ARi |
Long Term Effect on Survival Toxicity Therefor NOT FDA approved |
|
|
T/F According to the PLCO (NEJM 2009) study examining prostate screening, there was definite benefit |
F; study saw no changes in Mortality |
|
|
T/F According to the European Screening Study (NEJM 2009) there was a 40% reduction in pCA mortality |
F; 20% 48 NNT to save 1 |
|
|
T/F According to the Göteborg screening trial (Lancet Oncology 2010) there was a 44% reduction in pCA mortality |
T; 12 NNT to save 1 |
|
|
What possible sources of differences between American and European studies regarding pCA and screening |
Americans had shorter follow up time European pts had slightly more advanced disease |
|
|
T/F As a result of PSA screening test, there is a large # of over-dx and overtreatment, in the 1st 10 years |
T |
|
|
According to the JCO, perhaps early screening (in 40s). If normal, then forget |
T |
|
|
3 Methods to determine if pCA |
Abnormal PSA Abnormal DRE cAP during TURP |
|
|
T/F You can palpate T1 |
F; during T2 |
|
|
What percentage of pCA are T1 |
60-70% |
|
|
70-80% of pCA occur in the ____ portion of the prostate and the ___ zone (near ____) |
Posterior Median Zone Near Urethra |
|
|
During T3 pCA the cancer has invaded _____ and is Locally D______/A______ |
Seminal Vesicles Differentiated/advanced |
|
|
Differences between T2A and T2B |
Waiting to hear back from Dr. Chatta |
|
|
According to the Gleason's Score 1 and 2 = 3 = 4 and 5 = |
1 and 2 = Well Differentiated 3 = Mod Differentiated 4 and 5 = Poor Differentiation |
|
|
3 Factors for Low Risk Group |
PSA < 10 AND Gleason < 7 AND Stage T1c or T2a |
|
|
3 Factors for Intermediate Risk Group |
PSA 10-20 OR Gleason 7 OR (Gleason 3 + 4) Stage T2b |
|
|
3 Factors for Poor Risk |
PSA >20 OR Gleason >7 OR Stage T2c |
|
|
T/F Bone Scan and CT Scan is only nec. for intermediate and poor risk pts |
T |
|
|
Txt Strategy for Low Risk Intermediate Systemic |
Low Risk - Local therapy Intermediate - Local and Systemic (maybe) High Risk - Local and Systemic (definitely) |
|
|
Txt Choices |
No txt - active surveillance Radical Prostatectomy Radiation Hormone Therapy Combinations |
|
|
4 Types of Radiation used for pCA |
External Beam - Conformal Brachytherapy - Seeds Neutrons Protons |
|
|
In the JCO paper examining ~24,000 pts with pCA What was the result of pts with Gleason > 8? Gleason of 7? 6? |
8-10: 10% of total cases, but 45% of cancer deaths
7: 40% of cases, 50% of deaths 6: 50% of cases, 1 death |
|
|
What was the major finding of the PIVOT trial? |
|
|
|
T/F a Scandanavian study examining Surgery vs Watching Waiting reported differences, with better outcomes in surgery group |
T; maybe diff staging? |
|
|
T/F Active Surveillance for favorable-risk prostate cancer is feasible and seems safe in the 15 year time frame |
T
|
|
|
T/F Mortality rate is consistent with expected mortality in favorable-risk pts managed with initial definitive intervention |
T |
|
|
T/F EBRT alone had 20% better survival than EBRT + HT |
T; 3 years or longer provides benefit, however side effects |
|
|
T/F It is best to do short ADT txt (6 months only) for adjuvant therapy for pCA |
F; LADT = 30 month adjuvant txt much better (5% increase in survival) |
|
|
T/F 6 month Adjuvant therapy is good enough for Intermediate/high risk pts compared to XRT alone |
T |
|
|
T/F Delayed hormonal survival therapy improves survival in node positive pts |
F; IMMEDIATE |
|
|
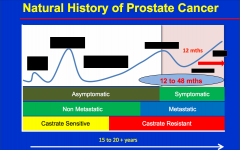
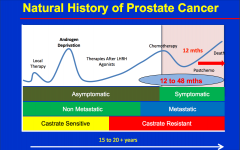
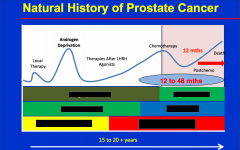
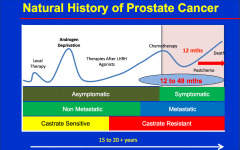
What is the 1st sign that disease is coming back |
Increase in PSA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 predictors of pCA survival |
Time to PSA rise Gleason PSA DT |
|
|
Does local control matter in locally advanced pCA |
Yes |
|
|
Does local control matter in metastatic patients |
Yes; RT improves FFS - evidence mounting |
|
|
Does hormone therapy improve salvage therapy |
YEs |
|
|
Major event with Estrogen therapy? |
DVT |
|
|
6 Methods of ADT |
|
|
|
T/F Existing therapies adequately suppress adrenal and/or intratumoral production of Androgen |
F |
|
|
What are the 3 indications of ADT |
|
|
|
T/F USe of ADT in pts with Biochemical progression is controversial |
T |
|
|
T/F Metastatic pCA pts are living longer |
T |
|
|
T/F Racial gap has increased |
F |
|
|
T/F PSA is good predictor of OS |
T |
|
|
T/F There is no significant survival advantage between Taxotere + ADT |
F; however mainly true for pts with high-volume disease |
|
|
*What are the big 3 SE of ADT |
Loss of Libido ED Hot Flashes |
|
|
*what are the SE of ADT that you can see |
Weight gain Gynecomastia Loss of Muscle Mass Decrease in penis and testes size Hair Chagnes |
|
|
*what are the SE of ADT that you can not see |
Loss of BMD Anemia Changes in blood chemistry/profile (lipids) HTN, Diabetes, CVD |
|
|
*what are the SE of ADT that you can feel |
Fatigue Depression Emotional lability Impaired Cog function |
|
|
T/F There is a correlation between ADT and Alzheimers |
T |
|
|
What constitutes CRPC |
Rising PSA |
|
|
T/F CRPC will develop in some pts who undergo ADT |
F; ALL |
|
|
T/F Androgen R is still functional in CRPC |
T |
|
|
2 Methods why CRPC happens |
Increased Androgen Synthesis Persistant AR signaling |
|
|
3 Methods to have increased Androgens in primary tumor |
Persistant Androgens in primary tumors Persistant Androgens in Mets Upregulation of steroidogenesis enzymes |
|
|
4 ways for persistant AR signaling |
AR Amplification AR splice variants AR signaling via alternate ligands (steroid superfamily) AR signling via P13K/MAPK |
|
|
How does Abiraterone work |
CYP17i - Shuts down androgen synthesis |
|
|
How does Enzalutamide work |
Anti-androgen - Compet AR Antag; prevents nuclear entry of AR. So no AR + DNA activity |
|
|
What 2 enzymes does Abiraterone work on |
17-alpha-hydroxylase c17-20 lyase i |
|
|
What do the Taxanes target |
Tubulin |
|
|
What were the 2 milestones in pCA regarding genetic blueprint |
SU2C TCGA |
|
|
Where is the highest amount of biopsy taken for the dream team biopsy trial |
Bone |
|
|
13% of biopsies were ____ 26% of biopsies were ____ 26% of biopsies were ____ |
Classical Small/Neuroendocrine Intermediate Atypical Carcinoma Mixed, but distinct, populations |
|
|
T/F A new histological subset of metastatic CRPC has been IDd which appears to be intermediate to adenocarcinoma and SCNC |
T |
|
|
T/F becuase this new cancer is histologically bland, it is mild form of cancer |
F; very aggressive |
|
|
What can be checked as a potential predictor to response (pCA) |
AR-V7 |
|
|
T/F Intelligent screening is in |
T |
|
|
T/F Local therapy for prostate cancer in ALL non-mets pts |
T |
|
|
T/F No use for Chemo in met prostate |
F |
|
|
What are 1st line for mCRPC |
Abiraterone and Enzalutamide |

