![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Projection:define |
Path of the CR as it enters and exits the body and hits the IR |
|
|
Protection is based on |
The anatomic position |
|
|
Define CR |
Central portion of the path the x-rays travel |
|
|
Relationship of the CR with IR in an AP or PA projection |
Perpendicular |
|
|
Axial |
Longitudinal angulation between long axis of body and CR of 10 degrees or more (AP Axial, PA Axial). |
|
|
Ways to achieve Axial projection |
Either angle CR to part or body part to CR |
|
|
CR skims a body part and frees it from superimposotion |
Tangential |
|
|
CR enters one side and exits the opposite side |
Rt lateral or Lt. Lateral |
|
|
Head, chest, or abdominal projection that specifies the side of the body closest to IR |
Rt or Lt lateral |
|
|
Lateral of extremities CR indicates... |
side entered and exited |
|
|
Name lateral projections of extremities |
Mediolateral, lateromedial |
|
|
The thumb is medial or lateral? |
Lateral |
|
|
The pinky is medial or lateral? |
Medial |
|

What projection is this? |
Tangential of the patella |
|
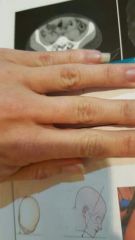
Projection? |
Tangential projection of the zygomatic arch |
|
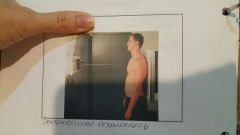
Projection? |
Anteroposterior |
|
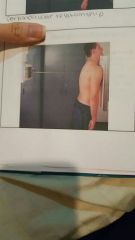
Projection? |
Posteroanterior |
|

|
AP axial- CR angled to part |
|
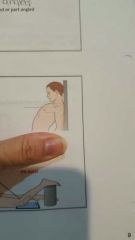
|
AP axial- part angled to CR |
|

|
PA axial |
|
|
Rt lateral |
|

|
Lateromedial wrist |
|

|
Mediolateral ankle |
|

|
Transthoracic lateral |
|
|
CR enters the body from a side angle |
Oblique |
|
|
Types of oblique projections |
AP oblique, PA oblique |
|
|
AP oblique |
|

|
AP oblique |
|

|
PA oblique |
|

|
PA oblique |

