![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Biotechnology
|
uses living organisms (produce or modified) ---
|
|
|
rDNA and monoclonal antibody (MAb) use for ---
|
development of pharmaceuticals, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases.
|
|
|
Techniques used to produce biotechnologic products list:
|
Recombinant DNA •Monoclonal antibody •Polymerase chain reaction •Gene therapy •Nucleotide blockade/Antisense
|
|
|
Recombinant DNA are ...
|
Two different DNA molecules are joined using - -Restriction endonucleases - DNA ligase --> plasmid
|
|
|
Uses of Recombinant DNA list
|
diagnose disease: synthetic suspected viral DNA and tag wt a dye --- mix them wt host ---> use Dye tag to ID target if they are hybridized
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibody definition ....
|
a laboratory-produced molecule that's carefully engineered to attach to specific cells.
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibodies production (Hybridoma - hybrid cell -- technology) procedure .....
|
fusing a specific plasma B cell with a myeloma (B cell cancer) cell (selected by special tissue culture and eliminate other B cell --> thus mono - specific one kind s.
|
|
|
Production of monoclonal antibodies steps ----
|
HGPRT- (cancer) - HGPRT+ (B cell) --- (hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase) an enzyme. HAT (hypoxanthine-aminopterin-thymine) medium KILL cell wo HGPRT (caner die) --> HGPRT+ (B cell harvest)
|
|
|
(HAMA) acronym ...
|
human antimouse antibody developed in 2-4 weeks -- side effect: such as chills, urticaria, wheezing --> and all HAMA will be clear out, Rapidly
|
|
|
Chimeric antibody --> (humanised: only binding parts are cat) is .....
|
antibodies from non-human species whose protein sequences have been modified to increase their similarity to antibody variants produced naturally in humans
|
|
|
First generation MAb : -omab all mice
|
The earliest type of monoclonal antibody that is entirely derived from mice. The suffix, -omab, indicates murine
|
|
|
Second generation MAb: -ximab human constant
|
This type of MAb has human constant region and murine variable region. It reduces high incidence of HAMA reaction. The suffix, -ximab indicates chimeric MAb.
|
|
|
Third generation of MAb: –zumab 90% human
|
This is humanized MAbs which are 90% human, containing only 10% mouse protein in the variable region. The suffix –zumab indicates a humanized Mab.
|
|
|
Fourth generation MAb: –umab. all human
|
This MAb is fully human. These MAbs are created in mice whose murine genes are inactivated and replaced with human sequences. The suffix is –umab.
|
|
|
Polymerase chain reaction definition
|
amplification (more than 100,000 fold -- enzymatic reaction occurs in repeated three cycles of a three-step process. •36 times repeat will produce 68 billion
|
|
|
Polymerase chain reaction STEP
|
Step 1: Denaturation (94°C.) •Step 2: Annealing (54°C) -to slow down Brownian motion •Step 3: polymerase help extension (72°C.) inc temp inc speed but not too high (denature sao)
|
|
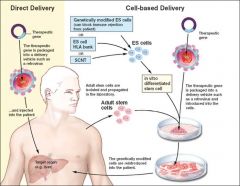
Gene therapy procedure .....
|
.... which exogenous genetic material is transferred into to somatic cells to correct an inherited or acquired gene defect or the addition of new functions to cells, such as the production of immune system mediator proteins that help to combat cancer and other diseases.
|
|
|
Gene therapy STEP
|
use retrovirus to deliver therapeutic gene into stem cell (directly inside patient or in vitro--> then reintroduced back into the patient)
|
|
|
Antisense technology
|
use Antisense bind specific mRNA molecules,to prevent synthesis of disease causing proteins. Antisense drug is considered as next generation drug
|
|
|
Antisense Mechanism
|
block activation site of RNA -- RNAse will destroy dsRNA (antisense+mRNA) --- antDNA bind to target DNA make triple helix
|
|
|
Lepirudin (Refludan): Lepirudin (rDNA) Anticoagulant drug:
|
is highly specific direct inhibitor of thrombin.
|
|
|
Antisense drug: Fomiversen sodium (Vitravene):
|
Used for local treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in patients with AIDS.
|
|
|
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) Efavirenz
|
addition drug to treat (HIV) -- slowing the spread of HIV in the body. (Norvir, Ritonavir in capsule chapter)
|
|
|
rDNA:Epoetin Alfa (Epogen, Procrit) ... erythroprotein
|
- A glycoprotein produced by rDNA technology, contains 165 amino acids in an identical sequence to that of the endogenous human erythroprotein. It is used for anemia due to cancer therapy, chronic dialysis, and zidovudine therapy (AZT).
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibodies examples .....
|
•AdalimUmab (Humara) ----------- •BasiliXImab (Simulect) •InfliXImab (Remicade) ------------- •BevaciZUmab (Avastin) •DacliZUmab (Zenapax) •TrastuZUmab (Herceptin)
|
|
|
Vaccines examples
|
•Hepatitis B Vaccine Recombinant (Engerix-B, Recombivax HB) ------ •Haemophilus B Conjugate Vaccine (HibTITER, Liquid PedvaxHIB, ActHIB) ----------•HPV (Cervarix, Gardasil
|

