![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
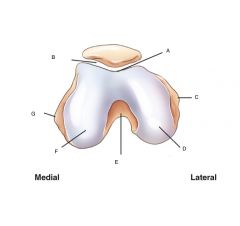
Axial View
Distal Femur and patella Label |
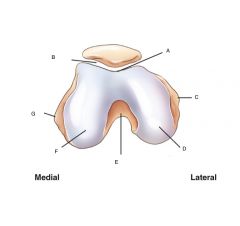
A. patellar surface
(intercondylar sulcus) (trochlear groove) B. Patellofemoral Joint C. Lateral Epicondyle D. Lateral Condyle E. Intercondylar fossa F. Medial Condyle G. Medial Epicondyle |
|
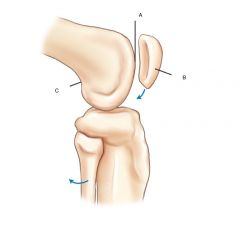
Distal Femur and patella- lateral view
|
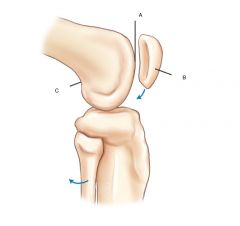
A. Patellar Surface
B. Patella (Sesamoid bone) C. popiteal surface |
|
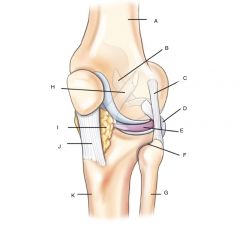
Knee joint and proximal tibiofibular joint
|
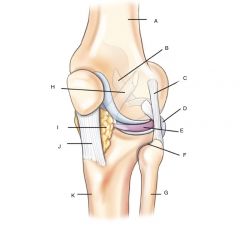
A. Femur
B. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) C. Fibular lateral collateral ligament (LCL) D. Tendon of popliteus muscle E. Lateral meniscus F. Proximal tibiofibular joint G. Fibula H. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) I. infrapatellar fat J. Patellar Ligament K. Tibia |
|
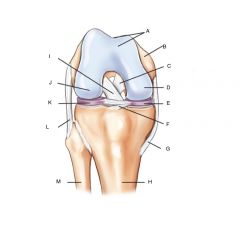
Right knee Joint
|
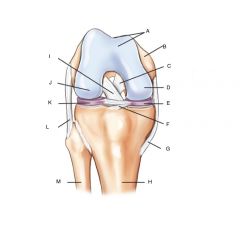
A. Patellar surface
B. Femur C. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) D. Medial Condyle E. Medial meniscus F. Transverse ligament G. tibal (medial) collateral ligament (MCL) H. Tibia I. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) J. lateral condyle K. Lateral meniscus L. fibular lateral collateral ligament (LCL) M. Fibula |
|
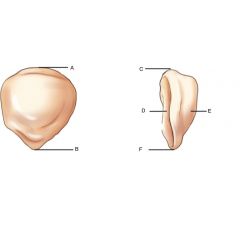
Label
Patella |
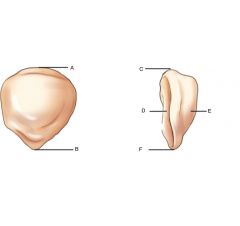
A. Base (superior border)
B. Apex (inferior surface) C. Base (superior border) D. Posterior surface (smooth) E. Anterior surface (rough) |
|
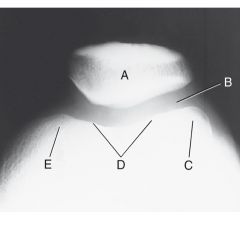
Label
Tangential projection (femoropatellar joint) |
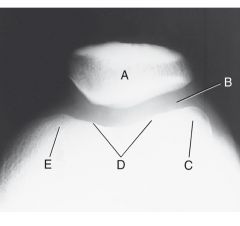
A. Patella
B. Femoropatellar joint C. Lateral condyle D. Patellar surface E. Medial condyle |
|
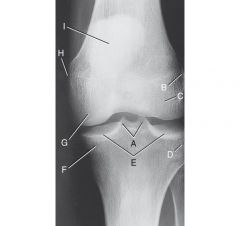
Label the AP knee
|
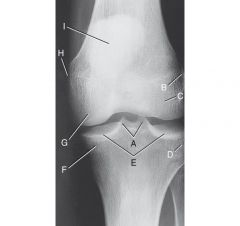
A. Medial and Lateral intercondylar tubercles, entensions of intercondylar eminence (tibial spine)
B. lateral epicondyle of femur C. lateral condyle of femur D. Lateral condyle of tibia E.Articular facets of tibia / tibial plateau F. Medial condyle of tibia G.medial condyle of femur H. Medial epicondyle of femur I. Patella (seen through femur) |
|
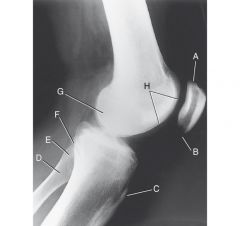
Laternal knee, true lateral
|
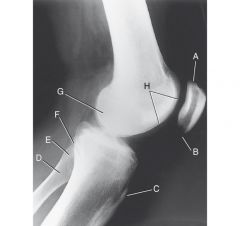
A. base of patella
B. Apex of patella C. Tibial tuberosity D. Neck of Fibula E. Head of fibula F. Apex (styloid process) of head of fibula G. Superimposed medial and lateral condyles H. Patellar surface (intercondylar culcus or trochlear groove) |
|
|
The patella is _______ or _______ above the knee joint. ( think distance )
|
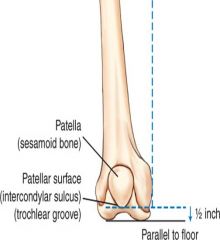
1/2 inch or 1.25 cm
|
|
|
What does sulcus mean?
|
groove or depression
|
|
|
What does trochlea mean?
|
pulley or pulley shaped structure
|
|
|
The patellar surface is also referred to as _________ and _________
|
intercondylar sulcus and trochlear groove.
|
|
|
What separates the two condyles of the femur?
|
intercondylar fossa
|
|
|
What is directly above the intercondylar fossa?
|
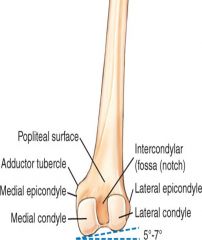
popliteal surface
|
|
|
Why must the CR be angled 5 to 7 degrees cephalad for a lateral knee?
|
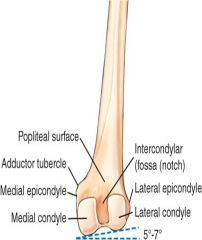
Because the medial condyle of the femur extends lower than the lateral condyle, the angle causes the two condyles to be directly superimposed when the femur is parallel to the IR.
|
|
|
Of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the patella, which one is rough and which one is smooth?
|
Posterior surface is smooth
Anterior surface is rough |
|
|
What is present on the posterolateral aspect of the medial condyle?
|
Adductor tubercle
|
|
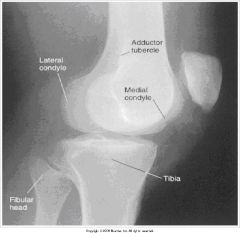
answer the following questions about this image.
1.)What does this image look like compared to a true lateral? 2.)How can this be corrected? |
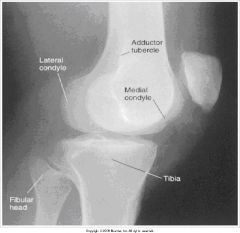
1.)- Fibular head less superimposed by tibia.
- The adductor tubercle is not in profile. 2.) the knee is over-rotated toward the IR, so rotate the knee and patella away from IR, medially. |
|
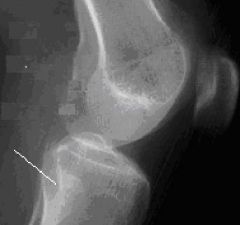
Answer the following
1.) What does this image look like compared to a true lateral? 2.) What needs to be done to correct this image? |
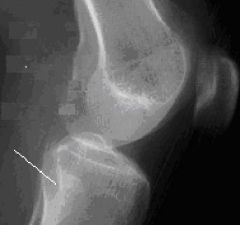
1.) The fibular head is completely superimposed by tibia
2.) This knee is under-rotated away from the IR - so rotate the knee and patella toward the IR laterally. |
|
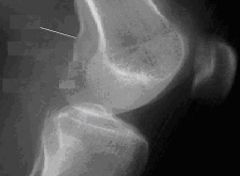
1.) What does this image look like compared to a true lateral?
2.) What can be done to fix this position? |
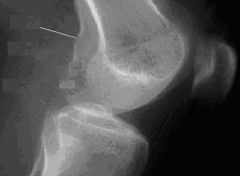
1.) You can see the adductor tubercle, which is posterior on the medial condyle.
2.) This position is under rotated, the condyles should be superimposed, so rotate the knee toward the IR, laterally |
|
|
Which two ligaments of the knee help stabilize the knee from the anterior and posterior perspective.
|
Cruciates
|
|
|
What is the upper, or superior portion of the patella called?
|
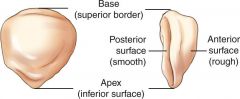
Base
|
|
|
Which condition can cause the tibial tuberosity to be pulled away from the tibial shaft?
|
Osgood-Schlatter disease
|
|
|
Which joint should be open or almost open for a well positioned AP oblique knee projection with medial rotation?
|
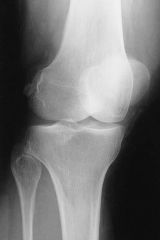
Medial oblique AP knee
Proximal Tibiofibular joint space open |
|
|
Which imaginary plane should be placed parallel to the IR for an AP projection of the knee?
|
Interepicondylar
|
|
|
How much should the knee be rotated internally for the AP knee projection?
|
3-5 degrees
|
|
|
How should the patella be demonstrated on a AP medially rotated OBL projection of the knee?
|
Around half of the patella should be seen free of superimposition ( same with lateral OBL projection)
|
|
|
If a patients ASIS to table measurement is 19-24 inches how should the CR be angled for an AP knee projection
|
Perpendicular
|
|
|
If a patients ASIS to table measurement is 25cm and above, how should the CR be angled for an AP knee projection.
|
5 degrees Cephalic
|
|
|
If a patients ASIS to table measurement is 18cm and below, how should the CR be angled for an AP knee projection.
|
5 degrees Caudal
|
|
|
How much should the knee be flexed for a true lateral projection?
|
20-30 degrees
|
|
|
How much should the CR be angled for a lateral knee projection? Where should the CR be placed?
How much should the knee be flexed? |
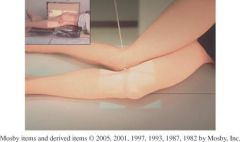
5 TO 7 degrees caphalad
1in. Distal to medial epicondyle True lateral, flexed 20-30° |
|
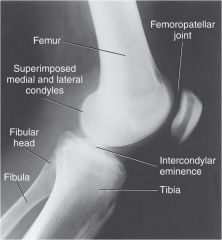
Describe what makes this projection a TRUE lateral knee?
|
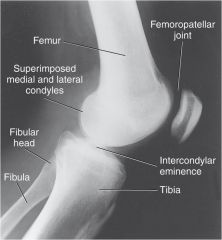
Femoral condyles superimposed
Patella in profile (indicates no rotation) Patellofemoral joint space open |
|
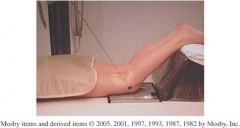
1.)What is the projection displayed above?
2.)How much should the knee be flexed for this projection? 3.)The CR should be perpendicular to what for this projection? |
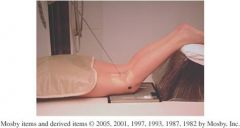
1.)*Camp Coventry, Intercondylar Fossa PA Axial knee
2.) 40 to 50 degree flexion of the knee 3.) The CR should be perpendicular to the lower leg |
|
|
For the Camp Coventry Projection, when the knee is flexed 40 degrees, the CR is angled _______ degrees. When the knee is flexed 50 degrees, the CR is angled ______ degrees.
|
40, 50
|
|
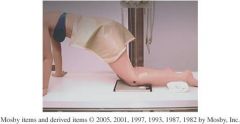
1.) What is the projection in the picture above?
2.)How many degrees should the patient lean forward for this projection 3.) What is the CR angle and position for this projection? |
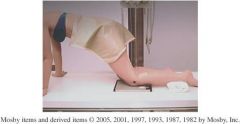
1.) Holmblad method
2.)20 to 30 degrees forward 3.) CR perpendicular to IR at midpopliteal crease |
|
|
When critiquing a lateral / medial OBL AP knee, how should the joint space appear.
|
The joint space should appear unequal
|
|
|
How much should the knee be flexed for a lateral patella.
|
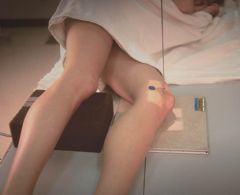
5 to 10 degrees
|
|
|
Name this projection.
Pt. prone 45° knee flexion CR 15-20° from long axis of lower leg at midfemoropatellar joint. |
Tangential (axial or sunrise/skyline) Patella
Hughston Method |
|
|
This projection can be performed using a wheelchair or lowered radiographic table.
|
Holmblad method (variation)
|
|
|
This projection requires 90 degrees knee flexion
|
Settegast method
|
|
|
Name this projection
- knee is flexed 40⁰ - 45 ⁰ -10 -15° angle from lower legs to be tangential to femoropatellar joint IR on mid-thigh, tilted to be perpendicular to x-ray beam |
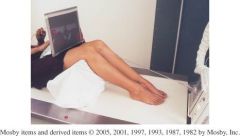
infrosuperior (Tangental, sunrise)
|
|
|
Name this projection
Prone My knee is flexed 40-50° 40-50° caudal angle, perpendicular to lower leg 40 ° flex = 40 ° cr angle |

Camp Coventry
(tunnel view, intercondylar fossa) |
|
|
Name this projection
My knee is flexed 45 ° I am prone The Cr is 15 to 20° from the long axis of the lower leg, to midfemoropatella joint I am a patella projection |
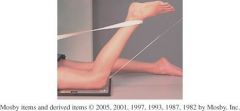
Hughston Method (Tangental)
|
|
|
I am supine
The IR is resting about 12 inches below the knee There is an apparatus usually used to hold the IR My knee is flexed 40 degrees |
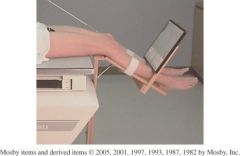
Merchant ( Tangental )
|
|
|
A young male patient comes to the radiology department with a clinical history of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Which single projection of the basic knee series will best demonstrate this condition?
|
Lateral knee projection
best demonstrates any separation of the tibial tuberosity from the shaft of the tibia |
|
|
A radiograph of a mediolateral knee projection demonstrates that the medial femoral condyle is projected inferior to the lateral condyle. What can the technologist do to correct this problem during the repeat exposure?
|
By angling the central ray 5 - 7 degrees cephalad, the medial femoral condyle will be superimposed with the lateral condyle.
|
|
|
A radiograph of the lateral patella reveals that the patella is drawn tightly against the intercondylar sulcus. Which position modification should be performed during the repeat?
|
decrease the amount of flexion of the knee
|
|
|
What is another term for the intercondyloid eminence?
|
intercondylar tubercles
|
|
|
which structures serve as shock absorbers within the knee joint
|
menisci
|
|
|
An AP knee radiograph reveals that the joint spaces are not equally open and the proximal fibula is superimposed over the tibia. Which specific positioning error lead to this radiographic outcome?
|
Lateral rotation of the lower limb
|
|
|
What are the 4 main ligaments of the knee joint?
|
Fibular lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
Tibial medial collateral ligament (MCL) Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) |
|
|
What are the two joints of the knee?
|
femorotibial joint
patellofemoral joint |
|
|
What is the classification of the knee joint
|
synovial
diarthrodial (freely movable) |
|
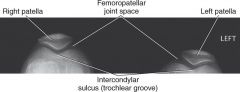
1.) Which projection is this?
2.) What criteria make this a good projection? |
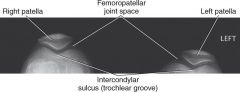
1.) Merchant bilateral Method
Tangential projection patella (axial or sunrise/skyline) 2.) Intercondylar sulcus and the patella are visualized with the femoropatellar joint space open. |
|
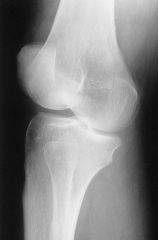
Is this a medial or lateral oblique knee? How can you tell?
|
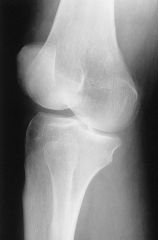
Lateral OBL knee
Fibula superimposed over midtibia |
|
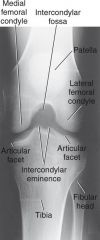
Which projection is demonstrated ?
Is this an acceptable image, why or why not? |
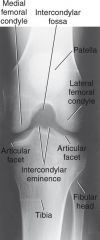
PA axial projection tunnel view knee
Yes it is acceptable because .. 1.) Intercondylar fossa in profile 2.)No rotation 3.)Articular facets and intercondylar eminence well visualized 4.)Optimal exposure factors |
|
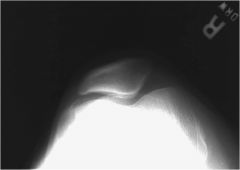
Overflexion of knee draws patella into _________________
|
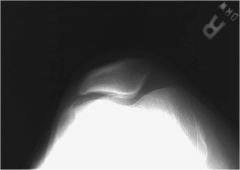
intercondylar sulcus.
|

