![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The TMJ is slightly _______ & ________ to our EAM.
|
The TMJ is slightly anterior & superior to our EAM
|
|
|
The TMJ is classified as a ______ joint
|
synovial
|
|
|
The TMJ has a _______ movement type similar to the knee.
|
bicondylar
|
|
|
The temporomandibular fossa is located on which cranial bone?
|
temporal
|
|
|
When the jaw opens, the ______ moves down and forward to the anterior aspect of the fossa.
|
condyle (head)
|
|
|
linear tomography can be performed for TMJ's, and for that the pt has to be in a _____ position.
|
lateral
|
|
|
Where is the CR placed for axiolateral TMJ's ?
|
1/2 inch anterior and 2 inches superior to upside EAM.
|
|
|
Where should the petrous ridges be for a partietoacanthial sinuses radiograph ?
|
below the maxillary sinuses
|
|
|
Where does the CR exit for parietoacanthial transoral sinuses.
|
acanthion
|
|
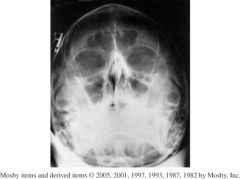
1.) Which Position ?
2.) How can rotation be assessed on this image ? 3.)How can you assess if the pt's neck extension is sufficient? |
1.) Parietoacanthial transoral (open-mouth Waters)
2.) Equal distance from the lateral orbital margin to the outer lateral skull on both sides. 3.)If the petrous ridges are below the maxillary sinuses. |
|
|
What is the ONLY modification between the pariteoacanthial sinuses projection and the pariteoacanthial transoral sinuses projection?
|
The jaw is dropped
|
|
|
For which sinuses projections does the OML form a 37 degree angle with the IR.
|
transoral open mouth waters and Parietoacanthial sinuses.
|
|
|
For sinuses, to visualize air-fluid levels, the CR must be _______ and the pt must be ______.
|
Horizontal
Erect |
|
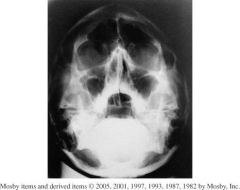
1. Which Projection is this?
2.) What structures(sinuses) should be shown? |
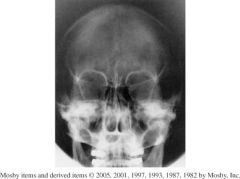
1.) PA Sinuses (Caldwell)
2.)Frontal Sinuses and Anterior Ethmoids (visualized lateral to each nasal bone) |
|
|
Where does the CR exit for PA Caldwell sinuses?
|
nasion
|
|
|
For SMV sinuses, if the CR is angled to be perpendicular with the IOML, will the air fluid levels still be visualized.
|
No, CR has to be horizontal.
|
|
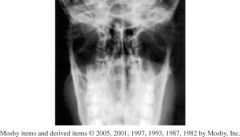
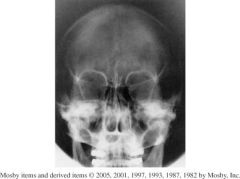
1.)Which Position?
2.)Which Structures should be shown in this image? 3.)How do you assess rotation for this image? |
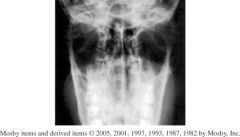
1.) AP axial TMJ's
2.) Condyloid process of the mandible and TM fossae. 3.) Condyloid processes should be visualized symmetrically, lateral to the cervical spine. |
|
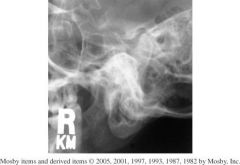
1.) Which Projection is this?
2.) Is the mouth open or closed in this projection? 3.) Which structures should be shown? 4.) How would you assess if this position is correct? |
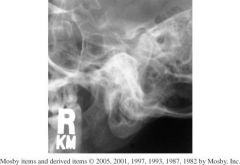
1.) Axiolateral Obl TMJ's
2.) Closed 3.) -TMJ nearest to the IR -Closed mouth image demonstrates condyle within the fossa. 4.) Correctly position image demonstrates TMJ free of superimposition of the opposite TMJ (15° rotation prevents this) & TMJ not superimposed by the cervical spine. |
|
|
paranasal sinuses are also called _______
|
accessory nasal sinuses
|
|
|
Only the _______ sinuses are part of the facial bone structure.
|
maxillary sinuses
|
|
|
Which sinus is present at birth?
|
Maxillary
|
|
|
which sinus develops last?
|
ethmoid
|
|
|
An older term for the maxillary sinuses?
|
Antrum (Antrum of Highmore)
|
|
|
Why is it important NOT to underexpose a sinuses projection.
|
Underexposure—can simulate pathologic conditions (false-positive)
|
|
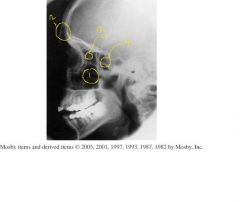
Label 1-4
5. Which Projection 6.) How would you asses tilt and rotation |
1.) Maxillary
2.) Frontal 3.) Ethmoid 4.) Spenhoid 5.) Lateral Sinuses projection 6.) Rotation-superimposed vertical structures like the rami or anterior and posterior clinoid processes. Tilt- superimposed horizontal structures like the orbital roofs and mandibular bodies. |
|
|
Where is the CR for axiolateral obl TMJ's.
|
1 1/2 inches superior to upside EAM
(to pass through downside TMJ) |
|
|
What is the CR angle for the axiolateral schuller method?
|
25° to 30° caudad
|
|
|
Which sinuses are seen within the mouth for a transoral open mouth waters?
|
Sphenoid
|
|
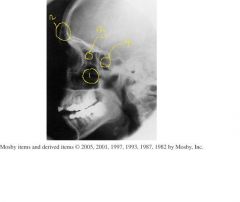
Identify 1-5
6.) Which Projection |
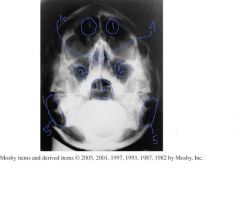
1.) Frontal sinuses
2.) Maxillary sinuses 3.) Sphenoid sinuses 4.) Ethmoid Sinuses 5.) Mastoid Air cells 6.) Transoral open mouth waters |
|
|
All paranasal sinus cavities communicate with one another and with the _________.
|
nasal cavity
|
|
|
T/F
The frontal sinuses are usually symmetric in shape. |
False
The frontal sinuses are rarely symmetric |
|
|
Which sinus is contained within the lateral masses.
|
Ethmoid sinuses
|
|
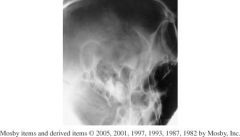
1.) Which Projection ?
2.) Which structures should be shown? 3.) How can you assess for rotation? 4.) Is the jaw open or closed? |
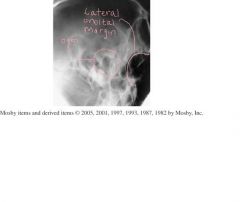
1.) Axiolateral Schuller TMJ
2.) TMJ nearest IR 3.) Rotation can be assessed using the superimposed lateral orbital margin. 4.)open mouth |
|
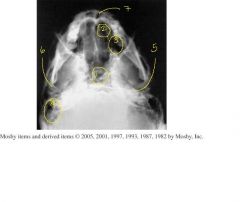
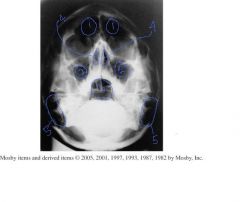
Label 1-7
8.) Which Projection? 9.) How do you know if the IOML was parallel to the IR for this image? 10.) How would you assess rotation and tilt? |
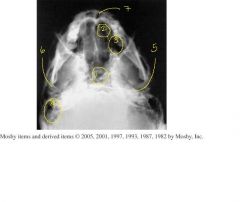
1.) Sphenoid sinuses
2.) Ethmoid sinuses 3.) Maxillary sinuses 4.) Mastoid Air cells 5.) Petrous ridges 6.) Mandibular condyle 7.) Nasal Fossa 8.) SMV sinuses projection 9.) IOML relationship is correct if mandibular condyles are anterior to petrous pyramids. 10.) Rotation and Tilt - petrous pyramids are visualized symmetrically. |
|
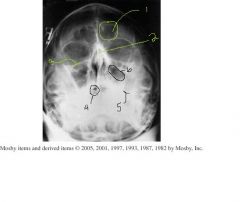
label 1-6
7.) Which Projection? 8.)How would you assess rotation? 9.) Where should this image be centered? |
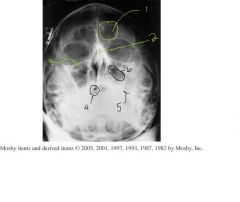
1.) Frontal sinus
2.) Bony nasal septum 3.) inferior orbital rim 4.) Sphenoid sinus 5.) Petrous ridge 6.) Maxillary sinus 7.) Pariteoacanthial waters projection 8.) Rotation can be assessed by equal distance from the lateral orbital margin to the lateral border of the skull. 9.) Centered to the acanthion. |
|
|
What is the CR angle for the Axiolateral OBL TMJ
|
15 caudad
|
|
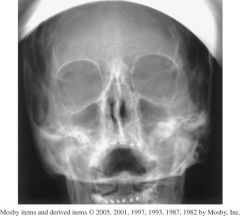
Assess this image based on positioning, collimation, and CR.
|
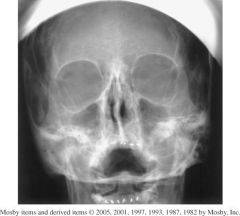
1.) Skull is underextended because the petrous ridges are within the maxillary sinuses.
- Tilted to PT right as evidenced by the unsymmetrical petrous ridges. 2. Collimation can come in on the sides. 3. The CR is too high, the maxillary sinuses should be centered. |
|
|
If the pt cannot stand for a lateral projection of the paranasal sinuses, it should be taken with ______
|
horizontal x-ray beam
|
|
|
which sinus is best demonstrated with a parietoacanthial waters projection
|
Maxillary
|
|
|
Which paranasal sinuses are best demonstrated with an SMV projection.
|
Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Maxillary
|
|
|
A radiograph of an SMV sinuses reveals that the distance between the mandibular condyles and lateral border of the skull is not equal. What is the positioning error
|
Tilt
|
|
|
A PA transoral projection reveals that the sphenoid sinus is superimposed over the upper teeth and nasal cavity, how do you fix this?
|
increase extension of the head and neck to projection the entire sphenoid sinus through the oral cavity.
|
|
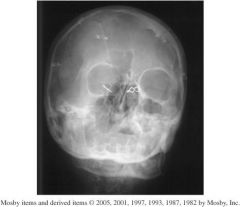
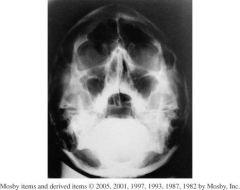
1.) Which Projection is this?
2.) What structures should be shown? 3.) Assess Positioning, Collimation, and CR. |
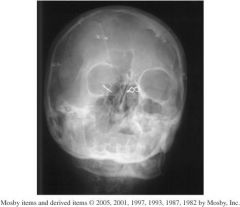
1.) Parietoacanthial waters projection
2.) Maxillary sinuses free of superimposition 3.)-Petrous ridges are projected into the lower aspect of the maxillary sinuses, so the skull is underextended. -The distance from the right lateral orbital margin and the lateral skull is not symmetrical on both sides indicating severe rotation. - No collimation is evident at all, cervical spine is present. -Centering is slightly low. -Pins blocking anatomy - No marker |
|
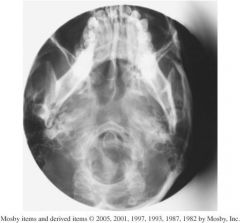
1.) Which projection?
2.) Structures shown? 3.) Assess this image according to positioning, collimation and CR? |
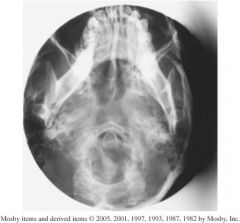
1.) SMV sinuses
2.) Sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary sinuses should be visualized, however the mandible is obstructing sinuses. 3.)- Mandibular condyles are not anterior to petrous ridges indicating correct IOML relationship was not obtained. - Petrous pyramids are not symmetrical so image is rotated. -distance from mandibular border to lateral border of skull on both sides is not the same. - collimation would be okay if the image was centered. - CR centering is off laterally which led to anatomy being cut off. |
|
|
T/F
The frontal sinuses are normally larger in men than women. |
True
|
|
|
T/F
The modified law method requires a tube angulation of 25 degrees caudad. |
False.
15° |
|
|
For a lateral sinuses projection if the greater wings of the sphenoid bone are not superimposed what positioning error has occured?
|
rotation
|
|
|
All of the paranasal sinuses are completely developed by _______.
|
late teens
|
|
|
5 functions of the paranasal sinuses are :
|
1.Resonating chamber for voice
2.Decrease weight of skull 3.Warm and moisten inhaled air 4.Acts as shock absorber during trauma 5.Possibly control immune system |
|
|
Which sinuses are like fingerprints?
|
frontal
|
|
|
Which sinuses are hardest to demonstrate?
|
Sphenoid
|
|
|
True or False
Mastoid air cells are part of the osteomeatal complex |
False
|

