![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The study of the movement of the body parts; also known as ___
|
Kinesology
- body mechanics |
|
|
One of the most common injuries for health care workers are ___ and ___
|
- lower back strain
- back injuries |
|
|
Body Movement and Alignment for Patients
- the 2 basic principles - 3 patient hazards of improper alignment |
Principles:
- maintain correct anatomic position of the patient - change patient's position frequently (every 2 hours) Patient Hazards: - pressure ulcers - muscle cramps / contractures - fluid collection in lungs |
|
|
Pressure Ulcers
- ___ occur from pressure on the skin, causing ___ - ___ is the local death of tissue from disease or injury - pressure ulcers are the area between a ___ and external surface - ___ is applied force causing the downward and forward pressure on tissue beneath the skin ( give ex) |
- decubitus ulcers / bedsores , tissue necrosis
- tissue necrosis - bony prominence - shearing force (ex: pulling bed clothes from underneath the patient) |
|
|
The 3 major factors of body mechanics
|
- center of gravity
- base of support - line of gravity |
|
|
Center of one's own weight; half of one's body weight is below and half above, half is to the left, and half is to the right
|
Center of Gravity
|
|
|
Balance or stability provided by the feet and their positioning
|
Base of Support
|
|
|
Direction of gravitational pull; imaginary vertical line through the top of the head, center of gravity, and base of support
|
Line of Gravity
|
|
|
The position when the patient is lying flat on his back; pillows placed under ___ and ___
|
Supine Position
- head and arms |
|
|
Variations of Supine Positions
- ___ elevate HOB 60 degrees; pillows placed under ___ and ___ - ___ elevate HOB 30 degrees; pillows placed under ___ and ___ - ___ elevate HOB 15 degrees; knees are elevated at 15 degrees - these positions improve ___ and ___ and promote ___ and ___ eliminiation |
- Fowler's (60); head and arms
- Semi-Fowler's (30); head and arms - Low-Fowler's (15) - cardiac output / respirations and urinary / bowel elimination |
|
|
Positions
- ___ patient rests on side (alleviates pressure on ___, puts weight on dependent shoulder and hip) - ___ a variation of side position (used for ___, ___, ___); pillows placed under ___ and ___ - ___ patient is lying face down ( good for ___ injury); pillows placed under ___, ___, and ___ - ___ patient is face down, head turned to side, chest, elbows and knees rest on bed and thighs are perpendicular to the bed |
- Side Lying / Lateral: bony prominence
- Sims: rectal exams, enemas, suppositories; head and turned leg - Prone: spinal cord injury; head lower abdomen, feet - Knee-Chest |
|
|
Positions
- ___ patient lies flat in his back with knees fixed and soles of feet flat on the bed; pillow placed under ___ - ___ used for examination of the pelvic organs |
- Dorsal Recumbant; head
- Dorsal Lithotomy |
|
|
A positioning device that helps prevent external rotation of hips and legs
|
Trocanter Roll
|
|
|
Moving a Patient Up in Bed
1.) ___ turning the patient as a single unit while maintaining straight body alignment at all times - gives NA's ability to ___ - takes ___ NA's 2.) ___ is used for patients who independently preform ADL's, but for some reason are immobilized or limited in activity 3.) ___ preformed in patients who cannot actively move - always ___ the part that you are doing the ROM on |
- 1.) Logrolling
- change soiled linens - 2.) Active ROM - 3.) Passive ROM - support |
|
|
Lifting and Transferring
- requires the use of ___ - before tranferring the patient, sit the patient up in bed and allow patient to ___ - ___ people should transfer the patient from bed to wheelchair if patient is unsteady, weak, or heavy - ___ requires less effort than pushing or lifting |
- proper body mechanics
- dangle legs - 2 people - pulling |
|
|
Lifiting and Transferring
~ transferring a patient from a bed to a stretcher - ___ and ___ people are transported on stretchers - takes ___ people - 5 transferring devices |
- critically ill , comatose
- 4 people - draw sheet, mechanical lift, gait belt, roller board, slide bar |
|
|
Safe Transferring
- patients who have been in bed for a long period of time may develop ___ |
- orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
Logrolling
- turn the patient as a ___ - ___ maintained at all times - used to change ___, can be preformed with or w/o a ___ - requires ___ people if patient cannot turn himself - leave a pillow under the patient's ___ |
- single unit
- body alignment - bed linen , lift sheet - 2 people - head |
|
|
Safe Lifting
- bending at the ___ and ___ lets the string muscles of the ___ do the lifting and prevents back strain |
- hips
- knees - legs |
|
|
Positioning the Patient in Bed
- a ___ is always applied over clothing - always move patient's towards their ___ side - use a ___ when the patient is unable to assist with the transfer process |
- transfer / gait belt
- stronger - mechanical lift |
|
|
Walking Aids
- 1.) Canes: hold on ___ side; use ___ leg - 2.) Walkers: use ___ side; use ___ leg - 3.) Crutches: go up the stairs with ___ leg, and down the stairs with ___ leg |
- 1.) Canes: strong side , unaffected leg
- 2.) Walkers: weak side , affected leg - 3.) Crutches: up w/ unaffected (good) leg , down w/ affected (bad) leg |
|
|
Range of Motion (ROM)
- Abduction - Adduction - Internal Rotation - External Rotation - Flexion - Extension |
- Abduction: away from midline
- Adduction: towards midline - Internal Rotation: towards midline - External Rotation: away from midline - Flexion: bend at elbow - Extension: flatten forearem |
|
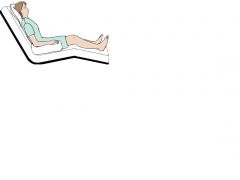
|
Fowler's Position
|
|
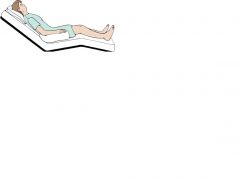
|
Semi-Fowler's Position
|
|
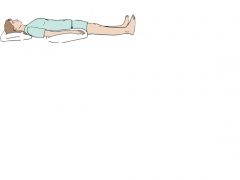
|
Supine Position
|
|
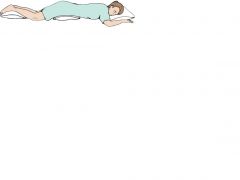
|
Prone Position
|
|
|
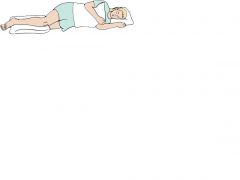
Side-Lying Position
|
|
|
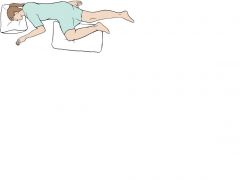
Sims Position
|
|
|
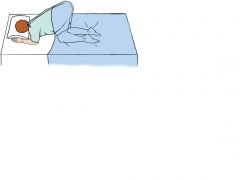
Knee-Chest Position
|
|
|
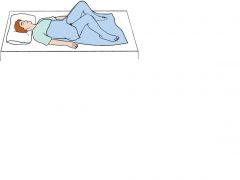
Dorsal Recumbant Position
|
|
|
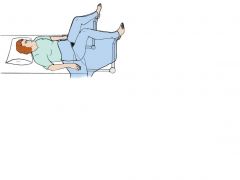
Dorsal Lithotomy Position
|

