![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osteoblasts and osteocytes are derived from what type of stem cell? What type of stem cell are osteoclasts derived from ? |
Mesenchymal stem cell Haematopoietic stem cells |
|
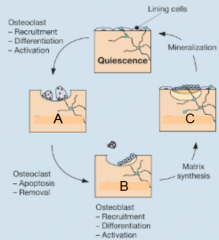
Label the missing stages in bone remodeling? |
A: resorption B: reversal C: formation |
|
|
How long does the remodeling phase last for? |
about 6 months |
|
|
How long does the resorption phase last for? |
about 10-14 days |
|
|
How long does the formation phase last for? |
about 150 days (5 months) |
|
|
Which enzyme is abundant within osteoclasts and is frequently used as a biomarker of bone metabolism? |
Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP) |
|
|
Which are the main cells involved in bone metabolism which express osteprotegerin? |
osteoblasts and bone marrow stromal cells |
|
|
What is the function of PU.1 |
Transcription factor required for the differentiation of early osteoclast precursors from haematopoietic cells |
|
|
What shared function do the following have: Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF) c-fos Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NFkB) Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (RANK) RANK Ligand (RANKL) |
Promote the differentiation of committed osteoclast precursors into mature osteoclasts. |
|
|
What is the role of osteoprotegerin in bone metabolism |
inhibits osteoclast formation and activity by binding to RANK-L - an activator of RANK. |
|
|
Name two substances which osteoclasts use to resorp bone. What respective functions do each of these substances have? |
hydrochloric acid and proteolytic enzymes hydrochloric acid degrades hydroxyapatite, allowing proteolytic enzymes to degrade collagen and other bone matric proteins. |

