![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Each triplet specifies only one amino acid |
Unambiguous |
|
|
A given amino acid can't be specified by more than one triplet codon |
Degenerate |
|
|
Once translation begins, condos are read with no break |
Commaless |
|
|
Any single ribonucleotide within a mRNA is part of one triplet |
Nonoverlapping |
|
|
Sequence of codons in a gene is... |
Colinear |
|
|
A single coding dictionary is used by viruses, prokaryotes, archaea, and eukaryotes |
Nearly universal |
|
|
Serves as intermediate in transferring genetic information from DNA to proteins |
mRNA |
|
|
Where is genetic information stored? |
DNA |
|
|
Where is the code located that translates DNA to protein? |
RNA |
|
|
Provide 64 codons to specify 20 amino acids |
Triplet code |
|
|
Continuous sequence of nucleotides |
Reading frame |
|
|
Insertions or deletions shift reading frame and change codons downstream |
Frame shift mutation |
|
|
What was revealed by frameshift mutations? |
Triplet nature codon |
|

|
Frameshift mutation |
|
|
Genetic code reads three nucleotides at a time in a continuance, linear manner |
Nonoverlapping |
|
|
During translation, genetic code is... |
Nonoverlapping |
|
|
The genetic code is… |
Degenerate |
|
|
What are encoded by a single codon? |
Tryptophan and methionine |
|
|
Genetic code shows order |
Chemically similar amino acid share one or two little bases in triplets coding them |
|
|
The initial two ribonucleotide so triplet codons are often more critical than the third |
Wobble hypothesis |
|

Less special constraint. Need not adhere strictly to established base pairing rules |
Third position |
|
|
Initiator codon. Initial amino acid incorporated into all proteins |
Methionine or AUG |
|
|
And bacteria: modified form of methionine |
N-formylmethionine (fmet) |
|
|
Only codon to encode methionine |
AUG |
|
|
Termination codons are |
UAG, UAA, UGA |
|
|
Do not code for any amino acid. Are not recognized by transfer RNA |
Termination codon |
|
|
Translation terminates when … |
These codons are encountered |
|
|
Mutation that produces a stop codon internally in gene. Translation is terminated. Partial polypeptide is produced. |
Nonsense mutations |
|
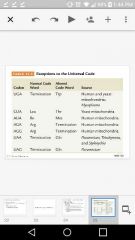
Revealed exceptions to universal genetic code |
Mitochondrial DNA |
|
|
What codon normally specifies termination ? Explain. |
UGA. mtDNA codon encodes tryptophan in yeast and in humans |
|
|
What Codar normally specifies isoleucine? Explain. |
AUA . Human mitochondria encodes internal insertion of methionine |
|
|
An alteration in DNA sequence Any base-pair change in sequence Single base pair substitution Deletion or insertion of base pairs Major alteration in chromosomal structure |
Mutation |
|
|
Change from one base pair to another |
Point mutation or base substitution |
|
|
Results in new triplet code for different amino acid |
Missense mutation |
|
|
Results in new triplet code for different amino acid |
Nonsense mutation |
|
|
New triplet code still codes for same amino acid |
Silent mutation |

