![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Etruscan Temple (Reconstruction) • Based on writings of Vitruvius • Tuscan order- variation of Doric order with unfluted shaft & simplified base, capital, and entablature |
|
|
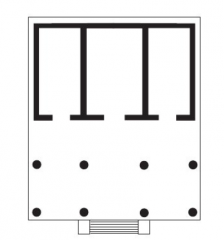
Plan of an Etruscan Temple • Almost even division between porch and interior space • Interior space separated into three rooms (probably housed cult statues) |
|

|
Dancers and Diners (Tomb of the Triclinium) Tarquinia, Italy 480–470 BCE • Colorful geometric decoration • Women AND men • Engaged in joyful customs & diversions of human life |
|

|
Tomb of Reliefs (Burial Chamber) Cerveteri, Italy 3rd century BCE • carved out of rock to resemble rooms in a house • Fully furnished • Extremely detailed |
|

|
Sarcophagus from Cerveteri c. 520 BCE • Husband and wife reclining • Lively, alert, warm eyes • Man once raised cup. Engaging gesture, genial host, invitation |
|

|
Portrait Head of an Elder c. 80 BCE • Time-worn faces embody wisdom & experience • Think portraits actually conform to particularly Roman idealization |
|

|
Denarius (w/ Portrait of Julius Caesar) 44 BCE • Propaganda • widely circulated coin • First Roman leader to place his own image on a coin (adopted by his successors) • "Caesar, dictator forever." |
|

|
Augustus of Primaporta Early 1st century CE Livia's villa at Primaporta, near Rome • See emperor as he wanted to be remembered • Portraiture for propaganda • Always young portrayals |
|

|
Gemma Augustea Early 1st century CE • Glorifies Augustus as triumphant over barbarians • Deified emperor • Assumed identity of Jupiter (king of the gods) • Personification of Rome with Livia's features • Dramatic action (Hellenistic) + Attention to descriptive detail & historic specificity (Roman) |
|
|
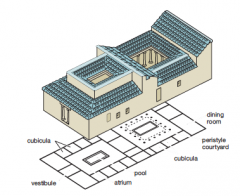
House of the Silver Wedding (Plan & Reconstruction Drawing) Pompeii 1st century CE • Small rooms laid out around 1 or 2 open courts, the atrium and the peristyle • Peristyle turned into outdoor living room |
|

|
Cityscape (House of Publius Fannius Synistor Boscoreale 50-30 BCE • Wall painting from a bedroom • Urban panorama • Intuitive perception- architectural details follow diagonal lines that the eye interpretsas parallel lines receding into the distance |
|

|
Still Life (House of the Stags) Before 79 CE Detail of a wall painting • Herculaneum- community near Mt. Vesuvius • Carefully arranged for clarity & balance |
|

|
The Arch of Titus Rome 81 CE • Erected by his brother Domitian • iconic combined with Corinthian • Mixing historical & mythological |
|
|
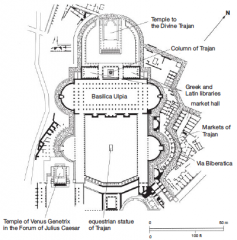
Trajan's Forum & Market 110-113 CE • Apollodorus of Damascus- military engineer • Basilica Ulpia- adaptable space for variety of administrative governmental functions -court of law -grand interior |
|

|
Trajan's Market Rome 100-112 CE • Commercial district (Shopping Mall) - had to make up for space that was • 150 individual shops |
|
|
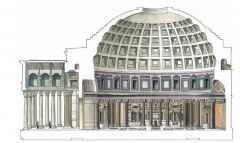
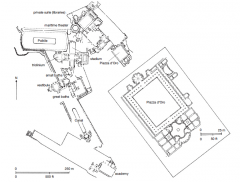
Pantheon (Reconstruction drawing) Rome 118–128 CE • Temple to Olympian gods • Hadrian's reign -gave credit to Agrippa who built on site |
|

|
Dome of the Pantheon • Dome was physical representation of the Universe - Oculus for natural light & elements to get in • More than half of the decoration still survives |
|
|
Hadrian's Villa Tivoli 125–135 CE • Half a square mile • Natural land formation and attractive views • Recreated favorite places throughout the empire |
|

|
Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius 176 CE Gilded Bronze • Dressed as a military commander • Mistaken as statue of Constantine (first Christian emperor • Trampled a crouching barbarian |
|

|
Portrait of a Tetrarch (Galerius?) Early 4th century CE • Radically new, hard style of geometric abstraction • Startlingly alert with searing eyes • Antithesis of Classicism • No clear sense of likeness • Individual is less significant than the powerful position he holds |
|

|
Audience Hall of Constantius Chlorus (Basilica) Trier, Germany Early 4th century CE • Centrally heated with hot air flowing under floor • Smaller windows made enthroned tetrarch appear larger than life & hall would seem longer than it really was |
|

|
Audience Hall of Constantius Chlorus (Basilica) Trier, Germany Early 4th century CE • Strong directional focus • No-nonsense, imposing buildings meant to impress subjects |
|

|
Arch of Constantine Rome 312–315 CE (dedicated July 25, 315) • Constantine's victory over Maxentius • Recycled sculpture -relief panels taken from monument celebrating victory of Marcus Aurelius over Germans -Trajan's conquest of Dacia -Tondi taken from monument to Hadrian |
|
|
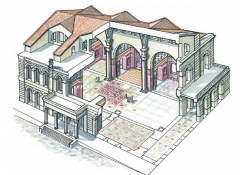
Basilica of Maxentius & Constantine (Basilica Nova) Rome • Constantine sought to impress people with visual symbols of authority -Put his own stamp on projects Maxentius started |
|

|
Constantine the Great Basilica of Maxentius & Constantine, Rome 325–326 CE • 30 foot statue placed inside apse • Permanent stand-in for emperor when conduct of business legally required his presence • Head combined Roman portraiture with abstract qualities from tetrarchs |
|

|
Platter Mildenhall, England Mid 4th century CE • Pagan imagery • Artists working for Christian patronscontinued to use themes involving Bacchus • Create elaborate figural compositions displaying nude or lightly draped human body in complex poses |
|

|
David Battling Goliath made in Constantinople 629–630 CE • One of "David's Plates" • David in halo as "good guy" • Classical personification of the stream that is the source of David's stones • Consummates victory by severing head |
|

|
Church of Santa Sabina Rome c. 422–432 • Constructed by Peter of Illyria • Basic elements of Early Christian basilica • Exterior is simple brick; interior is marble veneer |
|

|
Church of Santa Costanza Rome c. 350 • Mausoleum of Constantina (daughter of Constantine); Sanctified after her death • Tall rotunda with encircling barrel-vaulted passageway (ambulatory) • Covered in mosaics and veneers of marble |
|

|
Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus Grottoes of St. Peter, Vatican, Rome. c. 359 • Roman official who was newly baptized and died at age 42 • Center is a triumphant Christ -Appears as a Roman emperor, distributing legal authority -Resting feet on pagan god Coelus • Earthly Jesus makes histriumphal entry into Jerusalem, like a Roman emperor entering aconquered city. |
|

|
Oratory of Galla Placidia Ravenna c. 425–426 • Simulate passage from real world to supernatural realm • Brilliant mosaics • Filled with figures of standing apostles • Fountain represents eternal life in heaven |
|

|
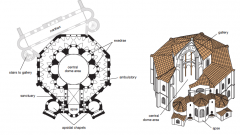
Church of Hagia Sophia Instanbul 532–537 • Body of original church now surrounded by later additions • Museum today • Nika Revolt in 532 burned down original structure • Embodied imperial power and Christian glory |
|
|
Church of Hagia Sophia Instanbul 532–537 • Longitudinal & central architectural planning • Pendentives (triangular curving vault sections) |
|

|
The Kaaba, Mecca • Represents center of Islamic world • Draped with black textile embroidered with Qur'anic verses in gold • Built for God by Abraham & Ishmael • Focus of pilgrimage & polytheistic worship • Emptied of pagan idols by Muhammed |
|

|
Dome of the Rock Jerusalem 691-692 • Islams view of itself as completing the prophecies of those faithsand superseding them • Golden dome supported by alternating piers and columns • 3rd most holy site in Islam • Where the patriarch Abraham prepared tosacrifice his son Isaac at the command of God • Byzantine tradition |
|

|
Great Mosque Kairouan, Tunisia 836–875 • Reflects the early form of themosque but is elaborated with later additions • Hypostyleprayer hall oriented toward Mecca •Repeated bays andaisles can easily be extended as the congregation grows in size |
|

|
Minbar Kutubiya Mosque, Marrakesh, Morocco 1125–1130 • Staircase where weekly sermon was delivered |
|

|
Qibla Wall w/ Mihrab & Minbar Sultan Hasan Madrasa-Mausoleum-Mosque Complex, Cairo 1356–1363 • Displayed piety, personal wealth & status • 4-iwan plan, each serving as a classroom for different branch of study • Students housed in multi-story cluster of tiny rooms around each iwan • Qibla served as a prayer hall |
|

|
Bowl with Kufic Border Khurasan 11th–12th century • White ground imitated prized Chinese porcelains • City connected to Silk Road, influenced by Chinese culture • Appeals to educated patron |
|

|
Shroud of St. Josse Khurasan or Central Asia Before 961 • Cloth for court as well as official gifts & payments • Good wishes common in Islamic art • Personalized for patron |
|

|
Arabic Manuscript Page Iraq 1199 • Naskhi- said to have been revealed & taught to scribes in a vision • Flowing lines alternate with eastern variety of Kufic • Surge in book production & increasingly elaborate & decorated cursive |
|

|
The Caliph Harun Al-Rashid Visits the Turkish Bath Afghanistan 1494 • Khamsa (5 poems) of Nizami |
|

|
Mosque of Sultan Selim Edirne, Turkey 1568–1575 • Minarets • Larger than the dome of Hagia |
|
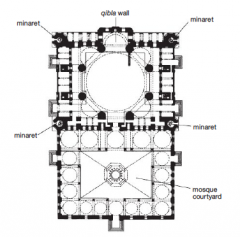
|
Mosque of Sultan Selim Edirne, Turkey 1568–1575 • Minarets • Larger than the dome of Hagia |
|

|
Illuminated Tugra of Sultan Suleyman Instanbul, Turkey 1555–1560 • Calligraphy put to political use • Document endowing an institution in Jerusalem established by Suleyman's powerful wife, Hurrem |
|
|
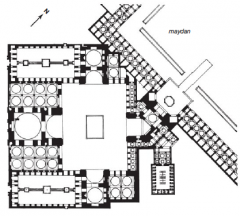
Masjid-I Shah (Plan) Isfahan • 4 iwan plan • Culmination of Timurid aesthetics w/ unprecedented scale in urban setting |
|

|
Masjid-I Shah Isfahan 1611–1638 • Domes made royal patronage seen through the city • 4 iwans face onto courtyard, 5th faces maydan |

