![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Solid
|
3-D Figures
The union of al pints on a simple closed surface and all pints in its interior |
|
|
Polyhedron
|
a simple closed surfaced formed by planar polygonal regions
|
|
|
Face
|
Each polygonal region
|
|
|
Vertices and Edges
|
the vertices and edges of the polygonal regions
|
|
|
Transformational Geometry
|
The study of manipulating objects by flipping, twisting, turing and scaling them.
|
|
|
Translation
|
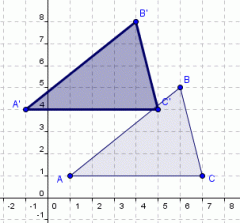
a transformation that slides an object a fixed distance in a given direction
|
|
|
Rotation
|
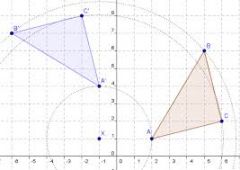
Transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point called the center of rotation
|
|
|
Reflection
|
Objects have the same shape and size but the figures face in opposite directions over a line of reflection
|
|
|
line of reflection
|
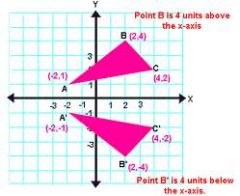
-The line where you can imagine a mirror placed
-the distance from a point to the line of reflection is the same distance from the points image to the line of reflection |
|
|
Glide Reflection
|
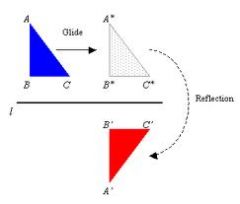
a combination of a reflection and a translation
|
|
|
Dilation
|
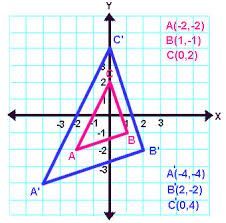
A transformation that shrinks an object or makes it bigger.
|
|
|
Tessellation
|
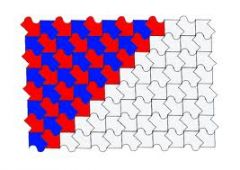
An arrangement of closed shapes that completely covers a plane without overlapping or leaving gaps.
|
|
|
Net
|
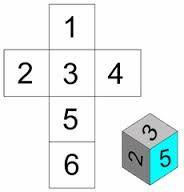
a 2-D figure that can be cut out and folded up to make a 3-D solid
|
|
|
Measurement (Length) conversions
|
Inches, Feet, Yards, Miles
12 inches=1 foot 36 inches=1 yard 3 feet= one yard 5,280 feet= 1 mile 1760 yards=1 mile |
|
|
Measurement (Weight) conversions
|
Ounces, pounds, tons
16 ounces= 1 pound 2000 pounds= 1 ton |
|
|
Measurement (Capacity) conversions
|
Fluid Ounces, Cups, Pints, Quarts, Gallons
8 fluid ounces= 1 cup 2 cups= 1 pint 4 cups= 1 quart 2 pints= 1 quart 4 quarts= 1 gallon |
|
|
Metric Units
|
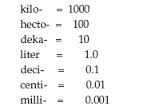
K H D U D C M
|
|
|
Square units
|
1 square foot= 144 square inches
1 square yard=9 square feet 1 square yard= 1296 square inches |
|
|
Circumference
|
The distance around a circle
C=2*pi*r or C=pi*d |
|
|
Area of a Circle
|
A= pi*r^2
area=pi*r squared |
|
|
Lateral Area
|
the area of the faces excluding the base
|
|
|
surface area
|
total area of all the faces including the base
|
|
|
volume
|
the number of cubic units in a solid,the amount of space a figure holds
|
|
|
Right Prisim
|
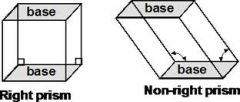
Volume=Bh
where B is the area of the base of the prism and h is the heigh of the prism. |
|
|
Rectangular Right Prism
Formulas |
S=2(lw+hw+lh)
V= lwh |
|
|
Regular Pyramid for volume
|
V=1/3 Bh
|
|
|
Right Circular Cylinder
Surface Area Volume |
S=2*pi*r (r+h)
V= pi*rsquared*h |
|
|
Right Circular Cone
|
V=1/3 Bh
|
|
|
Solving for rates:
|
1)write equation
2) multiply each term by the LCD of all fractions 3) this will cancel out all of the denominators and give an algebraic equation to be solved ex: Elly can feed animals in 10 min Jethro can feed them in 10 minutes, how long will it take them to feed them together? Elly can feel 1/15 of them in one min 2/15 in 2 min... x/15 in x minutes Equation: x/15 +x/10=1 (one job) -multiply by LCD of 30 and get 2x+3x=30 |
|
|
Adjacent Angles
|
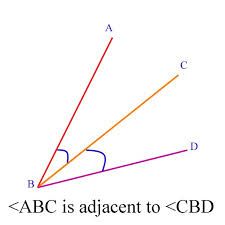
have common vertex and one common side but not interior points in common
|
|
|
Complementary Angles
|
add up to 90 degrees
|
|
|
Supplementary angles
|
add up to 180 degrees
|
|
|
Vertical angles
|
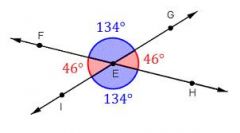
have sides that form two pairs of opposite rays
|
|
|
Corresponding angles
|
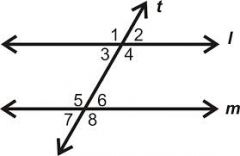
are in the same corresponding position on two parallel line cut by transversal
|
|
|
Alternate interior angles
|
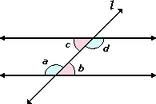
are diagonal angles on the inside of two parallel lines cut by a transferal
|
|
|
To make a circle graph/pie chart:
|
1)total all the information that is to be included
2)determine the central angle to be used for each sector of the graph using information/total information x 360=degrees in central angel |
|
|
Dependent event
|
the probability of the second event depends on the first event
ex: it is sunny on saturday /you go to the beach |
|
|
Odds
|
ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of unfavorable outcomes
|
|
|
sample space
|
list of all possible outcomes of an experiment
ex: tossing two coins : (HH, HT, TT, TH,) |
|
|
Fundamental counting principle
|
if there are (m) possible outcomes for one task and (n) possible outcomes for another task then there are
(m x n) outcomes all together. |
|
|
permutation
|
the number of possible arrangements of items without repetition where order is important
|
|
|
combination
|
the number of possible arrangements, without repetition where order of selection is not important
|
|
|
addition counting principle for of counting for mutually exclusive events
|
if A and B are mutually exclusive events
n (AorB)= n (A) + n(B) |

