![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Path of filtrate through nephron
|
Bowman's capsule → glomerulus → proximal convoluted tubule → descending limb → loop of Henle → ascending limb → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct/ system
|
|
|
|
blood vessels and nerves enter the kidney at?
|
hilum
|
|
|
|
what is the cortical tissue located between the renal pyramids?
|
renal columns
|
|
|
|
an obstruction in the afferent arteriole would result in?
|
lower rate of GFR, decrease pressure in glomerular capillaries
|
|
|
|
The openings of the urethra and the two ureters mark an area on the internal surface of the urinary bladder called the
|
trigone
|
|
|
|
Under normal circumstances virtually all the glucose, amino acids, and other nutrients are reabsorbed before the filtrate leaves the
|
proximal convoluted tube
|
|
|
|
pyretic acid
|
the end product of anaerobic glycolysis
|
|
|
|
the coronal plan is also known as the
|
frontal plane
|
|
|
|
when H2o combine hydrogen
|
becomes weakly positive
|
|
|
|
when H2o combine oxygen
|
forms a stable atom, and its electronegativity remains the same
|
|
|
|
water is
|
polar
|
|
|
|
tendon
|
connects muscle to bone
|
|
|
|
ligament
|
connects bone to bone
|
|
|
|
aponeurosis
|
broad sheetlike tendon that connects muscle to muscle or bone
|
|
|
|
fascicle
|
bundle of muscle or nerve cells surrounded by a connective tissue membrane
|
|
|
|
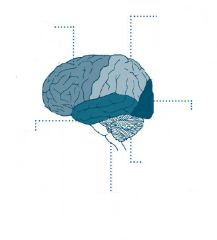
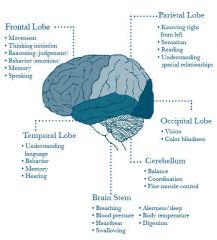
regulation of emotions is done by the
|
hypothalamus and limbic system
|
|
|
|
corpus callosum
|
carries information between right and left cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
|
brain functions depend on
|
adequate blood supply
|
|
|
|
abstract though is controlled by
|
cerebral cortex
|
|
|
|
autonomic function is associated with
|
brain stem activity
|
|
|
|
ADH is also known as
|
vasopressin
|
|
|
|
ADH action on the body
|
The hypothalamus sends a message to the pituitary gland which releases ADH. This travels in the blood to your kidneys and affects the tubules so more water is reabsorbed into your blood. As a result you make a smaller volume of more concentrated urine.
|
|
|
|
which ability would be impaired by damage to hair cells at the basal end of the cochlea?
|
hearing high frequency sounds, it is narrower and stiffer
|
|
|
|
which ability would be impaired by damage to hair cells at the apex of the cochlea?
|
low frequency sounds, it is wider and more flexible
|
|
|
|
Discriminating the direction of sound is done by
|
the temporal lobes of the brain
|
|
|
|
Loudness is dependent upon
|
sound intensity, the greater the sound, the greater the vibration of the basilar membrane which has greater nerve impulses to the brain
|
|
|
|
what compensatory response is likely to occur when the blood calcium level is low?
|
Osteoclast activity will be greater, fecal/urine calcium will be lower than normal
|
|
|
|
when does ejection of blood from he ventricles occur during an ECG?
|
between the QRS and T wave
|
|
|
|
the QRS wave reflects
|
the spread of the impulse though the ventricles forcing the blood into the aorta and pulmonary artery
|
|
|
|
the P wave reflects
|
the spread of an electrical impulse through the atria and their contraction, the beginning of the next cardiac cycle
|
|
|
|
the T wave represents
|
depolarization of the electrical tissue, right after the T wave the heart is at rest
|
|
|
|
in early atrial diastole
|
the atria are filling with blood
|
|
|
|
atrial systole
|
contraction of atria, forcing remaining blood into ventricles
|
|
|
|
in early ventricular diastole
|
the ventricles are receiving blood from the atria
|
|
|
|
in ventricular systole
|
the ventricles contract and force blood into aorta and pulmonary artery
|
|
|
|
in a normal heart, what decreases cardiac output?
|
increased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
|
|
|
|
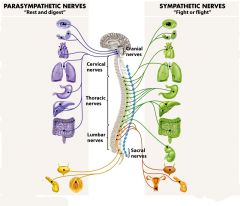
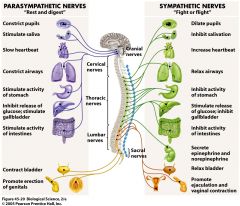
the parasympathetic nervous system has an
|
inhibitory effect on cardiac function
|
|
|
|
an increased stroke volume
|
increases the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle
|
|
|
|
as more blood returns to the heart
|
more blood is ejected
|
|
|
|
beta cells of the pancreas produce
|
insulin
|
|
|
|
alpha cells of the pancreas produce
|
glucagon, which raises blood sugar
|
|
|
|
delta cells secrete
|
somatostatin, which inhibits the secretion of insulin and glucagon
|
|
|
|
F Cells secrete
|
hormones which regulate the release of pancreatic digestive enzymes
|
|
|
|
Why does stimulating the sympathetic nervous system increase arterial BP?
|
cardiac output and total peripheral resistance both increase
|
|
|
|
The sympathetic nervous system releases what to stimulate cardiac output and vasoconstriction
|
epinephrine and norepinephrine
|
|
|
|
epinephrine and norepinephrine are released from where?
|
the adrenal medulla
|
|
|
|
what can result from hyper secretion of gastric juice
|
peptic ulcer
|
|
|
|
acute pancreatitis
|
results from severe injury to pancreas
|
|
|
|
cirrhosis
|
hardening of liver tissue
|
|
|
|
pertonitis
|
inflammation of the peritoneum related to infection
|
|
|
|
what is the herring
|
breuer reflex?
|
it prevents overinflation of the lungs, by sending nerve signals from the stretch receptors in the bronchioles and lungs to the vagus nerve. the impulse is then sent to the apneustic center and medullary rythmicity center and further inspiration is inhibited.
|
|
|
how is inspiration stimulated?
|
by high CO2 levels, low O2 levels, and falling pH levels
|
|
|
|
during cellular respiration a diminished supply of oxygen will result in the storage of hydrogen as which acid?
|
lactic
|
|
|
|
when oxygen is inadequate pyretic acid is
|
reduced by two hydrogen ions to for lactic acid
|
|
|
|
Lactic acid can be transported to the liver to be reformed into
|
glucose or pyretic acid
|
|
|
|
acetic acid
|
is formed when pyretic acid is decarboxylated and joined with CaA to enter the mitochondria during aerobic oxidation when the O2 supply is adequate
|
|
|
|
Which hormone increase the reabsorption of sodium and the secretion of potassium by the kidney?
|
aldosterone
|
|
|
|
where is aldosterone released?
|
the adrenal cortex
|
|
|
|
where is ADH released?
|
posterior pituitary
|
|
|
|
Thyroxine is released from
|
the thyroid gland
|
|
|
|
Thyroxine regulates
|
cell metabolism
|
|
|
|
Cortisol is released from
|
adrenal cortex
|
|
|
|
Cortisol
|
elevates blood sugar and reduces inflammation
|
|
|
|
The renin angiontensin mechanism regulates the production of which hormone?
|
aldosterone
|
|
|
|
describe the renin angiotensin mechanism
|
a decrease in blood volume leads the nephron juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. renin converts angiotensiongen to angiontensin I. AngiotensinI is converted to angiotension II in the lung. Angiostatin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
|
|
|
|
Cortisol is stimulated by
|
the pituitary ACTH
|
|
|
|
Glucagon is produced
|
in the alpha cells of the islets of langerhans and is stimulated by epinephrine
|
|
|
|
an increase in the renal bicarbonate reabsorption would tend to have which effect on body fluids?
|
increased pH
|
|
|
|
Bicarbonate absorbs
|
H+ reducing the available H+ and causing pH to increase
|
|
|
|
The more bicarbonate available
|
the greater the opportunity to absorb H+ and prevent a fall in pH
|
|
|
|
Bicarbonate
|
is a plasma solute, any increase in solutes will increase osmolarity
|
|
|
|
Which would be the effect of afferent impulses from lactating breasts to the hypothalamus?
|
prolactin levels would increase
|
|
|
|
impulses from a suckling infant induce and increase in
|
prolactin
|
|
|
|
the milk let
|
down reflex is a product of
|
oxytocin
|
|
|
what is the main source of progesterone following degeneration of the corpus luteum during pregnancy?
|
placenta
|
|
|
|
The placenta is able to convert cholesterol to
|
progesterone, which is necessary after the corpus luteum degenerates
|
|
|
|
follicle cells
|
produce estrogen and developing the secondary oocyte
|
|
|
|
theca cells
|
surround the follicle and are involved in the secretion of steroids
|
|
|
|
corpus albincans
|
is a degenerated corpus luteum that has lost its capacity to produce progesterone
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First order neuron |
conducts the nerve impulse from the receptor to the spinal cord or brain stem |
|
|
|
Second order neuron |
conducts the impulse from the brainstem- spinal cord to the thalamus (ALWAYS ENDS IN THE THALAMUS) |
|
|
|
Third order neuron |
conducts nerve impulses from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area |
|
|
|
If neuron origantes from face |
travels through a crainal nerve to the brainstem. |
|
|
|
If neuron originates from anywhere else |
enters a spinal nerve and enter the spinal cord |
|
|
|
Two general pathways that carry somatic sensory nerve impulses |
Posterior column medial lemnisus pathway, Anterolateral/ spinothalamic pathway. |
|
|
|
Posterior column medial lemnisus pathway |
carries nerve impules for propioception touch, pressure, and vibration. |
|
|
|
pathway: first order neurons |
Extends from the receptor enters one of the two tracts in the spinal cord and ends in the medula oblongota |
|
|
|
pathway: seconds order neurons |
extends from the medula oblongota and crosses over and extends up to the thalumus. |
|
|
|
pathway: third order neuron |
extends from the thalumus up to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex. |
|
|
|
Anterolateral/ spinothalamic pathway |
receive nerce impulses for pain temp tickle and itch |
|
|
|
Lateral spinothalamic tract |
carries impulses for pain and temp. |
|
|
|
spinothalamic: first order neuron |
extends from receptor- the grey mater of the spinal cord. |
|
|
|
spinothalamic: sedond order neuron |
extends from spinal cord and crosses over within- lateral/ anterior tract- thalamus. |
|
|
|
spinothalamic: third order neuron |
extends from the thalamus up to the primary somatosensory area. |
|

