![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
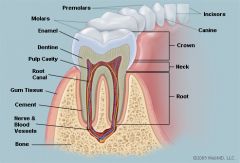
Teeth 2 incisors,1 canine, 2 premolars, 3 molars x4 4,2,4,6 top and bottom of one side 8,4,8,12 top and bottom throughout entire mouth |
|
|
Function of teeth |
Grinds food |
|
|
The white covering of the teeth that is visible |
Enamel |
|
|
Layer in the tooth beneath the enamel but encasing the pulp |
Dentin |
|
|
Where the tooth pulp is located. Includes the root canal. |
Pulp cavity |
|
|
The living part of the tooth, located in the center. Composed of nerves, blood vessels and lymph vessels. |
Pulp |
|
|
Small thin divisions that branch off from the top of the pulp cavity to the root. |
Root canal |
|
|
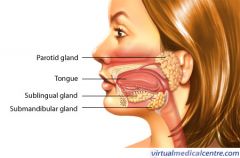
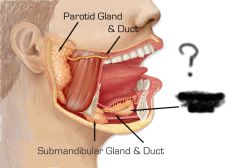
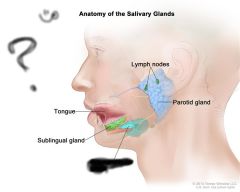
Salivary glands |
|
|
Function of salivary glands |
Secretes saliva |
|
|
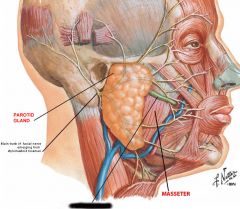
Parotid gland |
|
|
Parotid duct |
|
|
Sublingual gland |
|
|
Submandibular gland |
|
|
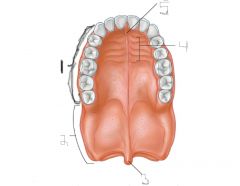
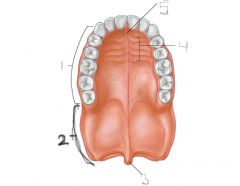
Hard palate |
|
|
Function of hard palate |
Seperates oral cavity from nasal cavity |
|
|
Soft palate |
|
|
Function of soft palate |
Blocks passage to nasopharynx during swallowing |
|
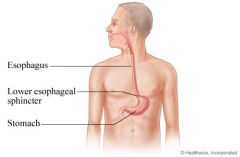
|
Esophagus, esophageal sphinter |
|
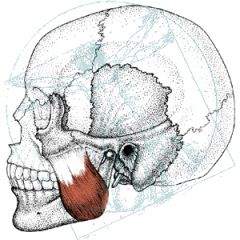
|
Masseter muscle |
|
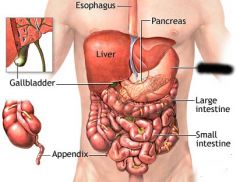
|
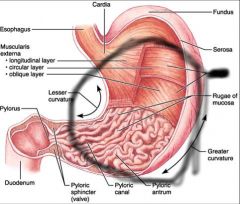
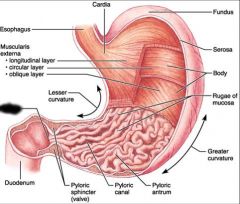
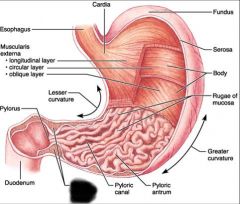
Stomach |
|
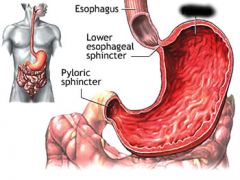
|
Fundus |
|
|
Stomach body |
|
|
Rugae (stomach folds) |
|
|
Pylorus |
|
|
Pyloric sphincter |
|
|
Function of stomach |
Secretion of some digestive enzymes such as pepsinogen |
|
|
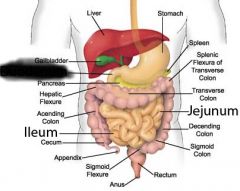
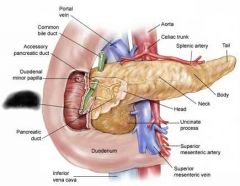
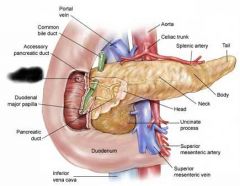
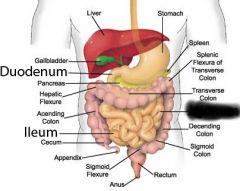
Duodenum |
|
|
Major duodenal papilla |
|
|
Minor duodenal papilla |
|
|
Jejunum |
|
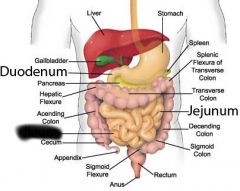
|
Ileum |
|
|
Function of small intestine |
Absorption of nutrients |
|
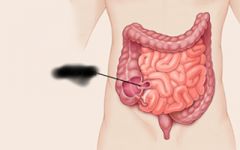
|
Ileocecal valve |
|
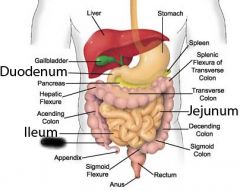
|
Cecum |
|
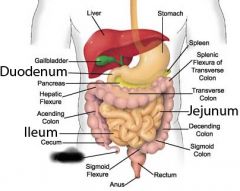
|
Appendix |
|
|
Ascending colon |
|
|
Transverse colon |
|
|
Descending colon |
|
|
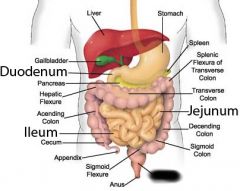
Sigmoid colon |
|
|
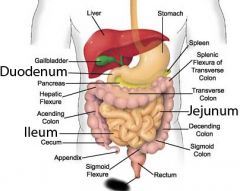
Rectum |
|
|
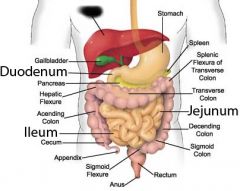
Anus |
|
|
Function of large intestine |
Absorbs water and electrolytes Stores and expels waste |
|
|
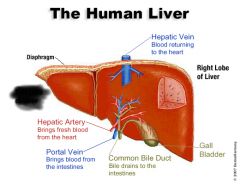
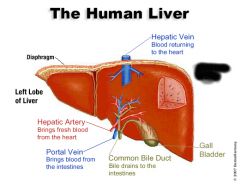
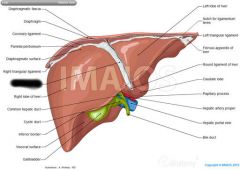
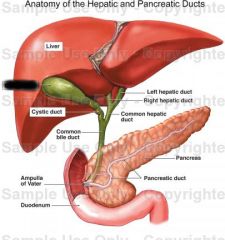
Liver |
|
|
Left lobe of liver |
|
|
Right lobe of liver |
|
|
Falciform ligament |
|
|
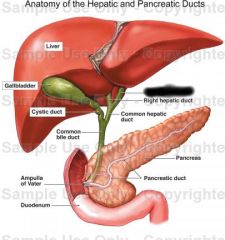
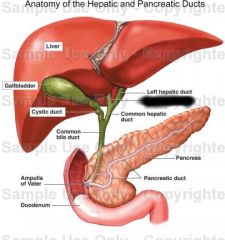
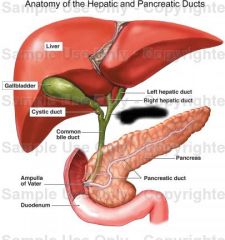
Left hepatic duct |
|
|
Right hepatic duct |
|
|
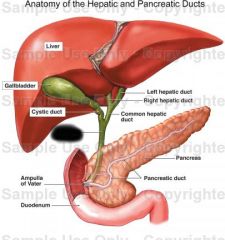
Common hepatic duct |
|
|
Common bile duct |
|
|
Function of common bile duct |
Carries bile from galbladder to duodenum |
|
|
Function of liver |
Bile production Detoxification |
|
|
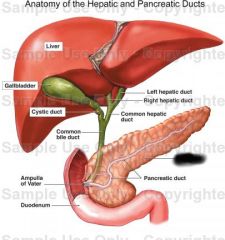
Gall bladder |
|
|
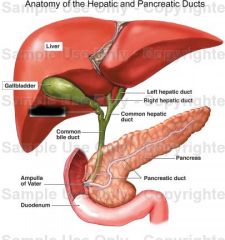
Cystic duct |
|
|
Function of cystic duct |
Connects gall bladder to common bile duct |
|
|
Function of gall bladder |
Stores bile |
|
|
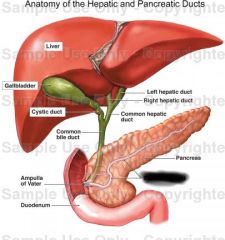
Pancreas |
|
|
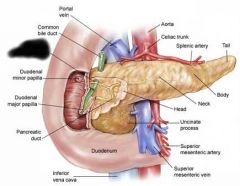
Pancreatic duct |
|
|
Accessory pancreatic duct |
|
|
Function of pancreas |
produces digestive enzymes and insulin |
|
|
Function of pancreatic duct and accessory pancreatic duct |
Carries digestive enzymes to duodenum |
|
|
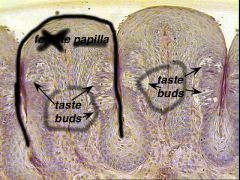
Tongue, papilla, tastebuds |
|
|
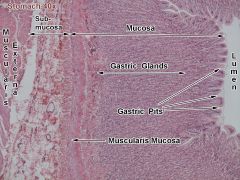
Mucosa, gastric pit, submucosa, muscularis |
|
|
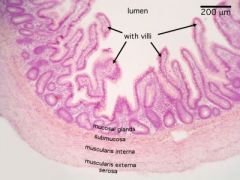
Mucosa, villi, submucosa, muscularis |
|
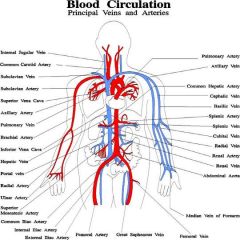
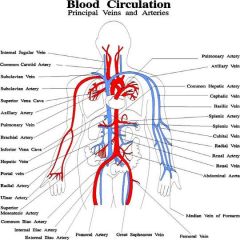
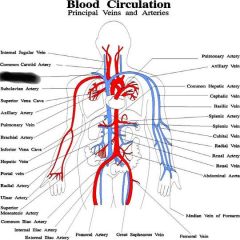
Red |
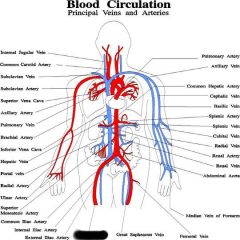
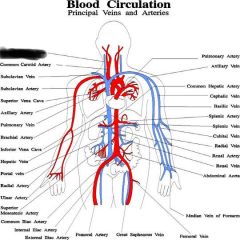
Arteries |
|
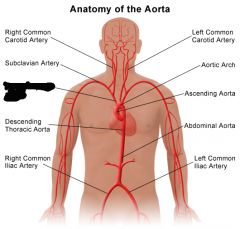
|
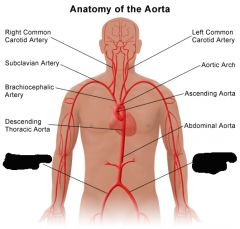
Brachiocephalic artery |
|
|
Right common carotid artery |
|
|
Right subclavian artery |
|
|
Right brachial artery |
|
|
Left common carotid artery |
|
|
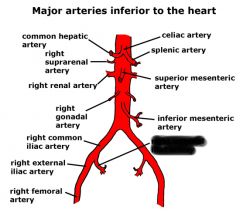
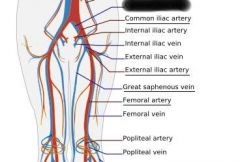
Right and left common iliac artery |
|
|
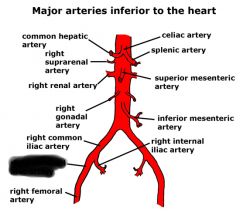
Right internal iliac artery |
|
|
Right external iliac artery |
|
|
Femoral artery |
|
blue |
veins |
|
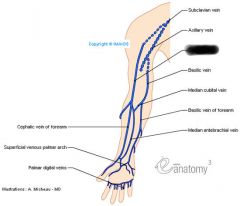
|
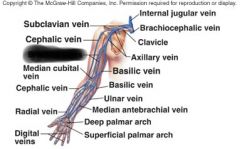
cephalic vein |
|
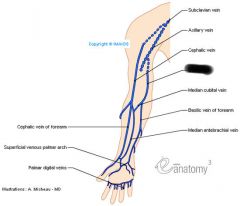
|
basilic vein |
|
|
subclavian vein |
|
|
brachial vein |
|
|
internal jugular vein |
|
|
brachiocephalic vein |
|
|
common iliac vein |
|
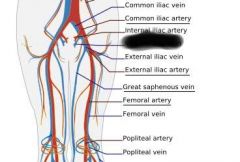
|
internal iliac vein |
|
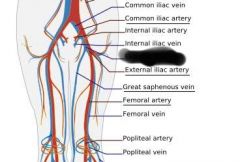
|
external iliac vein |
|
|
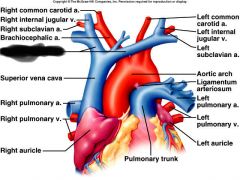
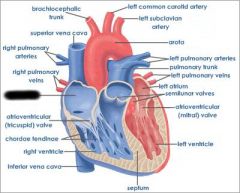
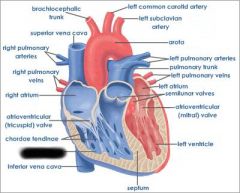
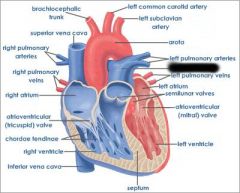
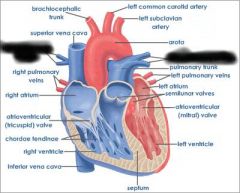
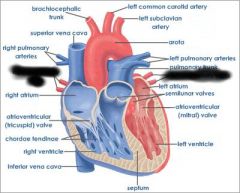
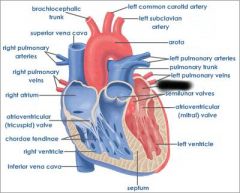
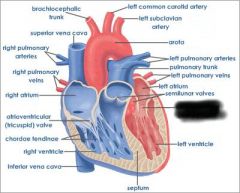
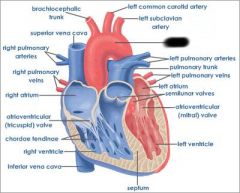
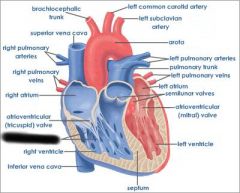
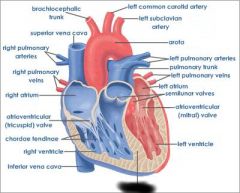
Right atrium (receives blood from vena cava and coronary sinus) |
|
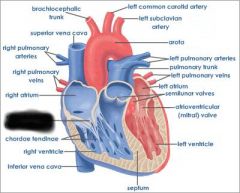
|
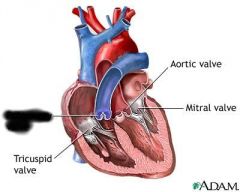
right AV valve (prevents blood from flowing back into atrium) |
|
|
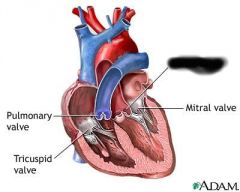
right ventricle (forces blood through pulmonary semilunar valve) |
|
|
Pulmonary semilunar valve (connects right ventricle and pulmonary trunk) |
|
|
aortic semilunar valve (connects left ventricle and aorta) |
|
|
Pulmonary trunk (receives deoxygenated blood from right ventricle) |
|
|
pulmonary arteries (transports deoxygenated blood to lungs) |
|
|
pulmonary veins (transports oxygenated blood to heart) |
|
|
coronary sinus (brings blood back to heart from cardiac muscle) |
|
|
left atrium (receives blood from pulmonary veins) |
|
|
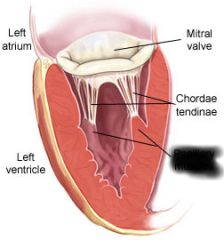
Left AV valve (prevents blood from flowing back into atrium) |
|
|
aorta (receives oxygenated blood from left ventricle) |
|
|
chordae tendinae (prevents cusps of AV valve from extending backward into atrium) |
|
|
papillary muscle (contracts to exert tension on chordae tendinae) |
|
|
interventricular septum (separates ventricles) |
|
|
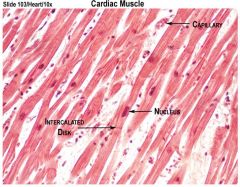
contracts to pump blood throughout body
intercolated discs allow for fast communication between heart cells so they can act in unison |
|
|
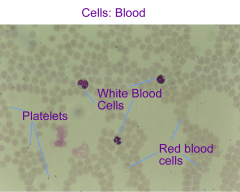
RBC- transports oxygen and co2 WBC- immune control platelets- blood clotting |
|
|
arteries carry blood away from heart veins carry blood to heart |
|
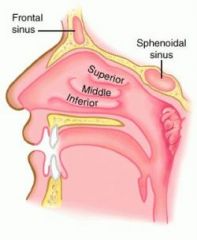
|
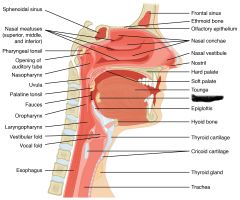
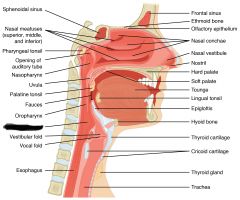
nasal concha cleans, moistens and warms incoming air |
|
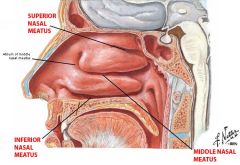
|
nasal meatus grooves between nasal concha |
|
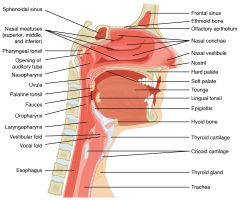
|
pharynx passageway for air and food |
|
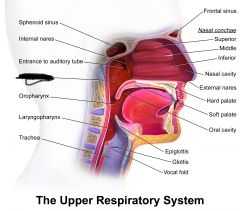
|
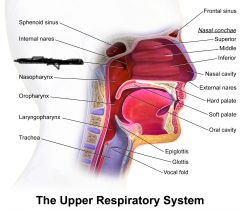
nasopharynx
|
|
|
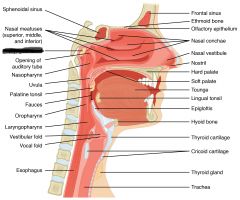
eustachian tube |
|
|
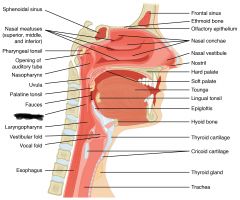
pharyngeal tonsil (intercepts pathogens) |
|
|
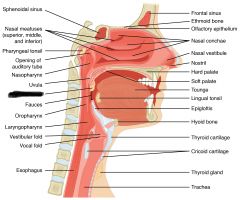
oropharynx |
|
|
palatine tonsil (intercepts pathogens) |
|
|
lingual tonsil (intercepts pathogens) |
|
|
laryngopharynx |
|
|
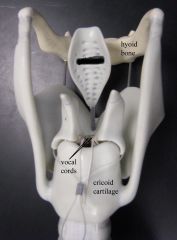
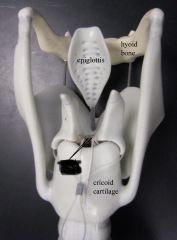
hyoid |
|
|
epiglottis (closes off glottis during swallowing to prevent choking) |
|
|
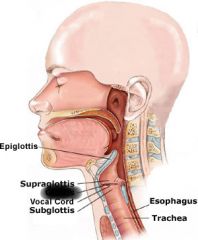
glottis |
|
|
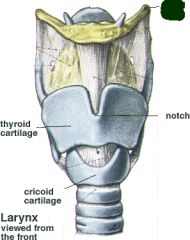
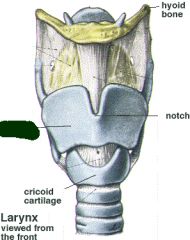
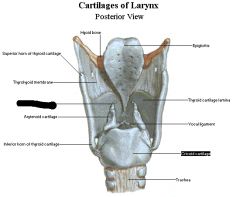
Thyroid cartilage |
|
|
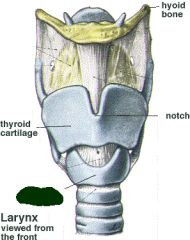
cricoid cartilage |
|
|
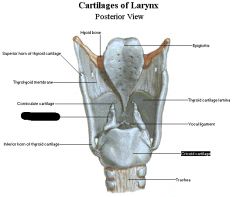
arytenoid cartilage |
|
|
corniculate cartilage |
|
|
vocal folds (produces voice) |
|
|
Trachea function |
helps clean, moisten and warm incoming air |
|
|
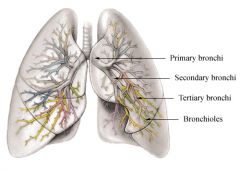
Primary bronchus and secondary bronchus divisions of the trachea delivering air to lungs |
|
|
function of lungs |
where gas exchange occurs to deliver oxygen to blood and exhale co2 |
|
|
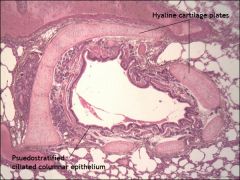
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium hyaline cartilage |
|
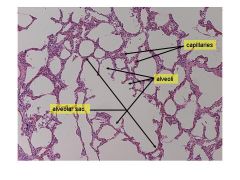
|
Alveoli simple squamous epithelium |

