![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Alliteration
|
Alliteration happens when words that begin with the same sound are placed close to one another. For example, “the silly snake silently slinked by” is a form of alliteration. Try saying that ten times fast.
|
|

Rhyme Scheme
|
the pattern of rhyming lines in a poem. (For example, aabbccdd or ababcdcd)
|
|

Irony
|
Irony involves saying one thing while really meaning another, contradictory thing.
|
|

Metaphor
|
A metaphor happens when one thing is described as being another thing. “You’re a toad!” is a metaphor—although not a very nice one. Metaphor is different from simile because it leaves out the words “like” or “as.” For example, a simile would be, “You’re like a toad.”
|
|

Internal Rhyme
|
the rhyme occurs inside a line, such as “Let’s BEAT the HEAT.”
|
|
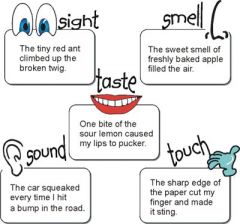
Imagery
|
Imagery is intense, descriptive language in a poem that helps to trigger our senses and our memories when we read it.
|
|

Meter
|
the number of feet in a line of poetry.
|
|

Simile
|
Similes compare one thing directly to another. For example, “My love is like a burning flame” is a simile. You can quickly identify similes when you see the words “like” or “as” used, as in “x is like y.” Similes are different from metaphors—for example, a metaphor would refer to the “burning flame of my love.”
|
|
|
Poetic stanza
|
a stanza is a unit within a larger poem.
|
|
|
Slant Rhyme
|
Two words are nearly rhymed but slightly different, such as “Lake” and “Fate”.
|
|
|
Allusion
|
An allusion happens when a speaker or character makes a brief and casual reference to a famous historical or literary figure or event.
|
|
|
Sight rhyme
|
Two words look alike but don’t sound alike, such as “Love” and “Jove” or “Daughter” and “Laughter.”
|
|
|
Symbolism
|
when the author uses an object or reference to add deeper meaning to a story. Symbolism can be subtle or obvious, used sparingly or heavy-handedly.
|
|
|
Allegory
|
An allegory is a kind of extended metaphor (a metaphor that weaves throughout the poem) in which objects, persons, and actions stand for another meaning.
|
|
|
Hyperbole
|
A hyperbole is a gross exaggeration. For example, “tons of money” is a hyperbole.
|

