![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
McGregor's Theory of X & Y
|
X- people need to be watched every minute
Y- people are willing to work without supervision and want to achieve |
|
|
Maslow's hierarchy of Needs
|

People are not motivated to work by security or money. Instead, the highest motivation is to contribute and to use their skills. "Self actualization"
|
|
|
David McClelland's Theory of Needs
|
(Acquired Needs Theory)
People are most motivated by achievement, affiliation, power. |
|
|
Herzberg's theory
|
Hygiene factors destroy motivation but improvement
alone is not sufficient to motivate. What motivates people is the work itself including responsibility, self actualization, personal growth, recognition. |
|
|
Responsibility assignment matrix
(RAM) |
A grid that shows the project resources assigned to each work package.
|
|
|
Resource Breakdown Structure
|

A hierarchical representation of resources by category and type.
|
|
|
Multi-criteria decision analysis
|
Utilizes a decision matrix to provide a systematic analytical approach for establishing criteria, such as risk levels, uncertainty, and valuation, to evaluate and rank many ideas.
|
|
|
Colocation
|
An organizational placement strategy where the project team members are physically located close to one another in order to improve communication, working relationships, and productivity.
|
|
|
Powers of the project manager
|
Formal – based on the position
Reward – stems from giving rewards Penalty (coercive) – the ability to penalize team members Expert- being the technical or project management expert Referent- another person like you, expecting you, I wanted to be like you |
|
|
Reasons for conflict
|
(In order)
Schedules project priorities resources technical opinions administrative procedures cost personality |
|
|
Collaborating
|
Problem-solving (WIN-WIN) -parties only discuss differences and try to incorporate multiple viewpoints in order to lead to consensus.
|
|
|
Compromising
|
Reconciling – finding solutions that bring some degree of satisfaction to both parties (lose-lose)
|
|
|
Withdrawal
|
Avoidance – parties retreat or postpone the decision on the problem
|
|
|
Smoothing
|
(Accommodating) Agreement rather than differences of opinion
|
|
|
Forcing
|
Directing – pushing one viewpoint at the expense of another. Win-lose.
|
|
|
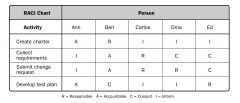
RACI chart
|
Responsible, accountable, consult, and inform. Describes responsibility assignment matrix that defines role assignments more clearly than RAM.
|
|
|
Stages of team development
|

The Tuckman Ladder. Forming , storming, norming, performing, adjourning
|

