![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
311 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Front (Term) How many processes are uniquely identified in the PMBOK. |
47 A package of inputs tools and outputs used together to do something necessary and valuable for the project. |
|
|
|
A package of inputs, tools, and outputs used together to do something necessary and valuable for the project. |
Process |
|
|
|
Each ___________ of a project produces one or more deliverables. |
Phase |
|
|
|
What is an "exit gate" or "kill point"? |
A decision point where phase deliverables are reviewed to determine whether the project should continue. |
|
|
|
A temporary group of related tasks undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. |
Project |
|
|
|
What are three important characteristics of a project.? |
A project is time-limited is unique is undertaken for a purpose |
|
|
|
What is a group of related project coordinated together called? |
A program |
|
|
|
A portfolio is aligned to the organization's __________. |
Strategic goals |
|
|
|
Describe progressive elaboration |
Not all the characteristics or requirements about a product are known when the project begins, instead they may be revisited often and refined. |
|
|
|
Define project management |
The use of skills knowledge and resources to satisfy project requirements. |
|
|
|
Define project success |
success is delivering the project within the boundaries of scope, cost, quality and risk |
|
|
|
What is used to measure help performance deviate from the plan?
If a plan changes and is approved the new plan becomes the__________. |
Baseline |
|
|
|
Project baseline is defined as the original plan plus all ___________. |
Approved changes |
|
|
|
At the end of each phase or project the difference between the plan and the result is called a___________. |
Variance |
|
|
|
Person ultimately responsible for the outcome of the project is whom |
The project manager |
|
|
|
A project ______________is significantly weaker than a project manager and are usually found in weak matrix or functional organizations |
Coordinator |
|
|
|
The ______________ is the weakest of the three project manager roles; and is a staff assistant who has little or no formal authority |
The project expediter |
|
|
|
The ___________ help prioritize projects and can make sure the project manager has the proper authority and access to resources |
Senior management |
|
|
|
The _________ is the departmental manager who usually owns the resources that are loaned to the project, and has human resource responsibilities for them |
Functional manager |
|
|
|
Also called a project champion |
Sponsor |
|
|
|
Responsible for multiple coordinated projects |
Program manager |
|
|
|
List the three types of organizations that undertake a project |
Functional, projectized , matrix |
|
|
|
Describe the functional organizational structure |
Description: very common, team works for the department, project manager has low influence or power. Who's in charge: functional department manager. Benefit: deeper company expertise by function, high professionalism stabilization, defined career paths of team. Drawbacks: project manager is weaker, projects have a low priority, resources not dedicated. |
|
|
|
Describe projectized organizational structure. |
Description: organization is structured by projects instead of functional departments, common in consulting environments. Who's in charge: project manager Benefits: project manager has complete authority, better communications, team loyalty, project loyalty, no limited resource issues. Cons: team only belongs to projects, not functional, team members workout of a job, limited professional growth. |
|
|
|
Describe matrix organizational structure. |
Description: hybrid with functional manager and project manager. A strong matrix equals project manager carries more weight. A week matrix equals functional manager has more authority. Who is in charge: shared between functional manager and program manager. Benefit: project manager can gain deep expertise of functional organization while empowered to manage resources on project. Cons: Higher overhead do to duplication of effort, conflict, contention, project Manager does not own resources, Loyalty lost. |
|
|
|
Roughly draw the project lifecycle |
See hint |
|
|
|
What is meant by triple constraint?
Show it graphically.
Triple constraint is also known as: |
Any change in a project will invariably influence time, cost, and or scope.
See it for drawing.
The triple constraint is also known as the iron triangle |
|
|
|
What is the "Work Authorization System" (WAS) |
It is used to ensure work gets performed at the right time and in the right sequence. |
|
|
|
What are enterprise environmental factors? (EEF)
Why are they important? |
EEF can be anything external to your project that affects your project.
Not considering EEFs will impact project as contingencies are not in place when EEFs occur |
|
|
|
Identify five OPA's (Organizational Process Assets) |
Templates, examples, software tools, historical information, lessons learned, databases, organizational policies and procedures, knowledge bases, special corporate competencies. Anything your organization owns or has developed can help on current or future projects |
|
|
|
Define project management plan. |
Project management plan is a single approved document that guides execution, monitoring and control, and closure |
|
|
|
Identify the five group decisions making techniques.
Which is less favored? |
Consensus, unamity, majority, plurality, and dictatorship.
Dictatorship is Least favored |
|
|
|
What is the project management information system (PMIS)? |
An automated system to support the project manager by optimizing the schedule and helping collect and distribute information. A system that helps produce and keep track of documents and deliverables. |
|
|
|
What system contains the configuration management system and change control system? |
The project management information system (PMIS) |
|
|
|
Identify three come and outputs and how they are used. |
1. Work performance data – raw data with no additional analysis applied. 2. Work performance information – work performance data that has been analyzed and processed. 3. Work performance reports – work performance information that is formalized into presentations or reports typically accompany formal recommendations, decisions, or conclusions about projects |
|
|
|
What is a change request?
When are they typically used? |
Formal Request to change some aspect of the project typically related to corrective action, preventive action, or defect repair. |
|
|
|
List five foundational process groups |
Initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, closing. |
|
|
|
The different inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs are combined to form: |
Processes |
|
|
|
Name the 10 knowledge areas. |
Integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communication management, risk management, procurement management, and stakeholder management. |
Each of the 47 project management processes fit into the 10 knowledge areas |
|
|
List the 24 processes in the planning process group |
See hint for answer |
|
|
|
List the two processes in the initiating process group |
Develop project charter, identify stakeholders |
|
|
|
List the 11 processes in the monitoring and controlling process group |
Monitor and control project work perform integrated change control, validate scope. Control scope. Control schedule. Control cost. Control quality. Control communication. Control risk. Control procurement. Control stakeholder engagement |
|
|
|
Things that are measured, inspected, reviewed, compared, monitored, verified and reported, fall under which process group |
Monitoring and controlling |
|
|
|
Monitoring and controlling is about influencing _______ _______ and not so much about _______ ________mistakes |
Future results fixing past |
|
|
|
Definitive estimates are refined during _________ and range from __________. |
Projects 5% to 10% |
|
|
|
Definitive estimates are refined during _________ and range from __________. |
Projects 5% to 10% |
|
|
|
Rough order of magnitude during the shooting ranges from _________% to _______% |
25% to 75% |
|
|
|
What is the formula for three point estimating? |
O+4M+P/6 |
|
|
|
Identify the variables of the three point estimating formula |
Optimistic. Most likely. Pessimistic. |
|
|
|
Identify three cost management tools |
Expert judgment. Analogous estimating. Parametric estimating. |
|
|
|
Identify three cost management tools |
Expert judgment. Analogous estimating. Parametric estimating. |
|
|
|
What is the output of plan cost management |
A cost management plan |
|
|
|
Identify three cost management tools |
Expert judgment. Analogous estimating. Parametric estimating. |
|
|
|
What is the output of plan cost management |
A cost management plan |
|
|
|
Where in the project management process is risk first discussed? |
In the charter. |
|
|
|
Who signs the charter? |
Project manager. Sponsor. |
|
|
|
Who signs the charter? |
Project manager. Sponsor. |
|
|
|
What is a deliverable? |
A product, service or result |
|
|
|
When do you identify all stakeholders? |
In the initiating phase. |
|
|
|
When do you identify all stakeholders? |
In the initiating phase. |
|
|
|
In and value management what is planned value (PV)? |
Work to be accomplished |
|
|
|
When do you identify all stakeholders? |
In the initiating phase. |
|
|
|
In and value management what is planned value (PV)? |
Work to be accomplished |
|
|
|
In earned value management what is earned value (EV)? |
Work performed |
|
|
|
When do you identify all stakeholders? |
In the initiating phase. |
|
|
|
In and value management what is planned value (PV)? |
Work to be accomplished |
|
|
|
In earned value management what is earned value (EV)? |
Work performed |
|
|
|
In earned value management what is actual cost (AC)? |
Occurred and recorded |
|
|
|
When do you identify all stakeholders? |
In the initiating phase. |
|
|
|
In and value management what is planned value (PV)? |
Work to be accomplished |
|
|
|
In earned value management what is earned value (EV)? |
Work performed |
|
|
|
In earned value management what is actual cost (AC)? |
Occurred and recorded |
|
|
|
Name 2 formal compression techniques |
Crashing. Fast tracking. |
|
|
|
PV = $600K CPI = .9 EV = $450K
How much was spent. |
~500K |
CPI = EV/AC |
|
|
CPI = .9 SPI = .7
What do these indicators tell you about the project? |
The project is behind schedule and you're spending too much money. |
|
|
|
Which cost management index is most reliable? |
CPI |
|
|
|
Which cost management index is most reliable? |
CPI |
|
|
|
What is EMV? |
Earned value management |
|
|
|
What is EVM? |
Expected monetary value |
|
|
|
A CPI value of less than 1.0 indicates what? |
A cost overrun for work |
|
|
|
A CPI value of less than 1.0 indicates what? |
A cost overrun for work |
|
|
|
The degree of quality management outputs answer what values? |
Yes or no |
|
|
|
Within quality management, what is the difference between precision and accuracy? |
Precision is multiple measurements: a measure of exactness. Accuracy is calibrated how close is it to the target: an assessment of correctness. |
|
|
|
List the seven basic quality tools in quality management |
Flowcharting, scatter diagrams, histograms, Pareto chart, cause-and-effect diagrams, check sheets, control charts. |
|
|
|
In quality management the SIPOC acronym stands for what? |
Supplies, inputs. process, outputs, customer |
|
|
|
The cause and effect diagram is also called what? |
Root cause diagram |
|
|
|
The cause and effect diagram is also called what? |
Root cause diagram |
|
|
|
When evaluating control charts, the "rule of seven" means or indicates what? |
If there are seven consecutive outputs above or below the mean the process is out of control |
|
|
|
In Quality management, if the project is "out-of-control" what steps must be taken? |
Assign a cause code |
|
|
|
In Quality management, if the project is "out-of-control" what steps must be taken? |
Assign a cause code |
|
|
|
True or false: Just in time quality leaves you with zero inventory |
True |
|
|
|
In Quality management, if the project is "out-of-control" what steps must be taken? |
Assign a cause code |
|
|
|
True or false: Just in time quality leaves you with zero inventory |
True |
|
|
|
Who has ultimate responsibility for quality of project? |
Project manager |
|
|
|
In Quality management, if the project is "out-of-control" what steps must be taken? |
Assign a cause code |
|
|
|
True or false: Just in time quality leaves you with zero inventory |
True |
|
|
|
Who has ultimate responsibility for quality of project? |
Project manager |
|
|
|
With sigma, what's variations provide what three qualities? |
Greater predictability, less waste in rework, a happier customer. |
|
|
|
What is RAM and how does it correspond to RACI |
RAM is a matrix chart in human resource management meaning responsibility assignment matrix. The RACI chart means responsible, accountable, consult, inform which identifies how individuals are involved, |
|
|
|
In a RACI chart how many "A" accountable personnel can be assigned to an activity? |
Only one |
|
|
|
In a RACI chart how many "A" accountable personnel can be assigned to an activity? |
Only one |
|
|
|
In human resource management the histogram is used to identify what? |
Resources used/time period. |
|
|
|
What are the five stages of Tuckman's team development? |
Forming, storming, norming, performing, adorning. |
|
|

One human resource management tool is performance appraisals, what is the difference between team performance assessment and project performance appraisals? |
Team performance assessment focuses on team performance. Project performance appraisals focus on individuals. |
|
|
|
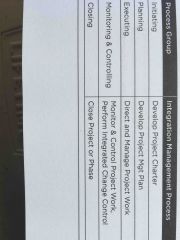
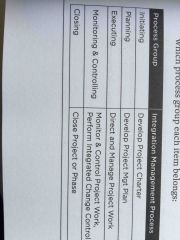
identify the six processes in the integration management knowledge area and which process group they belong to |
Initiating: develop project charter planning: develop project management plan executing: direct and manage project work monitoring and controlling: monitor and control project work, perform integrated change control closing: close project or phase |
|
|
|
What are the main outputs that are produced during each process of integration management |
Develop project charter: project charter
develop project management plan: project management plan
direct and manage project work: deliverables, work performance data, change request.
Monitor and control project work: change requests, work performance reports.
Perform integrated change control: approved change requests, change log.
Close project or phase: final product, service, or result transition |

|
|
|
What is a project charter? |
The document that officially starts the project |
|
|
|
What are the two key outputs associated with the process plan scope management? |
Scope management plan. Requirements management plan. |
|
|
|
Within scope management what are the two key outputs associated with the process collect requirements? |
With cormorants documentation. Requirements traceability matrix. |
|
|
|
Within scope management, what is the key output associated with the process define scope. |
Project scope statement |
|
|
|
Within scope management, what is the key output associated with the process define scope. |
Project scope statement |
|
|
|
Within scope management what is the key output associated with the process create work breakdown structure? |
Scope baseline |
|
|
|
Within scope management, what is the key output associated with the process define scope. |
Project scope statement |
|
|
|
Within scope management what is the key output associated with the process create work breakdown structure? |
Scope baseline |
|
|
|
Within scope management what is the key out put associated with the process validated school? |
Excepted deliverables |
|
|
|
Within scope management, what is the key output associated with the process define scope. |
Project scope statement |
|
|
|
Within scope management what is the key output associated with the process create work breakdown structure? |
Scope baseline |
|
|
|
Within scope management what is the key out put associated with the process validated school? |
Excepted deliverables |
|
|
|
Within scope management what is the key output associated with the process control scope? |
Scope change requests |
|
|
|
Truer faults. The requirements management plan is only the plan for how the requirements will be managed and not the requirements themselves. |
True |
|
|
|
The requirements management plan is important because it identifies what four activities. |
How requirements will be gathered, how decisions will be made, how changes to the requirements will be handled, and how the requirements will be documented. |
|
|
|
Also known as top-down estimating, is where an activity from a project previously performed within the organization is used to help estimate another activity's duration |
Analogous estimating |
|
|
|
If one team can install 100 feet of fence and one day that it would take 10 teams to install 1000 feet of fence in one day what kind of estimating is this an example of? |
Parametric estimating |
|
|
|
This form of estimating uses three data points for the direction instead of simply one these are Pesta mystic, most likely, and optimistic estimates |
Three point estimating also called PERT estimates |
|
|
|
What is the formula for PERT estimates? |
(Pessimistic + 4 x realistic + optimistic) / 6 |
|
|
|
When calculating standard deviation for an estimate what formula would you use? |
Standard deviation = (pessimistic - optimistic) / 6 |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a Beta and triangular distribution graphs? |
The Beta distribution looks like a standard deviation graph, the triangular distribution looks like a triangular shaped graph. |
|
|
|
What does the term critical path mean in project management |
A projects critical path is the combination of activities that, if any are delayed, will delay the projects finish |
|
|
|
What does the term critical path mean in project management |
A projects critical path is the combination of activities that, if any are delayed, will delay the projects finish |
|
|
|
Describe the critical chain method and how it differentiates from the critical path method. |
The critical chain method technique is done buy estimating each activity as aggressively as possible and then adding one lump sum buffer at the end of the network before the finish date which is used to manage activity that might be in danger of slipping |
|
|
|
Define resource leveling |
Resource leveling is when your resources needs meet up with the organizations ability to supply resources |
|
|
|
Define resource smoothing |
Resource moving looked at the schedule in light of resource constraints. Resource moving usually less disruptive to the schedule and resource leveling. |
|
|
|
Define resource smoothing |
Resource moving looked at the schedule in light of resource constraints. Resource moving usually less disruptive to the schedule and resource leveling. |
|
|
|
What are the two schedule compression techniques used in project management |
Crashing: involves adding resources to a project activity so that it be completed more quickly, crashing increases cost. Fast tracking: means that you reorder the sequence of activities so that some of the activities are performed in parallel or at the same time. fast tracking does not necessarily increase cost but always increase risk |
|
|
|
What is a milestone chart and when is it used |
And Melstone chart represents key events for the project because of the general level of information they provide they should be reserved for brief high-level project presentations. |
|
|
|
What is another term for bar chart |
Gantt chart |
|
|
|
What is another term for bar chart |
Gantt chart |
|
|
|
When is a Gantt chart used |
It is a good tool to use to communicate with management, is easy to understand at a glance |
|
|
|
What is the importance of a project network diagram |
Provides a powerful view of dependencies and sequences of each activity. It is the best representation for calculating the critical path and showing dependencies on the project. |
|
|
|
What is it mean by critical path and how is it determined |
Critical path is made up of activities that cannot be delayed without delaying the finish of the project. The critical path is determined by simply identifying the longest path through the system |
|
|
|
What is it mean by critical path and how is it determined |
Critical path is made up of activities that cannot be delayed without delaying the finish of the project. The critical path is determined by simply identifying the longest path through the system |
|
|
|
What does the term float mean |
Float or slack how much time in activity can slip before changes the critical path |
|
|
|
What is it mean by critical path and how is it determined |
Critical path is made up of activities that cannot be delayed without delaying the finish of the project. The critical path is determined by simply identifying the longest path through the system |
|
|
|
What does the term float mean |
Float or slack how much time in activity can slip before changes the critical path |
|
|
|
Define analogous estimating |
A form of expert judgment used when there's little information available |
|
|
|
What is it mean by critical path and how is it determined |
Critical path is made up of activities that cannot be delayed without delaying the finish of the project. The critical path is determined by simply identifying the longest path through the system |
|
|
|
What does the term float mean |
Float or slack how much time in activity can slip before changes the critical path |
|
|
|
Define analogous estimating |
A form of expert judgment used when there's little information available |
|
|
|
What does heuristics mean |
Rules for which no formula exists usually derived through trial and error |
|
|
|
What is a monte Carlo analysis |
Computer simulation that throws a high number of what if scenarios at the project schedule to determine probable results |
|
|
|
What is precedents diagramming method |
Also called activity on the road. A type of network diagram where the boxes are activities and the arrows are used to show dependencies between the activities |
|
|
|
Name the plan that describes all the processes of estimate cost, determine budget, and control cost will be carried out? |
The cost management plan |
|
|
|
Name the plan that describes all the processes of estimate cost, determine budget, and control cost will be carried out? |
The cost management plan |
|
|
|
An estimating tool that uses the actual results of projects that have been performed by an organization is called what? |
Analogous estimating |
|
|
|
Name the plan that describes all the processes of estimate cost, determine budget, and control cost will be carried out? |
The cost management plan |
|
|
|
An estimating tool that uses the actual results of projects that have been performed by an organization is called what? |
Analogous estimating |
|
|
|
The estimating tool often used in projects with a high degree of historical information and works best for linear scalable projects is called what? |
Parametric estimating |
|
|
|
Name the plan that describes all the processes of estimate cost, determine budget, and control cost will be carried out? |
The cost management plan |
|
|
|
An estimating tool that uses the actual results of projects that have been performed by an organization is called what? |
Analogous estimating |
|
|
|
The estimating tool often used in projects with a high degree of historical information and works best for linear scalable projects is called what? |
Parametric estimating |
|
|
|
An estimating tool which produces a separate estimate for each scheduled activity these individual estimates are then aggregated up to a summary node on the WBS |
Bottom-up estimating |
|
|
|
Name the plan that describes all the processes of estimate cost, determine budget, and control cost will be carried out? |
The cost management plan |
|
|
|
An estimating tool that uses the actual results of projects that have been performed by an organization is called what? |
Analogous estimating |
|
|
|
The estimating tool often used in projects with a high degree of historical information and works best for linear scalable projects is called what? |
Parametric estimating |
|
|
|
An estimating tool which produces a separate estimate for each scheduled activity these individual estimates are then aggregated up to a summary node on the WBS |
Bottom-up estimating |
|
|
|
What are the three components of the scope baseline? |
The project scope statement, the WBS, and the WBS dictionary. |
|
|
|
Name the plan that describes all the processes of estimate cost, determine budget, and control cost will be carried out? |
The cost management plan |
|
|
|
An estimating tool that uses the actual results of projects that have been performed by an organization is called what? |
Analogous estimating |
|
|
|
The estimating tool often used in projects with a high degree of historical information and works best for linear scalable projects is called what? |
Parametric estimating |
|
|
|
An estimating tool which produces a separate estimate for each scheduled activity these individual estimates are then aggregated up to a summary node on the WBS |
Bottom-up estimating |
|
|
|
What are the three components of the scope baseline? |
The project scope statement, the WBS, and the WBS dictionary. |
|
|
|
What is another term for the project budget? |
The cost baseline |
|
|
|
This component of the project management plan shows what costs are projected and when their projected to being cured. Is the plan against which the actual costs are measured. |
Cost performance baseline |
|
|
|
This component of the project management plan shows what costs are projected and when their projected to being cured. Is the plan against which the actual costs are measured. |
Cost performance baseline |
|
|
|
This method of measurement measures the actual performance against the original plan |
Earned value management (EVM) |
|
|
|
This component of the project management plan shows what costs are projected and when their projected to being cured. Is the plan against which the actual costs are measured. |
Cost performance baseline |
|
|
|
This method of measurement measures the actual performance against the original plan |
Earned value management (EVM) |
|
|
|
The term in earned value management that describes how much was originally planned for the project cost is what? |
Budgeted at compensation (BAC) |
|
|
|
This component of the project management plan shows what costs are projected and when their projected to being cured. Is the plan against which the actual costs are measured. |
Cost performance baseline |
|
|
|
This method of measurement measures the actual performance against the original plan |
Earned value management (EVM) |
|
|
|
The term in earned value management that describes how much was originally planned for the project cost is what? |
Budgeted at compensation (BAC) |
|
|
|
The term and management that describes how much work should have been completed at a point in time based on the plan. derived by measuring planned work completed at a point in time. |
Planned value (PV)also known as budgeted cost of work scheduled (BCWS) |
|
|
|
The earned value management tool which describes how much work was actually completed during a given period of time. Derived by measuring actual work completed at a point in the schedule. |
Earned value (EV) also known as budgeted cost of work performed or (BCWP) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for planned value? |
PV equals planned % complete x BAC |
|
|
|
What is the formula for planned value? |
PV equals planned % complete x BAC |
|
|
|
What is the formula for earned value? |
EV = Actual % Complete x BAC |
|
|
|
What earned value management term describes the money spent during a given period of time? |
Actual cost also known as actual cost of work performed (AC) (ACWP) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule performance index? |
SPI = EV/PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term which describes projecting the total cost of completion based on project performance up to a point in time? |
Estimate at completion(EAC) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule performance index? |
SPI = EV/PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term which describes projecting the total cost of completion based on project performance up to a point in time? |
Estimate at completion(EAC) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimate at completion? |
EAC = BAC/cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule performance index? |
SPI = EV/PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term which describes projecting the total cost of completion based on project performance up to a point in time? |
Estimate at completion(EAC) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimate at completion? |
EAC = BAC/cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes projecting how much will be spent on the project, based on past performance. |
Estimate to completion (ETC) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule performance index? |
SPI = EV/PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term which describes projecting the total cost of completion based on project performance up to a point in time? |
Estimate at completion(EAC) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimate at completion? |
EAC = BAC/cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes projecting how much will be spent on the project, based on past performance. |
Estimate to completion (ETC) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimate to completion? |
ETC = EAC – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule performance index? |
SPI = EV/PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost variance? |
CV = EV – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term which describes projecting the total cost of completion based on project performance up to a point in time? |
Estimate at completion(EAC) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimate at completion? |
EAC = BAC/cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes projecting how much will be spent on the project, based on past performance. |
Estimate to completion (ETC) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimate to completion? |
ETC = EAC – AC |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term which describes the difference between what was budgeted and what will actually be spent? |
Variance at completion (VAC) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between what we expected to spend and what was actually spent? |
Cost variance (CV) |
|
|
|
What is the earned value management term that describes the difference between where we plan to be in the schedule and where we are in the schedule? |
Schedule variance (SV) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule variance? |
SV = EV – PV |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations during a given period of time. |
Cost performance index (CPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cost performance index |
CPI = EV / AC |
|
|
|
The earned value management term that describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting cost expectations from the beginning up to a point in time. Also used to forecast the project's costs at completion |
Cumulative CPI |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cumulative CPI |
Cumulative CPI = cumulative EV / cumulative AC |
|
|
|
Earned value management which describes the rate at which the project performance is meeting schedule expectations up to a point in time. |
Schedule performance index (SPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for schedule performance index? |
SPI = EV/PV |
|
|
|
What is the formula for variance at completion |
VAC = BAC – EAC |
|
|
|
Which earned value management tool describes performance that must be achieved in order to meet financial and schedule goals? |
To complete performance index (TCPI) |
|
|
|
Which earned value management tool describes performance that must be achieved in order to meet financial and schedule goals? |
To complete performance index (TCPI) |
|
|
|
What is the formula for the term to complete performance index |
TCPI = (BAC – EV)/remaining funds |
|

