![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

plate tectonic theory
|
theory that the lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that slowly move on top of the asthenospere
|
|

lithospere
|
cool,ridgid,outermost layer if earth that is divided into enormous pieces called tectonic plates; consist of the crust and the right uppermost part of the mantle
|
|
asthenospere
|
the soft layer of the mantle below the lithosphere on which the plates move due to convection currents
|
|
plasticity
|
having characteristics of a solid when still but liquid when in motion
|
|
convection current
|
the heating and rising and cooling and falling if any liquid substance the mantle has convection. currents which cause the plates to move
|
|
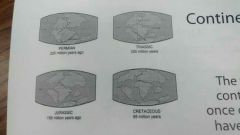
continental drift
|
the theory that continents were once connected but have drifted apart
|
|
|
Alfred wegener
|
meteorologist who postulated the continental drift theory
|
|

fossil evidence
|
impressions of organisms left in rock layers that indicate the organisms once lived in the area
|
|

harry hess
|
a geology processed at Princeton university who theorized the process of sea floor spreading
|
|

sea floor spreading evidence
|
a parallel pattern of rock material found at identical locations on each side of the mid-alantic ridge reveals rock of the same geologic age and polarity
|
|

magnetic reversal
|
a change in magnetic poles as evidenced by rock layers at points of sea floor spreading
|
|

divergent boundary
|
the boundary between two tectonic plates moving a way from each others on land creates rift valleys on the sea floor creates new ocean crust
|
|

convergent boundary with subduction
|
the boundary between two tectonic plates moving. toward each other resulting in volcanic activity when a denser ocean plate subducts below continental plate
|
|
sunduction
|
a plate is forced below when one plate is denser than another as they converge occurs at continental to oceanic boundaries and oceanic to oceanic boundaries
|
|
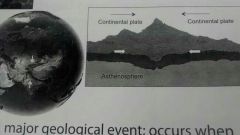
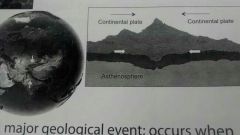
convergent boundary with mountain building
|
a major geological event occurs when continental plates of equal density converge
|
|
transform boundary
|
the boundary between two plates that slide pass one another sudden shifts result in major geological events such as earthquakes and the release of stored energy
|
|
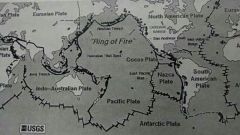
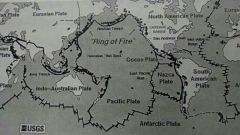
ring of fire
|
ring of volcano's around the pacific due to subduction of geological plates in the pacific rim region
|

