![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are vascular bundles arranged in monocot stems/roots?
|
Stems-scattered
Roots-prominent endodermis xylem in ring in center |
|
|
How are vascular bundles arranged in dicot stems/roots?
|
Stems-ring
Root-xylem forms "x" in the center |
|
|
What is the importance of a cuticle?
|
To prevent the loss of water.
|
|
|
What does xylem carry and where does it carry it?
|
Water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves
|
|
|
What does phloem carry and where does it carry it?
|
Sugars in any direction
|
|
|
What are stomata? Where are they mostly found?
|
They are pores on the underside of a leaf that aid in gas exchange.
|
|
|
Why are leaves green?
|
Because they contain chlorophyll a which reflect green light
|
|
|
What is an example of an endergonic reaction?
|
Photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is an example of an exergonic reaction?
|
Cellular Respiration
|
|
|
How are endergonic and exergonic reactions linked?
|
The energy in cells to run endergonic reactions come from exergonic reactions.
|
|
|
What is an ATP molecule made up of?
|
ribose sugar, adenine, 3 phosphate groups
|
|
|
List where photosynthesis, light reactions, Calvin cycle, glycolysis, aerobic respiration occur.
|
Photosynthesis-chlorophyll
Light reactions-thylakoid Calvin Cycle-stroma glycolysis-cytoplasm aerobic respiration-mitochondrion |
|
|
What is chlorophyll and why is it significant for photosynthesis?
|
Chlorophyll are light absorbing pigments
-- They absorb the light |
|
|
How is chlorophyll like an enzyme?
|
acts like a catalyst
|
|
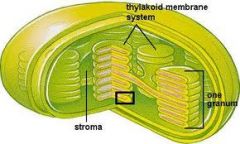
Chlorophyll...find granum, thylakoids and stroma
|
refer to pic
|
|
|
What are photosystems I and II?
|
Clusters of pigments
|
|
|
What are the 5 steps of the electron transport chain of the light phase?
|
1) light excites electrons in chlorophyll a molecules of PSII.
2)electrons move to a primary electron acceptor (ATP is produced) 3) electrons are transferred along a series of molecules called the electron transport chain. 4) light excites electrons in chlorophyll a molecules of PSI. 5) electrons are transferred along a second electron transport chain. |
|
|
What happens at the end of the second electron transport chain?
|
electrons combine with NADP+ and H+ to form NADPH.
|
|
|
What is NADP+?
|
an organic molecule that accepts electrons
|
|
|
What is the significance of the splitting of water during the light phase?
|
1. Produces electrons for the restoring of photosystem II.
2. Oxygen is released as bypoduct. |
|
|
What is chemiosmosis?
|
It is an important part of light reactions where ATP is produced
|
|
|
How is ATP synthase involved in chemiosmosis?
|
It is an enzyme that helps make ATP
|
|
|
What is the significance of NADPH and ATP for the Calvin cycle?
|
NADPH and ATP are what provide energy for the Calvin cycle
|
|
|
What are the products of the light phase of photosynthesis?
|
ATP, NADPH, oxygen gas, H+
|
|
|
What are the three steps of the Calvin cycle?
|
1. CO2 enters stroma and combines with RuBP to form 6-C compound that immediately splits into 2 PGA
2.Each PGA gains phosphate from ATP/NADPH donates electrons to create PGAL. 3. 3 ATP are used to rearrange the 5 remaining PGAL into 3 RuBP. |
|
|
How many molecules of CO2 does it take to produce 1 molecule of PGAL?
|
3
|
|
|
How many ATP and NADPH does it take to produce 1 molecule of PGAL?
|
9 ATP
6 NADPH |
|
|
What are the three stages, in order, of cellular respiration?
|
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain
|
|
|
Glycolysis
|
2ATP & glucose ---> 2 pyruvic acid & 4 ATP
Net gain of 2 ATP |
|
|
What are the main events of the Krebs cycle?
|
--CO2 produced
--Electrons are given off when NADH and FADH2 release hydrogen atom --2 ATP produced |
|
|
How is ATP created during the electron transport chain?
|
electrons release energy as they move from molecule to molecule down the chain
|
|
|
How much ATP is produced during the chain?
|
34
|
|
|
How many NET ATP are generated during glycolysis?
|
2
|
|
|
How many NET ATP are generated during the electron transport chain of cellular respiration?
|
34
|
|
|
How many NET ATP are generated during the Krebs cycle?
|
2
|
|
|
How many NET ATP are generated during cellular respiration?
|
38
|
|
|
What does alcoholic fermentation result in the production of?
|
ethyl alcohol and CO2
|
|
|
What type of fermentation takes place in human cells?
|
Lactic Acid Fermentation
|
|
|
Match--
calvin cycle |
photosynthesis
|
|
|
Match--
pyruvic acid is broken down with out oxygen |
anaerobic respiration
|
|
|
Match--
pyruvic acid is formed |
anaerobic respiration and anerobic respiration
|
|
|
photosystems I and II
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
lactic acid is formed
|
anaerobic respiration
|
|
|
glucose and oxygen are needed
|
aerobic respiration
|
|
|
occurs in yeast cells when no oxygen is available
|
anaerobic respiration
|
|
|
PGAL is produced
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
light and dark reactions take place
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
krebs cycle takes place
|
aerobic respiration
|
|
|
water is split
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
chemiosmosis takes place
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
Acetyl CoA is formed
|
aerobic respiration
|
|
|
the basis of bread baking
|
anaerobic respiration
|
|
|
What is this equation for?
6CO2+6H20+light energy---->C6 H12 O6+6O2 |
Photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is this equation for?
C6 H12 O6+6O2----->6H2O+6CO2+38ATP |
Cellular respiration
|
|
|
The Krebs cycle begins with _______________
|
Acetyl CoA
|
|
|
During the second stage of the Calvin cycle, PGA gets ________ because it ________ electrons to form PGAL.
|
reduced--------gains
|
|
|
OIL RIG
|
Oxidation involves loss
Reduction involves gain |
|
|
What is free energy?
|
the energy available to do work
|
|
|
What is an exergonic reaction?
|
chemical reactions that release energy
|
|
|
What is an endergonic reaction?
|
chemical reactions that require a NET input of energy
|
|
|
What is a redox reaction?
|
reactions in which electrons are transferred between atoms
|
|
|
what is a oxidation reaction?
|
where a reactant loses one or more electrons, thus becoming more positive in charge
|
|
|
what is a reduction reaction?
|
where a reactant gains one or more electrons, thus becoming more negative in charge
|
|
|
ATP?
|
Adenosine triphosphate
|
|
|
ADP?
|
Adenosine diphosphate
|
|
|
What is ADP made of?
|
adenine, ribose sugar, two phosphate groups
|
|
|
Photosynthesis consists of two independent pathways called the ___________ reaction and the ___________ cycle.
|
light-dependent
calvin |
|
|
What is an accessory pigment?
|
they trap wavelengths of light that cannot be absorbed by chlorophyll a and then transfer the energy to chlorophyll a molecules for use in photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is NADPH+?
|
it is an electron acceptor
|
|
|
NADP+ + 2e- + 2H+ -----> ______
|
NADPH
|
|
|
What happens at the end of the second electron transport chain?
|
The electrons combine with NADP+ and H+ to form NADPH.
|
|
|
For each turn of the Calvin cycle (1 PGAL molecule), it takes:
__ CO2 __ ATP __ NADPH |
For one turn of the Calvin cycle it takes 3 CO2, 9 ATP, 6 NADPH
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration?
|
A process by which glucose is broken down to release energy
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration with oxygen called?
|
Aerobic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration without oxygen?
|
Anaerobic
|
|
|
Which type of process is simpler? Aerobic or anaerobic
|
Anaerobic
|
|
|
Which type of process produces the most energy? Aerobic or anaerobic?
|
Aerobic
|
|
|
What is another name for fermentation?
|
Anaerobic Respiration
|
|
|
Where does Anaerobic respiration occur?
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
What is the first step of Anaerobic respiration?
|
Glycolysis
|
|
|
Where does glycolysis occur?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
What is the equation for Anaerobic Respiration?
|
2ATP + glucose -----> 2pyruvic acid molecules + 4ATP
-------------------------------------------- Net gain of 2 ATP |
|
|
When cells use oxygen quicker than it can be delivered to cells, pyruvic acid turns into lactic acid. this is called _______ ______ ____________
|
Lactic Acid Fermentation
|
|
|
What happens when lactic acid builds up?
|
The cell's cytoplasm becomes acidic and the increased acidity may reduce the capacity of muscles to contract, resulting in muscle fatigue, pain and cramps.
|
|
|
Aerobic Respiration is followed by ________
|
glycolysis
|
|
|
Where does Aerobic respiration take place?
|
Mitochondrion
|

