![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four characteristics that all plants have in common? |
-Eukaryotic -Multicellular -Autotrophic -Have cell walls |
|
|
What is the study of plants? |
Botany |
|
|
How are plants and fungi different at a cellular level? |
Plants have chloroplasts, while fungi do not. |
|
|
What are four uses for plants? |
-Medicine -Oxygen -Clothing -Poison(ing my sister) |
|
|
What is the process in which plants make energy and produce oxygen? |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
What is the equation for photosynthesis? |
6CO2 + 6H2O -----> C6H12O2 + 6O2 |
|
|
What is the difference between vascular and nonvascular plants? |
-Vascular plants have: -Xylem (transports water) -Phloem (transports food and nutrients) -Nonvascular plants absorb minerals and nutrients and lack: -Vessels -Roots -Stems -Leaves |
|
|
What is the difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms? |
Angiosperms are flowering plants, while gymnosperms are wind-pollinated. |
|
|
What are the main functions of the vascular system in a plant? |
To transport water and nutrients between the roots and leaves. |
|
|
What structure surrounds a plant's stoma? |
Guard cells |
|
|
How do guard cells keep the plant from being dehydrated? |
They collapse on the stoma when they are dehydrated. |
|
|
What is germination? |
The development of a plant from a seed or spore. |
|
|
What is primary growth? |
Plant growth that elongated the plant |
|
|
What is secondary growth? |
Plant growth that widens the plant |
|
|
What are annual plants? |
Plants with a life cycle that lasts one year |
|
|
What are perennial plants? |
Plants that bloom year after year |
|
|
What are the three types of vascular plants? |
-Ferns -Gymnosperms -Angiosperms |
|
|
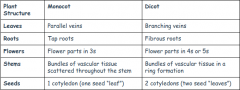
What are the two types of angiosperms? |
-Monocots -Dicots |
|
|
|
|
|
What is the function of a flower? |
The plant's reproductive structures |
|
|
What is the function of the stamen? |
The male reproductive parts of a flower |
|
|
What is the function of the anther? |
The anther is the part of the stamen which produces pollen |
|
|
What is the function of the filament? |
The filament supports the anther |
|
|
What is the function of the pistil? |
The pistil is the female reproductive parts of the flower. |
|
|
What is the function of the ovary? |
The ovary is where the ovules (or eggs) are stored until they are fertilized |
|
|
What is the function of the locules? |
The locules are the segments within the ovary that hold the ovules. |
|
|
What is the function of the ovules? |
The ovules, or eggs, become seeds when fertilized. |
|
|
What is the function of the stigma? |
The stigma is the female reproductive part of a flower that collects pollen and is sticky and moist when mature. |
|
|
What is the function of the style? |
The style connects the stigma to the ovary. |
|
|
What is the function of the petals? |
The petals attract pollinators to the flowers because of their bright colors and (sometimes) smells. |
|
|
What is the function of the sepals? |
The sepals are the outermost leaves that protect the flower when it has not yet bloomed. |
|
|
What is the function of the receptacle? |
The receptacle is the part of the branch on which the flower forms. |
|
|
What is the function of pollen/pollen grains? |
Pollen is responsible for fertilizing the ovules (eggs) by being pollinated and sticking to the stigma. |
|
|
What is pollination? |
Pollination is the transfer of pollen to the stigma or ovary of a flower. |
|
|
What part of a flower becomes the fruit? |
The ovary |
|
|
What is the function of the xylem? |
To transport water between the root and stems. |
|
|
What is the function of the phloem? |
To transport food & nutrients between the roots and stems. |
|
|
What is a herbaceous stem? |
A stem with little or no wood in its structure. Mostly seen in flowers, etc. |
|
|
What is a woody stem? |
A stem with secondary tissue and an increased diameter. Mostly seen in trees. |
|
|
What is a cambium? |
A plant tissue from which the cellular division and growth of the xylem, phloem, and cork of a stem occurs, causing secondary growth of the plant. |
|
|
What is the function of the stomata? |
A microscopic opening in the plant leaves that allows the exchange of gases to occur. |
|
|
What is the function of the guard cells? |
Cells surrounding the stomata that are filled with water and regulate the water loss of the plant. |
|
|
What is the function of the chloroplasts? |
A part of the cells of the plant in which photosynthesis occurs. |
|
|
What is the function of the epidermal walls? |
A layer of cells that covers the surface of the leaf. |
|
|
What is the primary function of a leaf? |
To create food & energy for the rest of the plant. |

