![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the three essential macronutrients? |
N, P, K |
|
|
|
An element is considered essential if |
1) in its absence the plant can't complete its normal lifecycle. 2) is an essential plant constituent or metabolite. |
|
|
|
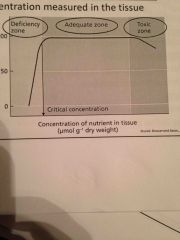
Critical Concentration |
A plants requirement for a particular element - the concentration measured in the tissue |
|
|
|
Nutrients that are part of carbon compounds |
N, S |
|
|
|
N requirements (needed for...) |
Required in greatest amounts Absorbed in the form of Nitrate ion (NO3-) |
|
|
|
N functions |
Constituent of proteins, nucleic acids, hormones, chlorophyll |
|
|
|
N (deficiency symptoms) |
Chlorosis, first evident in older leaves, anthocyanin accumulation |
|
|
|
N (excess) |
Shoot growth vs root development, delay in the onset of flowering. |
|
|
|
S (Function) |
Taken up as sulfate anion (SO42-) Protein structure-disulfide bonds,(-S-S-) between neighboring cysteine & methionine) secondary/tertiary structure, protein folding; Fe-S proteins (ferredoxin-photosynthesis)
|
|
|
|
S (function cont..) |
(iso)thiocyanates-flavor of mustard, horseradish, turnips, cabbages as defense against herbivores. Vitamins-thiamine,biotin Coenzyme A - respiration, fatty acid metabolism |
|
|
|
S (deficiency) |
*is rare-micro-organisms that oxidize sulfides & decompose organic sulfur; volcanoes, geysers are the source of atmospheric SO2 & SO3 Symptoms-evident in younger leaves: chlorosis around the vascular tissue, due to reduced protein synthesis - affects chlorophyll stabilization in the thylakoid membranes. |
|

