![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Woolgrass |
Scirpus cyperinus |
|
|
Wild Ginger |
Asarum canadense |
|
|
Bluestem Goldenrod |
Solidago caesia |
|
|
Zig-Zag Goldenrod |
Solidago flexicaulis |
|
|
White Snakeroot |
Eupatorium rugosum |
|
|
Doll's Eyes |
Actaea pachypoda |
|
|
Jack-in-the-Pulpit |
Arisaema triphyllum |
|
|
False Solomon's Seal |
Smilancina racemosa |
|
|
Bottle Brush Grass |
Elymus hystrix |
|
|
Enchanter's Nightshade |
Circaea lutetiana |
|
|
Early Meadowrue |
Thalictrum dioicum |
|
|
Jewelweed |
Impatiens capensis |
|
|
Large-flowered Trillium |
Trillium grandiflorum |
|
|
Big Bluestem |
Andropogon gerardii |
|
|
Little Bluestem |
Schizachyrium scoparium |
|
|
Indian Grass |
Sorghastrum nutans |
|
|
Switch Grass |
Panicum virgatum |
|
|
Showy Tick-Trefoil |
Desmodium canadense |
|
|
Round-Headed Bush-Clover |
Lespedeza capitata |
|
|
Butterfly Milkweed |
Asclepias tuberosa |
|
|
Canada Wild Rye |
Elymus canadensis |
|
|
Brown-eyed Susan |
Rudbeckia hirta |
|
|
Sand Wormwood |
Artemisia campestris |
|
|
Common Milkweed |
Asclepias syriaca |
|
|
Teasel |
Dipascus sylvestris |
|
|
Queen Anne's Lace |
Daucus carota |
|
|
Brown Knapweed |
Centaurea jacea |
|
|
Common Ragweed |
Ambrosia artemisiifolia |
|
|
Red Clover |
Trifolium pratense |
|
|
Birdsfoot Trefoil |
Lotus corniculatus |
|
|
Cow Vetch |
Vicia cracca |
|
|
Evening Primrose |
Oenothera biennis |
|
|
Vernal pools are temporary pools of water that provide habitat for distinctive plants and animals. They are wetlands devoid of fish that allow safe development of juvenile insect and amphibian life unable to survive predation. |
What is a vernal pool? |
|
|
Fraxinus, Juglans, Carya, Gymnocladus, Rhus, Ailanthus, Rubus, Rosa, Sambucus, Robinia |
Name genera with compound leaves. |
|
|
Fraxinus, Acer, Vibrunum, Cornus, Sambucus, Lonicera |
Name genera with opposite leaf arrangement. |
|
|
Vibrunum acerifolium (Maple-leaved viburnum), Physocarpus opulifolius (Ninebark), Viburnum opulus (European Cranberry), Viburnum trilobum (Highbush Cranberry), Plantanus occidentalis (Sycamore), Liquidambar styraciflua (Sweetgum), Liriodendron tulipifera (Tulip Tree) |
Name non-maple species with leaves similar to maples. |
|
|
Sugar Maple - Seedcase plump, keys drooping clusters on stalks usually longer than wings. Paired keys shed at one unit. Red Maple - Angle between wings 60 degrees, seedcase swollen, keys shed individually. Silver Maple - Seedcase ribbed, angle between wings 90 degrees, often one seed will mature Manitoba Maple - less than 45 degree angle, seedcase elongated and wrinkled. Norway Maple - Wings spread very wide, almost parallel |
Describe the characteristics of Acer fruit within the genus. |
|
|
Red Oaks have leaves with 7-9 lobes, each lobe wider towards the base, notches rounded. Black Oaks have leaves with 5-7 lobes, each lobe with parallel sides, notches u-shaped. |
What is the difference between a Red Oak leaf and a Black Oak leaf? |
|
|
Cornus racemosa, Cornus sericea have white fruit. Cornus alternifolia, Cornus obliqua, Cornus rugosa. Cornus florida has red fruit. |
What species in Cornus have light colored fruit? Dark fruit? Red fruit? |
|
|
Juglans nigra or most Juglans |
What tree's twigs smell like limes or aftershave? |
|
|
Sassafras albidum |
What tree's twigs smell like limes or rootbeer? |
|
|
Ailanthus altissima |
What tree's twigs smells like burnt peanut butter or dog poop? |
|
|
Imbricate scales are overlapping like shingles. Valvate means 2 scales hinged open like a clam shell. |
What does imbricate and valvate bud scales mean? |
|
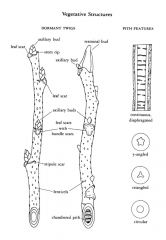
|
Label the twig. |
|
|
Furry/hairy surface |
What does a "pubescent bud or stem" mean? |
|
|
American Beech - Fagus grandifolia |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Bur Oak - Quercus macrocarpa |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Common Buckthorn - Rhamnus cathartica |

Name dat twig! |
|
|
Staghorn Sumac - Rhus typhina |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Black Walnut - Juglans nigra |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Ironwood - Ostrya virginiana |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Basswood - Tilia americana |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Bitternut Hickory - Carya cordiformis |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Poison Ivy - Toxicodendron radicans |

Name that twig! |
|
|
White Ash - Fraxinus americana |

Name that twig! |
|
|
Green Ash - Fraxinus pennsylvanica |

Twig? |
|
|
Black Ash - Fraxinus nigra |

Twig? |
|
|
Sugar Maple - Acer saccharum |

Twig? |
|
|
Manitoba Maple - Acer negundo |

I say, what twig is this? |
|
|
Hawthorn - Crataegus sp. |

Name the twig! |
|
|
Nannyberry - Viburnum lentago |

Twig? |
|
|
Gray Dogwood - Cornus racemosa (Note orange tinge of year one growth. Did not include Red-Osier as very obvious. Red-osier has white pith.) |

Twig? |
|
|
Trembling Aspen - Populus tremuloides |
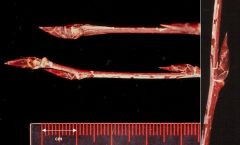
Twig? |
|
|
Redberried Elder - Sambucus pubens |

Name this twig. It has red spongy pith. |
|
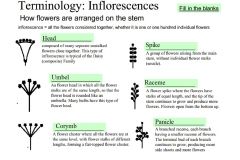
|
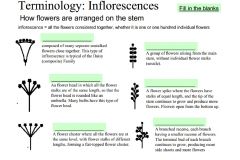
Fill in the blanks. |
|
|
Poaceae: Grasses have nodes (joints) from the blades to the ground. Stems are hollow and round. Leaf sheaths usually open, leaves in 2 vertical rows. Flowers with scales, fruits are grains. |
How do you identify a grass? |
|
|
Cyperaceae: Stems are solid, usually 3-sided. Leaves in 3 vertical rows. Leaf sheaths closed. Flowers with one scale, fruit in an achene. |
How do you identify a sedge? |
|
|
Juncaceae: solid at nodes, not jointed, round. Leaves are usually basal, leaf sheaths open. Flowers 3-parted, usually with 6 scales. Fruit a capsule with many seeds. |
How do you identify a rush? |
|
|
"Cool season grasses start their growth in early spring and continue to grow while cool temperatures and rain prevails. In the summer, these grasses usually go dormant, often 'browning out.' Some even die out and regrow in the spring from seed." They break under snow or wind, and tend to grow quickly and establish in their first year. |
What is a cool season grass? |
|
|
Warm season grasses grow best in hot, dry summer conditions, when temperatures are between 75 to 90 degrees F. Break dormancy in the spring. These grasses go dormant in the fall, after the first frost. Form bunches (bunch grasses). Extensive root system, takes 3-5 years to establish. |
What is a warm season grass? |
|
|
Goldenrods have fewer than 10 rays, heads less than 8 mm across, usually yellow. There are two genera: the true goldenrods (Solidago) and grass-leaved goldenrods (Euthamia). Over 23 species in Ontario. Old field goldenrods have 3 veins on leaf. |
What defines a goldenrod? |
|
|
Asters have numerous rays of white, pink, blue, purple, or a mixture of these colors. Flower heads usually over 8 mm across. Aster spp. have fewer than 40 flower rays, Fleabanes (Erigeron spp.) have over 40. |
What defines an aster? |
|
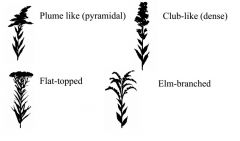
|
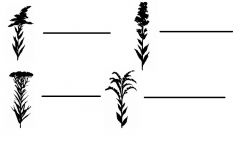
Name the goldenrod types. |
|
|
A collection of pressed, dried and labelled specimens. Can be a permanent record of vegetation in the area, include bryophytes, mosses, gymnosperms, angiosperms. Kept in museums, universities and botanical gardens. |
What is a herbarium? |
|
|
Plants are usually air-dried and mounted on acid-free, standard-sized cardboard paper. Fruits can be stored in alcohol or formaldehyde. |
How are plants preserved in a Herbarium? |
|
|
Specimens are deposited to:
- To support naming of new species. - Support research done with a specific plant. - To support floristic study of specific region. |
Why are plants collected, preserved and documented in Herbaria? |
|
|
Herbarium collections contain information about:
- distribution, frequency, abundance of species and whether these parameters change over time. - used in taxonomic and ecological studies |
Why have a herbarium anyways? |
|
|
Away from UV light and kept dry. In metal boxes or cabinets closed and dust proof. Temperature should be around 20 C and humidity not over 60%. Large seeds and fruit stored separately. |
How are herbarium specimens stored? |
|
|
A taxonomic system must be used for organization. Can be divided by families or genera alphabetically, or arranged geographically. |
How are herbariums organized? |
|
|
Wear white gloves when handling specimens to avoid chemical contamination and acid. Modern herbaria use freezers to kill pests. |
How do herbaria deal with damage and pests? |
|
|
It is part of the Juniper genus, Juniperus spp. |
What is Eastern Red Cedar if not a cedar? |
|
|
Junipers have awn-like leaves and may have scales as well. Fir needles are not sharp, have sucker like attachments to stem, flattened. Spruce have pointed, stalked needles, square shaped. Cedars have scales that are scale like and closely overlapping. Pine needles are in bunches of 2 to 5 needles depending on the species. Hemlock needles have white thin stripe underneath. Tamaracks and other larchs have numerous needles in soft bundles. |
What are Juniper leaves like? Fir leaves? Spruce leaves? Eastern white cedar leaves? Pine leaves? Eastern Hemlock leaves? Tamarack? |
|
|
1) Identification of natural areas. 2) Facilitation of comparisons among different natural areas regardless of community type. 3) Long-term monitoring of remnant natural area quality. 4) Monitoring of habitat restoration efforts. |
What are some applications of a Floristic Quality Index? |
|
|
No, you should use other means of evaluating systems, like ELC. |
Can the Floristic Quality Index be used by itself? |
|
|
Each plant is given a score of 0 to 10 based on its fidelity. 0 to 3 are plants found in many different communities including disturbed sites. Plants of 9 or 10 are indicator species, which can only be found in very specific, pristine communities. |
What does the Coefficient of Conservatism mean? |
|
|
Represents the degree of weediness of a plant. -1 to -3.
-1 = Little to no impact on natural areas -2 = cause problems but only relatively infrequently or localized -3 = can be a serious problem |
What is the Weediness Index? |
|
|
Represents the degree to which a plant can persist in a dry or wet habitat. -5 to +5.
-5 = Obligate Wetland -3 = Facultative Wetland 0 = Facultative 3 = Facultative Upland 5 = Obligate Upland |
What is the Wetness Index? |
|
|
Label given to species to denote rareness. S1 to S5.
S1 = Critically Imperiled S2 = Imperiled S3 = Vulnerable S4 = Apparently secure S5 = Secure
SH = Possibly extirpated SX = Presumed extirpated S1/S2/S3 = Undecided |
What is Species Rarity or SRank (provincial)? |
|
|
4 systems including: marsh, swamp, bog, fen. |
How many wetland systems in Ontario and what are they? |
|
|
An open, non-peat forming, mineral wetland with lots of water flow. Carex and Scirpus (sedges). Marsh Mallow, Monkey Flower. |
What is a marsh? |
|
|
A wetland where trees and/or shrubs dominate. Black Ash, Swamp White Oak, Birches. Nannyberry, Willows, Spicebush. |
What is a swamp? |
|
|
The rarest of wetlands in Ontario. Grow brown moss versus Sphagnum. Have orchids, acid-loving sedges and grasses. |
What is a fen? |
|
|
A wetland dominated by Sphagnum that forms peat soils. |
What is a bog? |

