![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Line
|
Extends forever in either direction
|
|
|
|
Collinear
|
Points that lie on the same line
|
|
|
|
Line segment
|
A piece of the line between points
|
|
|
|
Endpoints
|
Points that end the line segment
|
|
|
|
Supplementary angles
|
Angles that add up to 180 degrees
|
|
|
|
Vertical angles
|
Angles that are opposite from each other and always equal each other
|
|
|
|
Perpendicular lines
|
2 lines that meet in a 90 degree angle
|
|
|
|
Parallel lines
|
When two lines in the same plane are drawn so that they could extend into infinity without ever meeting
|
|
|
|
Isosceles triangle
|
Has 2 equal sides . The angles opposite those sides are also equal
|
|
|
|
Equilateral triangle
|
Has three equal sides and three equal angles. Because of the three equal angles must add up to 180 degrees, all three angles of an equilateral triangle are always equal to 60 degrees
|
|
|
|
Right triangle
|
Has one inside angle that is equal to 90 degrees
|
|
|
|
Hypotenuse
|
The longest side of a right triangle ( the one opposite the 90 degree angle)
|
|
|
|
Pythagorean theorem
|
A formula used to decide any side of a right triangle
|
A^2+ B^2= C^2
|
|
|
Right triangle triples
|
1) 3 - 4 - 5 (and its multiples)
2) 5-12-13 (and its multiples) 3) 7-24-25 ( and its multiples) |
|
|
|
Isosceles right triangle
|
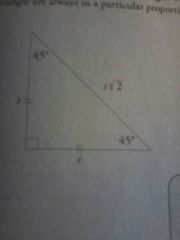
the sides and angles of the isosceles right triangle are always in a particular portion
|
|
|
|
The 30 - 60 - 90 triangle
|
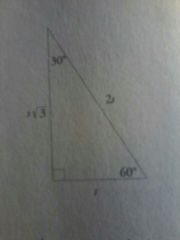
Always has the same proportions
|
|
|
|
Area of a triangle
|
Area = base ×height /2
|
|
|
|
Similar triangles
|
Two triangles are called similar if their angles have the same degree measures. This means their sides will be in proportion
|
Because the sides of the two triangles are in the same proportion, you can find the missing side , X, by setting up a proportion equation
|
|
|
Quadrilateral
|
The interior angles of any four - sided figure add up to 360 degrees
|
|
|
|
Rectangle
|
1. A four sided figure who is for interior angles are each equal to 90 degrees
2. The diagonals are equal |
Area = base × height
Perimeter = the sum of all four of its sides |
|
|
Square
|
1. A rectangle whose four sides are all equal in length
2. The diagonals are perpendicular |
Perimeter = 4s
Area = s^2 |
|
|
Parallelogram
|
1. A four sided figure made up of two sets of parallel lines
2. Opposite sides are parallel and equal 3. Opposite angles are equal 4. Adjacent angles are supplementary, they add up to 180 degrees |
The area of a parallelogram is also base × height, but because of the shape of the figure, the height of the parallelogram is not necessarily equal to one of its sides. Height is measured by a perpendicular line drawn from the base to the top of the figure
|
|
|
Trapezoid
|
A four sided figure in which two sides are parallel
|
The area of a trapezoid is the average of the two parallel sides times the height, or 1/2 ( base 1 + base 2 )( height) OR divide the trapezoid into two triangles and a rectangle and add up the two areas together
|
|
|
Radius
|
1. This distance from the center of a circle to any point on the circle
2. All radii in a circle are equal |
|
|
|
Diameter
|
The distance from one point on the circle through the center of the circle to another point on the circle
|
Diamete = 2r
|
|
|
Circumference
|
The outer perimeter of the circle
|
Circumference= 2×pi×r OR pi× d
|
|
|
Angle facts
|
1. There are 90 degrees in a right triangle
2. When two straight lines intersect, angles offset each other are equal 3. There are 180 degrees in a straight line 4. Two lines are perpendicular when they meet at a 90 degree angle 5. Bisect means to cut exactly in half 6. There are 180 degrees in a triangle 7. There 360 degrees in any four sided figure |
|
|
|
Triangle facts
|
1. The longest side is opposite the largest angle
2. The shortest is opposite of the smallest angle 3. All angles add up to 180 degrees 4. Area =1/2 ( base × height) 5. The height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex 6. Perimeter is the sum of the sides 7. The third side of any triangle is always less than the sum and greater than the difference on the two other sides |
|
|
|
Rhombus
|
1. Opposite sides are parallel
2. Opposite angles are equal 3. Adjacent angles are supplementary, they add up to 180 degrees 4. All four sides are equal 5. The high is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite side 6. The diagonals are perpendicular |
Area = base × height
|
|
|
Circle
|
There are 360 degrees in a circle
|
|
|
|
Chord
|
1. Any line segment connecting two points on the edge of a circle
2. The longest chord is called the diameter |
|
|
|
Area of a circle
|
The amount of space within the boundaries of a circle
|
Area=pi×r^2
|
|
|
Sector
|
1. Any part of the area formed by two radii and the outside of the circle
2. The area of a sector is proportional to the size of the interior angle |
|
|
|
Arc
|
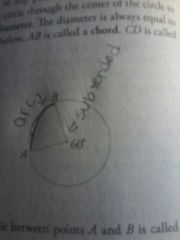
The curved portion of a circle between two points
|
|
|
|
Subtended
|

The angle formed by drawing lines from the center of the circle to 2 points
|
|
|
|
Ray
|
A ray extends infinitely in one direction but has an endpoint
|
|
|
|
Tangent
|
1. Tangent means intersecting at one point. For example, a line tangent to a circle intersects exactly one point on the circumference of the circle. Two circles that touch at just one point are also tangent
2. A tangent line to a circle is always perpendicular to the radius drawn to that point of intersection |
|
|
|
Circumscribed
|
Surrounded by a circle as small as possible
|
|
|
|
Congruent
|
Equal in size
|
|
|
|
Diagonal of a polygon
|
A line segment connecting opposite vertices
|
|
|
|
Inscribed angle in a circle
|
An angle in a circle with its vertex on the circumference
|
|
|
|
Plane
|
A flat surface extending in all directions
|
|
|
|
Polygon
|
A closed figure with two or more sides
|
|
|
|
Regular polygon
|
A figure with all equal sides and angles
|
|
|
|
Surface area
|
The sum of areas of each face of a figure
|
|
|
|
Vertex / vertices
|
A corner point. For angles, its where to rays meet. For figures, its where two adjacent sides meet
|
|

