![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Zygote/ Blastocyst travels fallopian tube in _______ days and implantation occurs _____ days later. Thus, hCG can be occurring as early as the ___ day after conception!
|
Zygote/ Blastocyst travels fallopian tube in ~3 days and implantation occurs 2-3 days later. Thus, hCG can be occurring as early as the 6th day after conception!
|
|
|
When implantation is occurring, ________________ attach to the endometrium.
|
trophoblasts
The inner layer is cytotrophoblasts, the outer multinnucleated layer is the syncitiotrophoblast. |
|
|
How are the following transfered from mom to fetus?
A. antibodies - name the type of antibody! B. amino acids C. glucose D. calcium E. O2, CO2, drugs F. electrolytes |
A. antibodies - name the type of antibody! : via pinocytosis, only IgG
B. amino acids - active transport C. glucose -facilitated transfusion D. calcium - active transport E. O2, CO2, drugs - simple diffusion F. electrolytes - free exchange |
|
|
What is NOT trasnferred across the placenta?
A. cholesterols B. triglycerides C. free fatty acids D. all of the above |
D. all of the above
|
|
|
hCG is highest in which time of the pregnancy?
|
2nd and 3rd month of the first trimester
|
|
|
What does the human placental lactogen (hPL) do? When does it peak?
|
Allows fetus to obtain glucose from mom. All about glucose! If too much, could inadvertently cause mom to have GDM. It increases mom's mobilization of Free Fatty Acids. Increases mom's cellular resistance to insulin (which thus increases the amount of maternal glucose available to be given to the fetus).
Peaks ~ 28 weeks, so screening mum for gestational diabetes is good about then too. |
|
|
Regarding placental hormones, [ PGI2 / thromboxane ] vasoconstricts whereas [ PGI2 / thromboxane ] vasodilates. What does an increased thromboxane:PGI2 ratio suggest?
|
thromboxane = vasoconstricts
PGI2 = vasodilates An increased thromboxane: PGI2 ratio suggests possible preeclampsia!! |
|
|
How is progesterone made by the placental compartment?
|
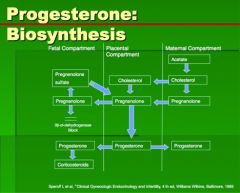
|
|
|
How is estrogen made by the fetoplacental unit?
|
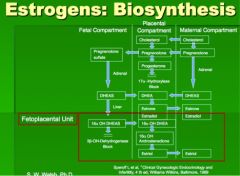
|
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about progesterone biosynthesis by the fetoplacental unit?
A. Cholesterol is a major precursor that comes from the maternal compartment. B. Between approximately the 8-12 weeks of gestation, the cytotrophoblast cells of the placenta develop the capacity to convert cholesterol to progesterone C. Concentrations of progesterone in the fetal compartment are higher than in the maternal compartment. D. Amniotic fluid levels of progesterone are relatively low. E. The step from pregnenolone --> progesterone occurs exclusively in the placental compartment portion of the fetoplacental unit. |
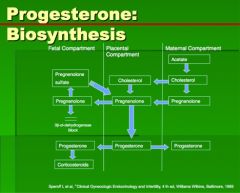
FALSE is B. Between approximately the 8-12 weeks of gestation, the cytotrophoblast- SHOULD BE SYNCITIOTROPHOBLASTS - cells of the placenta develop the capacity to convert cholesterol to progesterone
|
|
|
________________ produced by the fetal and maternal adrenal glands is the major precursor for placental synthesis of estrone and estradiol.
|
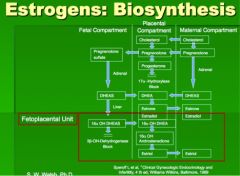
DHEA , or dehydroepiandrosterone
The major precursor for placental estriol synthesis, however, is 16-alpha-OH-DHEAS which is secreted only by the fetus! Thus, the measurements of estriol in the plasma or urine of the mom used to be used as an indicator of fetal well-being and fetoplacental function since both a healthy fetus and healthy placenta are necsseary for its production. |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE?
A. Estrogen synthesis by the placenta relies on precursors from the fetal and maternal adrenals thus estrogen biosynthesis is indirectly affected by fetal and maternal ACTH and function of the adrenal glands B. Estrogen decreases and progesterone increases uterine motility, irritability and contractility. C. Estrogen produces a lengthening and branching of the mammary gland duct system while progesterone produces alveolar growth. D. Estrogen and progesterone suppress lactation during pregnancy. E. Progesterone promotes sodium excretion by the kidneys weakly and thus opposes the action of aldosterone which is slightly increased during the luteal phase and during pregnancy. F. All the above are true |
B. Estrogen INCREASES and progesterone DECREASES uterine motility, irritability and contractility.
|
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE?
A. Both estrogenand progesterone tend to promote fat deposition B. Estrogen increases the quantities of plasma binding proteins (ex.CHBG, TBG) C. Estrogen increases the size of the pituitary gland by stimulating the lactotrophs and the synthesis of prolactin D. Progesterone has immunosuppressive properties. E. All the above are true |
E. All the above are true
|
|
|
At implantation, a layer of trophoblast cells separate and start to invade the endometrium. Trophoblast cells release growth factors and cytokines during the implantation process. Endometrial stromal cells, under influence of progesterone and stimulated by invasion of trophoblast cells, enlarge and accumulate _____________ and ____________, making them special cells called ______________.
|
accumulate glycogen and lipids --> decidual cells. Formation of the decidua is an inflammatory reaction characterized by the induction of COX2.
|
|
|
The ________ cells are the major hormone producing cells of the placenta. They are also the major metabolic cells regulating transport of nutrients, gases and other substances between mom and fetus.
|
trophoblast cells
|
|
|
In normal pregnancy, the trophoblast erodes away ____ of the spiral arteries (how much) all the way into the myometrium.
|
2/3 of the spiral arteries.
This erodes away sympathetic innervation of the vessels so the vessels do not vasoconstrict under stress of hte mother. Erosion allows a free unimpeded flow of blood into the intervillous spaces assuring abundamt blood flow for the placenta and baby. In preeclampsia, invasion of the spiral arteries is deficient. |
|
|
Which of the following are transferable substances across the placenta?
A. bacteria B. heparin C. transferrin D. IgM antibodies E. uric acid |
E. uric acid
is a common waste product from the baby that is transported across the placenta. Nutrients like O2, water, carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids and electrolytes can cross too. |
|
|
True or False:
The transport of hormones across the placenta is complex and not necessarily related to size or solubility. |
TRUE
Large protein hormones, such as growth hormone, prolactin, TSH, insulin and ACTH, do not cross. The placental protein hormones, hCG and hPL, are secreted primarily toward the maternal circulation and do not cross back to the fetus. The small hypothalamic peptides, such as TRH and GnRH, readily cross, but CRF does not. These hypothalamic peptides are also produced by the placenta. The thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, and the catecholamines, epinephrine and norepinephrine, do not cross the placenta even though they are of a small molecular weight. The transport of steroids is very interesting because it is selective despite the similar chemical structures and molecular weights of the various classes of steroids. The glucocorticoids are readily transported across the placenta, but estrogens, progestogens and androgens are not. Arachidonic acid metabolites, prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes, are not transported. |
|
|
True or False:
Betamethasone, a synthetic glucoccorticoid, readily crosses the placent and is used routinely to mature the fetal lungs before a premature delivery. |
True, it crosses the placenta.
|

