![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
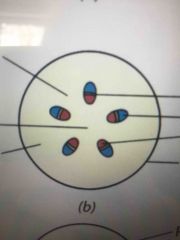
Shoot Primary tissue |
|
|
|
Hypogeal |
Cotyledon below soil |
|
|
Phanerocotylar |
Cotyledon escape seed coat |
|
|
Cryptocotylar |
Cotyledon in seed coat |
|
|
Draw germination preteens for bean pea onion and corn |
- |
|
|
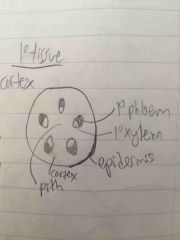
Root primary meristem To primary tissue |
All first words are apical meristem Protoderm -> epidermis Ground meristem -> ground tissue Protocambium -> primary xylem and primary phloem |
|
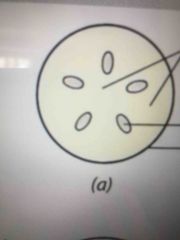
Front (Term) |
Ground meristem Procambium Protoderm |
|
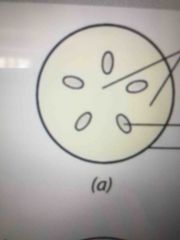
Shoot Primary meristem |
Ground meristem Procambium Protoderm |
|
|
Functions of wood? |
Water conducting, support, and storage |
|
|
How do annual rings form? |
Periodical activity of vascular cambium |
|
|
Difference between early and late wood |
Early- vessels larger in diameter and thin walled
Late- smaller vessels with thick walls |
|
|
Inner bark |
Vc, secondary phloem, cork cambium, phelloderm |
|
|
Outer bark |
Dead, tissue outside cork cambium: phloem, dead secondary phloem, crushed primary phloem, cortex epidermis |
|
|
Wood |
Secondary xylem |
|
|
Label winter and summer branches |
- |
|
|
Mesophytic - why dorsiventral? |
-Abaxial side of lamina has prominent rib -Epidermis, stomata on abaxial side -In mesophyll, palisade parenchyma oriented towards adaxial surface and spongy parenchyma towards abaxial surface -in major vein, xylem of vbundle oriented towards adaxial surface and phloem towards abaxial surface |
|
|
Mesophytic - why dorsiventral? |
-Abaxial side of lamina has prominent rib -Epidermis, stomata on abaxial side -In mesophyll, palisade parenchyma oriented towards adaxial surface and spongy parenchyma towards abaxial surface -in major vein, xylem of vbundle oriented towards adaxial surface and phloem towards abaxial surface |
|
|
Xerophytic- compared to mesophytic |
-sunken stomatal crypts w/ trichomes and stomata -thickened cutical layer -sclerenchymatous multi epidermis/hypodermal layer |
|
|
Mesophytic - why dorsiventral? |
-Abaxial side of lamina has prominent rib -Epidermis, stomata on abaxial side -In mesophyll, palisade parenchyma oriented towards adaxial surface and spongy parenchyma towards abaxial surface -in major vein, xylem of vbundle oriented towards adaxial surface and phloem towards abaxial surface |
|
|
Xerophytic- compared to mesophytic |
-sunken stomatal crypts w/ trichomes and stomata -thickened cutical layer -sclerenchymatous multi epidermis/hypodermal layer |
|
|
Hydrophytic- compared to mesophytic |
-stomata on adaxial surface -reduced cutical layer -highly aerenchymatous mesophyll -reduced vascular system -epidermis composed of thin walled cells, contain chloroplasts |
|
|
Floral shoot structure labeled |
- |
|
|
Botanical definition of flower |
Reproductive shoot, bearing microsporophylls and megasporopa and sterile appendages of perianth surrounding sporophyll components |
|
|
Characteristics of a flower |
Short shoot, limited intermodal elongation, heterophyllic, determinate and synorganization in floral structures |
|
|
Characteristics of a flower |
Short shoot, limited intermodal elongation, heterophyllic, determinate and synorganization in floral structures |
|
|
Synorganization in floral structure |
Synepalous calyx- Union of sepals Synpetalous carolla- Union of petals Synandrous androecium- fusion of stamen Syncropous gynoecium- consists of two or more carpels, called a pistil |
|
|
Label pineapple, strawberry, orange, Apple |
- |
|
|
Primary growth root vs shoot |
R: 1 xylem alt. w/ 1 phloem S: 1 xylem and 1phloem in vascular bundle
R: later organs form endogenously S: lateral organs form exogenously
R: 1 xylem exarch S: 1 xylem endarch
R: protostele S: Eustele
R: only vascular cambium S: fascicular & interfascicular cambium |
|
|
Root and shoot 2 growth |
R: less cork produced S: more cork produced for protection
R: epidermis removed S: ruptures epidermis
R: phellogen differentiates in pericycle parenchyma S: phellogen differentiates in cortex |
|
|
Epigeal |
Cotyledon above soil |

