![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When is fear adaptive and when does it become a problem? |
When feat is a useful cautionary reflex it is considered adaptive, when it's excessive and persistent THEN it is considered an anxiety disorder |
|
|
How does the DSM V differentiate between fear and anxiety? |
Fear is an emotional response to a real or perceived imminent threat Anxiety is anticipation of future threat |
|
|
For the following anxiety disorders, detail what sufferers are anxious about. 1. specific phobias 2. social anxiety disorders 3. obsessive compulsive disorder 4. generalised anxiety disorder 5. panic disorder 6. post-traumatic stress disorder |
1. specific things, e.g. spiders 2. being criticised or negatively evaluated by others 3. harming others, upsetting thoughts 4. almost everything 5. bodily sensations like heart attack, dying, etc. 6. reactions to traumatic event reminders |
|
|
According to DSM V, what count as a) anxiety disorders b) trauma and stress-related disorders c) obsessive compulsive and related disorders |
a) specific phobias, separation anxiety disorder, selective mutism, social anxiety disorder, generalised anxiety disorder, panic disorder, agoraphobia
b) PTSD
c) OCD |
|
|
What does the demographic and prevalence of anxiety disorders look like? |
18% prevalence in any given year Women more likely to develop them than men |
|
|
Describe 'extinction' in fear conditioning |
Operant conditioning: animal hears sound played and receives a shock; over time the mouse responds fearfully to the sound alone.
Extinction training: after repeated exposure to the sound without the shock, the mouse unlearns the previous association and fear response. |
|
|
How can a variation of the classical operant conditioning/extinction fear conditioning be used to analogise how anxiety persists |
If a mouse is given an escape route and keeps avoiding the shock box after the association has been learned, it will never discover that the tone is no longer followed by a shock and the anxiety will persist. |
|
|
Describe the Little Albert experiment |
1. A baby was conditioned to fear a picture of a rat by paring the presentation of the picture with a loud disruptive noise. 2. Predicted that extinction of the fear response would be achieved if the learned association between the rat and the noise became less strong than the association between the rat and no noise. 3. In practice this did not happen: excitatory learning is universal whereas inhibitory learning is situation dependent and so must be done in every new situation from scratch. |
|
|
What functional differences characterise anxiety disorders? What behavioural effects does this have? |
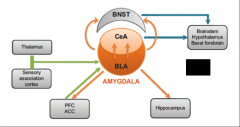
Hyper-responsivity of the amygdala Hypo-responsivity of the VMPFC
amygdala > excitatory learning strengthened vmPFC > inhibitory learning weakened |
|
|
Describe Cook and Mineka's 1989 experiment investigating vicarious fear learning. |
1. started with monkeys in a lab that had no associated fears 2. were shown images of other monkeys showing fear responses to a snake 3. presented with a fake snake > showed fear responses 4. this is an example of emotional contagion and social attribution 5. not seen when artificial flowers replaced the snake. |
|
|
Outline the proposed genetic component of anxiety |
Not one gene but many Accounts for moderate variability of susceptibility and vulnerability Relates to traits of neuroticism and behavioural inhibition Non-specific effect on vulnerability to cognitive disorders - particular disorder results from interaction between genes and environmental influences |
|
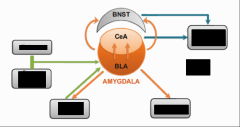
Outline the neurobiology of anxiety disorders |
|
|
|
What tasks and tests are used to measure attentional biases in anxiety disorders? |
The emotional stroop task: anxious participants have significantly greater reaction times than controls in general and in particular for threat vs non-threat words.
|
|
|
Describe the dot-probe task used to detect attentional biases in anxiety patients |
1. blank screen with central fixation point 2. 500ms display of a negative emotional word on one side and a neutral non-emotional word on the other side 3. display with a probe on one side of the screen 4. participants must react as quickly as possible to indicate which side of the screen the dot was on - anxious patients respond more quickly when the probe was on the same side as the threat cue (congruent trials) indicating an attentional bias towards threat 5. controls showed the opposite bias |
|
|
What role might the serotonin transporter 5-HTT play in attentional biases? |
Fox et al., 2009 Dot probe task with negative/positive pictures
Results: participants with the SS/SL allele pair showed no bias, participants with the LL allele pair showed greater vigilance to pictures with positive valence and greater avoidance of the negative valence pictures. i.e. short-allele carriers didn't show this protective bias |
|
|
How can we test interpretation biases in anxiety disorders? |
Use of ambiguous homophones Use of ambiguous sentences Fill in the gaps speeded-response tasks |

