![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the main endocrine glands?
|
1. Hypothalamus
2. Anterior and Posterior pituitary 3. Thyroid 4. Parathyroid 5. Adrenal Cortex 6. Adrenal Medulla 7. Gonads 8. Placenta 9. Pancreas 10. Kidney |
|
|
1. Which hormones are Amine Hormones?
2. What are the amine hormones derived from? |
1. Catecholamines - Epi, NE, and Dopamine
Thyroid Hormones 2. Tyrosine |
|
|
Which hormones are steroid Hormones?
|
1. Cortisol
2. Aldosterone 3. Estradiol and Estriol 4. Progesterone 5. Testosterone 6. 1,25Dihydroxycalceferol |
|
|
1. What is the function of Human Placental Lactogen?
2. What is the disease associated with HPL? |
1. Under conditions of starvation, this blocks insulin from going into the mother and shunts it over to the fetus.
2. Gestational Diabetes |
|
|
What hormones does the Adrenal Cortex make?
|
Androgens that go to the gonads
|
|
|
What hormones do the Gonads make?
|
Estrogen (from DHEA) and Testosterone (from DHT)
|
|
|
What hormones does the Corpus Luteum make?
|
Progesterone, Prolactin, Estrogen
|
|
|
What hormones does the Placenta make?
|
HCG, Estriol, Progesterone, and Prolactin (Human Placental Lactogen)
|
|
|
What hormone does the Kidney make?
|
1,25 DihydroxyD
Renin (not a steroid) |
|
|
What hormones does the Adrenal Corex make?
|
Glomerulosa - Not under Pituitary Control - Makes Aldosterone
Fasiculata - Makes Cortisol Reticularis - Makes Androgens |
|
|
What hormones does the Adrenal Medulla make?
|
Epi (only made in the adrenal medulla), NE
|
|
|
What hormones does the Thyroid make?
|
T3 and T4
|
|
|
What is the feedback loop for the Adrenal Cortex?
|
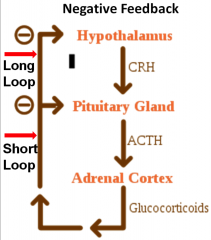
CRH - Corticotropin Releasing Hormone
ACTH - Adrenal Corticotropin Hormone Adrenal glands stimulate cortisol to make Glucose and Free Fatty Acids out of your body This is what helps you get up in the morning |
|
|
1. What is the function of Pro-Opiomelanocorticotropin?
2. What kind of hormone is it? 3. What is an example of its effects? |
1. Makes natural Endorphins, Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone, and ACTH
2. Stress Hormone 3. Runner's High |
|
|
What happens if you don't make Erythropoetin in the kidney?
|
Low Hematocrit
|
|
|
What is the function of Cortisol?
|
Raises Lipids and Glucose, Dissolves Protein, Redistributes Fat
|
|
|
1. What is the effect of Exogenous Steroids on the pituitary?
2. What is the effect of Exogenous Testosterone on your heart and testicles? |
1. Causes feedback inhibition:
Cortisol screws up your bones and skin (acne) 2a. Testosterone ages your heart and causes high glucose and lipids. Premature aging of coronaries because of all the energy taken to make the glucose and lipids 2b. Testosterone will SHUT OFF GnRH and FSH (feedback inhibition), which will atrophy the testicles |
|
|
What is the feedback loop involving the Thyroid?
|
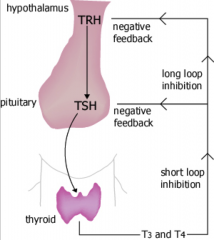
T3 and T4 will stop the production of TSH AND downregulate the TRH receptors on the pituitary
|
|
|
What is the feedback loop involving the Liver?
|
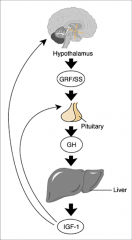
|
|
|
What is the feedback loop involving the Gonads?
|
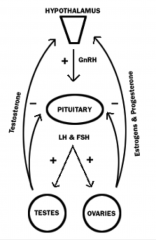
This is the only place where we have ONE PRECURSOR hormone (GnRH) making 2 DIFFERENT Pituitary Hormones
|
|
|
What is the feedback loop for Oxytocin Parturition?
|
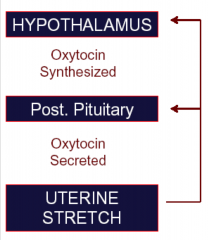
1. Uterine Contraction Dilates Cervix
2. Dilated cervix releases oxytocin from Posterior Pituitary 3. Oxytocin Contracts Uterus 4. Uterine contraction dilates cervix 5. Dilating cervix and uterine contraction increases Oxytocin 6. BOOM!!! |
|
|
What hormones are made in the posterior pituitary?
|
1. Oxytocin
|
|
|
What is the feedback loop for Menstrual Cycle/Ovulation?
|
Positive Feedback
1. FSH and LH make estrogen 2. Estrogen makes LH and FSH 3. FSH and LH make estrogen 4. BOOM!!! |
|
|
1. What is the mechanism of Down-Regulation?
2. What is the mechanism of negative feedback? |
1. A hormone shuts off receptors for itself
2. A hormone shuts off production of itself by going backward to the hypothalamus or pituitary and shutting off its own stimulant |
|
|
What is the only hormone that is made constantly?
|
Thyroxin - keeps you as a homeotherm
|
|
|
What is rate-limiting in hormone function?
|
The amount of hormone available
|
|
|
1. What class of diabetes medications increases insulin sensitivity?
2. Why does exercising increase insulin sensitivity? |
1. Thiazolidinediones (Thioglidozone "glidozones")
2. Exercising muscle does not need insulin. Restin muscle is insulin resistant |
|
|
How would you stop the growth of prostate cancer?
|
Give GnRH agonists (Leuprolide and Goserelin) and a Testosterone Receptor Antagonist (Fludimide)
Chronic release of any hormone will cause downregulation LH and FSH levels will drop accordingly and testosterone will drop as well |
|
|
What is Finasteride and what is it used for?
|
5-alpha-Reductase Inhibitor
Used for BPH (benign prostatic hypertrophy) and Male Pattern Hair Loss |
|
|
What is the definition of Hormone Sensitivity?
|
The hormone concentration that produces 50% of the maximal response
|
|
|
1. What does the Hypothalamus make that it stores in the Posterior Pituitary?
2. How do these substances get to the posterior pituitary? 3. Which nuclei in the Hypothalamus make which of these hormones? |
1. ADH and Oxytocin
2a. Made in Hypothalamus 2b. Transported in infundibulum 2c. Stored in Posterior Pituitary 3a. Paraventricular Nucleus - Oxytocin 3b. Supraoptic Nucleus - ADH |
|
|
What hormones are secreted from the anterior pituitary and where do they go?
|
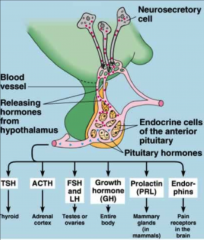
|
|
|
Which hormone is under chronic inhibition?
|
Prolactin
|
|
|
What is the difference b/w the anterior and posterior pituitary?
|
1. Anterior is Endocrine cells. Posterior is neurons (neurohypophysis)
2a. Anterior - Makes TSH, FSH, LH, GH, ACTH, Prolactin 2b. Posterior - Stores ADH, Oxytocin |
|
|
What is the only thing that has feedback inhibition from the Adrenal Gland?
|
Cortisol - anything that removes cortisol, eliminates feedback inhibition on the pituitary and hypothalamus
|
|
|
What is the #1 Cause of Pituitary Tumors and what causes it?
|
Prolactinoma
Causes: Amenhorrea and Galactorrhea |
|
|
What is derived from POMC (Proopiomelanocortin)?
|
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropin Hormone)
|
|
|
What are the two hormones that control Growth Hormone release?
|
Stimulatory: GHRH
Inhibitory: Somatostatin (minor) --> Binds a receptor on the somatotroph and stimulates a Gi protein |
|
|
What is stimulated by GHRH to produce physiologic processes?
|
Adenylyl Cyclase --> Makes cAMP
Phospholipase C --> Makes IP3 --> Ca2+ |
|
|
1. What is the function of Arginine regarding hormones?
2. Why is it mostly useless to test for GH? |
1. Protein building hormone that stimulates gluconeogenesis
2. Short half-life in the middle of the night |
|
|
Why is IGF "insulin-like" if it is anti-insulin (raises glucose)?
|
IGF is how Growth Hormone makes proteins
Insulin makes proteins |
|
|
Why does GH increase Glucose levels and increase Insulin resistance?
|
Decreases glucose uptake into the cells, so you can use it for the brain
|
|
|
What is the only protein-bound peptide hormone?
|
IGF
|
|
|
What is the best initial test for Growth Hormone, and what it this a functional test for?
|
Glucose: GH raises glucose to give you energy, so if you give glucose, it should decrease GH effect and your glucose should not rise
If the glucose level is not suppressed, you have a disease (Functional test for acromegaly) |
|
|
How does GH increase Protein Growth?
What is the function of IGF? |
1. Indirectly, through IGF (somatomedin), which is produced by the liver
2a. Increases uptake of AAs 2b. Increases protein, DNA, RNA synthesis 2c. Increases growth 2d. Tyrosine Kinase receptor |
|
|
1. What happens when GH is increases Pre-pubertal?
2. What about post-pubertal? |
1. Gigantism
2. Acromegaly |
|
|
What are the characteristics of acromegaly?
|
1. Increased bone, cartilage, tongue, and organ size
2. Joint abnormalities 3. Neuropathy: compression of carpal tunnel 4. Hypertension 5. Hyperlipidemia, Hyperglycemia 6. Cardiomegaly 7. Colonic Polyps 8. Teeth grow out of alignment |
|
|
What is the best initial test for acromegaly?
|
IGF level
|
|
|
What cancer is someone with acromegaly most at risk for?
|
Colon cancer (IGF fertilizes colonic polyps and makes them grow)
|
|
|
What will Acromegaly NOT enlarge?
|
Glands EXCEPT sweat glands
|
|
|
What is the effect of exogenous HGH on humans?
|
In dwarfism - Nothing
In healthy people - You become diabetic and hyperlipidemic |
|
|
1. What are the effects of prolactin?
2. What can stimulate prolactin exogenously by accident? |
1. Breast development, Lactogenesis, Inhibition of Ovulation
2. Nipple piercings - Interferes with Dopamine |
|
|
What are the consequences of Prolactin excess?
|
1. Prolactin Stimulates Pituitary for FSH and LH
2. No LH --> no ovulation --> No fertilization --> Infertility and Galactorrhea |
|
|
What are the functions of ADH?
|
1% change in Osmolarity: V2 hits the tubules and increases water permeability and reabsorption in the collecting ducts
10% change in Volume: Vasopressin - V1 raises blood pressure, contracts vasculature |
|
|
1. What is Diabetes Insipidus?
2. What causes it? 3. What are the symptoms? 4. How do you treat it? |
1. Deficiency of ADH --> Water excretion
2a. CNS Damage 2b. Nephrogenic: High Ca2+ or Low K+ 2c. Lithium inhibits ADH 3a. Increased urine volume 3b. Decreased urine Na+ 3c. Decreased urine Osmolality 4. Thiazides - no idea why it works, though |
|
|
1. What is SIADH?
2. What causes it? 3. What are the symptoms? 4. How do you treat it? |
1. Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH
2a. CNS or Lung pathology 2b. Drugs or Cancer 3a. Low serum [Na+] - it's diluted by increased water retention 3b. High urine Na+ and Osmolarity 3c. CNS symptoms 4a. Mild: restriction of fluids 4b. Severe: Hypertonic Saline - 3% salt - the rapid shift can cause a seizure and can only be used via IV 4c. "vaptans" - Conivaptan, Tolvaptan - ADH receptor Antagonists and Demeclocycline |
|
|
Where are thyroid hormones synthesized?
|
Follicular epithelial cells of the thyroid gland
|
|
|
1. What are the competitive inhibitors of the Na+/I- cotransport (that we don't use in clinical practice)
2. What is the effect of inhibiting this pump? |
1. Perchlorate and Thiocyanate
2. Interfere with synthesis of Thyroid Hormones |
|
|
1. What inhibits Thyroid Peroxidase?
2. What is this drug an effective treatment for? |
1. Propylthiouracil (PTU)
2. Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
What is the Wolff Chaikoff Effect?
|
When high levels of I- decrease organification of I2
|
|
|
1. What is the effect of Hepatic Failure on Thyroid Binding Globulin (TBG) levels and the actions of the thyroid?
2. What is the effect of pregnancy on the same system? |
1. Hepatic failure --> Decreased protein synthesis --> Decreased TBG --> Transiently Increased Free T3 and T4 --> Negative feedback --> Inhibition of synthesis of thyroid hormones
2. Pregnancy --> high Estrogen --> Increased hepatic protein synthesis --> Increased TBG levels --> Increased bound T3 and T4 --> transient decrease of free T3 and T4 --> Increased synthesis of thyroid hormones --> Normalized free T3 and T4, but increased OVERALL hormone |
|
|
1. What causes decreases in TBG?
2. What causes Increases in TBG (thyroid binding globulin)? |
1. Decreases - Liver Disease, Androgens, Nephrotic Syndrome
2a. Estrogens - inhibit breakdown of TBG 2b. Pregnancy |
|
|
1. How is T4 converted to T3?
2. What is reverse T3 (rT3) and what does it do? 3. How is T4 converted to rT3? |
1. Enzyme 5'Ionidase - It removes one I2
2. rT3 is inactive T3. It does nothing 3. Target tissues convert it |
|
|
What is the difference b/w the reaction of brain 5'-ionidase and the same in other tissues to starvation?
|
In the brain, there is no inhibition. In other tissues, it is inhibited by starvation, lowering O2 consumption and BMR.
|
|
|
1. What is Grave's Disease and what is it caused by?
2. What happens to levels of TSH in Grave's Disease? |
1. A form of Hyperthyroidism - Caused by increased levels of Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulins (from IgG) binding to the TSH receptor
2. TSH goes down because thyroid hormones are produced in large quantities and they inhibit TSH secretion by negative feedback |
|
|
1. How can the conversion of T4 to T3 be altered so that more rT3 is produced?
2. What increases the conversion to T3? |
1. Pregnancy
Beta Blockers Hepatic and Renal Failure Fasting Stress 2. Obesity |
|
|
Why do thyroid hormones increase heat production, oxygen consumption, and BMR?
|
They produce Na+/K+ pumps for most tissues, which use ATP that create heat and then more ATP has to be generated, so that uses more energy and O2.
|
|
|
What does metabolic rate increase?
|
O2 consumption
Temp Na+/K+ ATPase Glucose absorption in the gut Effects of Catecholamines Glucagon GH Lipolysis |
|
|
1. What is the effect of Thyroid hormones on Heart and Lungs?
2. What can cause an infarct of a marginal heart? |
1. Increased:
Cardiac Output Stroke Volume Ventilation Beta 1 Receptors 2. Too much Thyroxine |
|
|
What is Thyroid Hormone's effect on growth?
|
Permissive to growth hormone
Builds proteins at normal levels Dissolves proteins at high levels |
|
|
What is Thyroid Hormone's effect on CNS and Neural?
|
No T4, No brain growth
Increases sympathetic activity |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hyperthyroidism?
|
Everything FAST
Tachycardia Sweating Weight Loss Heat Intolerance Nervous Tremor Exophthalmos Increased bowel movements Increased cardiac output A-fib Chest pain/Angina Osteoporosis Insomnia |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
|
Everything SLOW
Bradycardia Dry Skin Weight gain Cold intolerance Depressed and demented Decreased reflexes Constipation Growth retardation Decreased cardiac output |
|
|
1. What causes Hypothyroid?
2. How do you test for it? 3. How do you treat it? |
1. Autoimmune destruction
Burnt out Hashimoto's Iodine Deficiency Rarely pituitary or hypothalamic deficiency 2. High TSH, Low T4 3. Replace hormone |
|
|
1. What causes Hyperthyroid?
2. How do you test for it? 3. What does it mean if there is low uptake? 4. How do you treat it? |
1. High T4
2. Radioactive iodine uptake 3. Pituitary: high TSH Subacute Thyroiditis: Tender gland Silent (painless) Thyroiditis Exogenous abuse of hormone 4. Propythiouracil or Methimazole inhibit peroxidase Propanolol blocks BOTH beta 1 and beta 2 receptors Radioactive iodine ablates the gland SEVERE ACUTE: Dexamethasome (steroids) decrease peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 Iodine blocks hormone production Iodine blocks T4 to T3 conversion |
|
|
1. Why will you not die without your adrenal medulla?
2. What is the protein effect of the adrenal medulla/catecholamines? |
1. You make NE in the nerves and it maintains BP. It's only Epi that is exclusive to the adrenal medulla
2. Nothing |
|
|
1. What are the symptoms of Pheochromocytoma?
2. What is the best initial test? 3. What is the treatment? |
1. Episodic hypertension, flushing, and diarrhea
2. Urinary catecholamines and metanephrines 3. Phenoxybenzamine (IV alpha blocker) |
|
|
1. What controls Aldosterone release in the Glomeruloca of the adrenal cortex?
2. What controls Cortisol (glucocorticoid) release in the Fasciculata of the adrenal cortex? 3. What controls Androgen release in the Reticularis of the adrenal cortex? |
1. Aldosterone --> Increased by Angiotensin II and Hyperkalemia (K+) - Aldosterone gets rid of K+ and raises BP
2. Cortisol --> Increased by ACTH - Cortisol makes sugars and free fatty acids 3. Androgens --> Increased by ACTH. Makes DHEA, Androstenedione |
|
|
1. What enzyme converts Cholesterol to Pregnenalone in the steroid hormone synthesis process?
2. What stimulates this enzyme? 3. What happens to this process if you lose your pituitary? |
1. Desmolase
2. Stimulated by ACTH 3. Nothing. You still have enough desmolase activity |
|
|
1. What is the purpose of Metyrapone?
2. How does it work? |
1. Used to test for Pituitary Insufficiency
2a. Inhibits 11-Hydroxylase 2b. Blocks Production of Aldosterone and Cortisol 2c. W/o cortisol --> No feedback inhibition on Pituitary 2d. If Pituitary is normal, then ACTH rises 2e. If Pituitary is insufficient, then ACTH does not rise |
|
|
1. What is Ketoconazole used for?
2. Why do we not use it anymore? |
1a. Blocks adrenal steroid synthesis at multiple places
1b. Blocks desmolase 1c. Used for prostate cancer? 2. We have Fludamide and GnRH agonists now. |
|
|
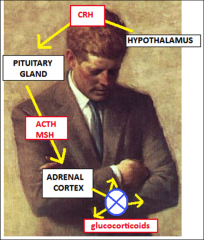
1. When are adrenal hormones highest and lowest?
2. What is the chain of regulation leading to production and then inhibition? 3. Is production constant or pulsatile. |
1. They are diurnal. Highest in AM - Max 30 minutes before waking; Lowest in PM
2. Hypothalamus makes CRH --> Pituitary makes ACTH and MSH --> Adrenal Cortex makes Cortisol --> Pituitary is inhibited by Cortisol (ONLY negative feedback from the adrenals) 3. PULSATILE. The only hormone made constantly is THYROXIN |
|
|
What are the normal stimulants of Cortisol?
|
1. Decreased blood cortisol
2. Hypoglycemia --> Raises blood glucose 3. Trauma --> Stress hormone 4. Infection --> Stress hormone 5. Stress (physical or emotional) 6. Alpha Adrenergic Stimulation --> Stress hormone |
|
|
1. What does the Dexamethasone Suppression Test assess?
2. How does it work and what are normal and abnormal reactions? |
1. Tests feedback inhibition on the pituitary and hypothalamus.
2a. Normal - Decreases ACTH and CRH --> Decreases Cortisol and Dexamethasone doesn't show up as a glucocorticoid in the bloodwork 2b. Abnormal - Cortisol and ACTH stay high |
|
|
1. Where are the sources of hypercortisolism?
2. How does one test for Hypercortisolism? 3. What is a normal result of each of the 2 tests? |
1a. Adrenals - usually
1b. Pituitary - common 1c. Hypothalamus - rarely 2a. 24 hour urine cortisol (so you don't detect one stress spike and use that to diagnose) 2b. 1mg overnight Dexamethasone Suppression Test 3a. 24hr - Low urine cortisol 3b. Dex - Morning cortisol should drop |
|
|
What is the result of High Dose Dexamethasone on:
1. Pituitary Lesions 2. Adrenal Lesions 3. Ectopic Overproduction of ACTH |
1. Pituitary Lesions - Suppress ACTH
2. Adrenal Lesions - DO NOT SUPPRESS ACTH 3. Ectopic Overproduction of ACTH - DO NOT SUPPRESS ACTH |
|
|
What is the effect of Adrenal Androgens in Males and Females, respectively?
|
Males - no effect
Females - Pubic Hair, Axillary Hair, Libido |
|
|
What is Cortisol's effect on glucose?
|
1. Makes glucose via AA, FA, and protein breakdown
2. Increases Gluconeogenesis 3. Inhibits Insulin 4. Decreases Muscle and Adipose uptake of glucose 5. Decreases Glucose Use |
|
|
a. How does Cortisol act as an anti-inflammatory agent?
b. What does Lipocortin do? |
a. INCREASES Lipocortin, which inhibits PLA2 (phospholipase A2)
b1. Blocks Leukotriene production b2. Blocks Prostaglandins production b3. Blocks Interleukin-2 b4. Blocks T-cell proliferation b5. Blocks Histamine release from mast cells b6. Blocks Serotonin release from platelets |
|
|
What effect does Cortisol have on vascular reactivity?
|
1. Increases vascular reactivity
2. Up-regulates Alpha-1 receptors 3. Increases NE effect 4. Raises BP 5. Increases Catecholamine effect on increasing vasoconstriction |
|
|
What is the effect of Cortisol on bone?
|
BREAKS DOWN BONE:
1. Decreases osteoblasts 2. Increases Osteoclasts 3. Helps resorb bone 4. Uses AA from bone to make sugar (gluconeogenesis) |
|
|
What are the effects of Aldosterone on Principle cells and Intercalated cells in the kidney?
|
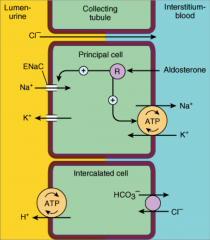
|
|
|
1. What is Addison's Disease?
2. What are the symptoms of Addison's Disease? 3. How can we test for Addison's? 4. What is the treatment for Addison's? |
1. Adrenal Insufficiency - Autoimmune (90%) destroys all zones of the adrenal cortex
2. Weakness, Fatigue, Weight Loss, Low BP, Low Glucose, Hyperpigmentation (Increased ACTH and MSH), Decreased Pubic Hair (women) 3a. 90% - High K+, Metabolic Acidosis, High ACTH (b/c no feedback inhibition from cortisol) 3b. 5-10% - Have Low ACTH because of pituitary or hypothalamic failure. Also have low MSH, so no hyperpigmentation. No acid/base problems. No hyperkalemia b/c there is enough ACTH to stimulate desmolase, so you have enough aldosterone to maintain BP, K+, and Acid/base status. 4. Steroid Replacement: Prednisone and Hydrocotrisone |
|
|
1. What are the symptoms of Cushing's Disease?
2. What are the lab abnormalities associated with it? |
1a. Hypercortisolism - Hypertension, Fat re-distribution, Truncal Obesity, Moon Face, Neck Hump, Muscle wasting, striae, osteoporosis.
1b. Women get menstrual abnormalities, acne, and hair loss (because of increased androgens) 2. Hyperglycemia, Hypokalemia, Metabolic Alkalosis, Hyperlipidemia |
|
|
What is seen in each of the following etiologies of Cushing's Syndrome:
1. Pituitary 2. Adrenal 3. Ectopic |
1. Pituitary Etiology - ACTH high, Suppresses with high dose Dexamethasone
2. Adrenal - ACTH Low 3. Ectopic (same as tumor effect) - ACTH High, does NOT suppress with Dexamethasone |
|
|
What is Cushing's reflex and what does it indicate?
|
High BP and Bradycardia indicates Intracranial Pressure
|
|
|
1. What causes Conn's Syndrome?
2. What are the symptoms of Conn's Syndrome? 3. How is it treated? |
1. Aldosterone-secreting tumor
2. Hyperaldosteronism - Hypertension, Hypokalemia, Alkalosis, Muscle weakness (from low K+), High Aldosterone (w/o presence of renin) 3. Spironolactone - Aldosterone Antagonist |
|
|
What are the consequences of the following types of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)?
1. What are the symptoms of 21 Hydroxylase Deficiency? 2. What are the symptoms of 17 Hydroxylase Deficiency? 3. What are the symptoms of 11 Hydroxylase deficiency? 4. What do all of the CAH patients have in common? |
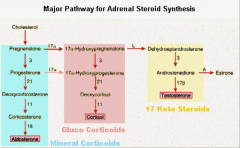
1. Normal BP and Virilization
2. No Androgens or Cortisol. High BP b/c of excess 11DOC. Shuts off Aldosterone. All treated with Steroids (Prednisone). Prednisone shuts off ACTH. 3. Overproducing adrenal androgens. High BP (from 11DOC) and virilization. 4. None have cortisol. All have high ACTH, None have aldosterone |

